



Technology is transforming governance in India by promoting transparency and efficiency through initiatives like Digital India, Aadhaar, and UMANG. These tools enable faster, corruption-free services and data-driven policies. However, challenges such as the digital divide, cybersecurity risks, and data protection remain crucial for inclusive governance.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: NEWSONAIR
The integration of technology in governance utilizes digital tools to enhance government-citizen interaction, service delivery, transparency, and responsiveness throughout public administration.
Enhanced Public Service Delivery
Governments are using digital technology to efficiently deliver essential services like health, education, and social welfare directly to citizens.
The UMANG (Unified Mobile Application for New-Age Governance) app offers over 2,300 services across 23 languages from central to local government bodies, with 8.21 crore registrations as of May 2025. (Source: DD News)
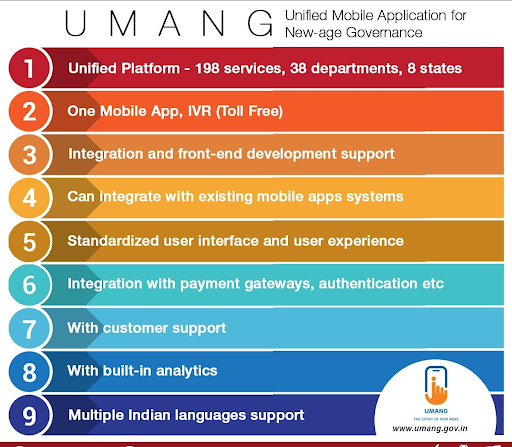
Promoting Transparency and Accountability
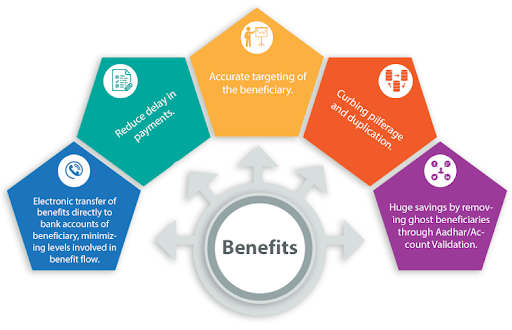
Digital platforms, like the Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) system, enhance transparency by creating verifiable digital records and reducing discretion, directly transferring welfare benefits to beneficiaries and thus minimizing corruption.
Between 2009 and 2024, DPT saved ₹3.48 lakh crore by reducing welfare delivery leakages. This resulted in a reduction of subsidy allocations from 16% to 9% of total government expenditure. (Source: PIB)
The Government e-Marketplace (GeM) portal has improved transparency in public procurement, with transactions reaching ₹5.4 lakh crore in 2024-25. (Source: PIB)
Promoting Citizen Participation and Engagement
Technology has enhanced citizen engagement with the government through platforms like MyGov, allowing individuals to contribute ideas and participate in policy development.
Social media connects diverse populations and facilitates dialogue, while mobile applications increase public involvement by providing accessible information and government services.
Boosting Administrative Efficiency
Automation and digital workflows are transforming government operations by reducing manual effort, accelerating processes, and lowering costs.
Strengthening National Security and Data Management
Advanced technologies improve law enforcement, border management, and critical infrastructure protection, while digital systems facilitate secure data management for national security and policy.
The development of digital public infrastructure (DPI) like Aadhaar, UPI, and DigiLocker provides a robust framework for secure digital interactions.
Foundational Digital Infrastructure
Digital Services and Platforms

Persistent Digital Divide
Cybersecurity Threats and Data Privacy
Ethical Considerations of AI
Gaps in Capacity Building and Digital Literacy
Bridge the Digital Divide
Expanding broadband infrastructure in rural areas and implementing tailored digital literacy programs are essential for digital inclusion. Initiatives like BharatNet are key to providing high-speed internet to all Gram Panchayats.
Strengthen Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
A comprehensive strategy for strengthening national cybersecurity involves national policies, advanced threat detection, updated data protection, a skilled workforce, and public education on online safety.
Develop Ethical AI Frameworks
Establish clear guidelines for the responsible development and deployment of AI in public services, ensuring algorithmic fairness, transparency, and accountability.
Encourage Public-Private Partnerships
Collaborate with private sector technology firms and startups to leverage their expertise, innovation, and resources in developing and implementing e-governance solutions.
Promote Interoperability
Ensure seamless integration and data exchange between different government systems and platforms to provide citizens with a truly unified experience.
Digital transformation initiatives, like Digital India and DBT, are crucial for modern governance, promoting efficiency and transparency, but require continuous effort to overcome challenges such as the digital divide and cybersecurity threats to achieve a truly digital and united nation.
Source: NEWSONAIR
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Technology is a powerful tool to ensure transparency and accountability in governance, but it is not a panacea for all administrative ills. Critically analyze. 250 words |
E-governance (electronic governance) is the application of information and communication technology (ICT) to government functions and processes in order to enhance efficiency, transparency, and accountability, and to provide citizens and businesses with better access to information and services.
SMART governance is an acronym associated with e-governance, which stands for: Simple (simplified rules and procedures), Moral (ethical administration), Accountable (clear responsibility for actions), Responsive (quick service delivery), and Transparent (information available in the public domain).
The DBT scheme aims to transfer subsidies and social welfare benefits directly into the bank accounts of beneficiaries. It leverages the "JAM Trinity" (Jan Dhan accounts, Aadhaar unique IDs, and Mobile phones) to eliminate middlemen, prevent leakages, and ensure funds reach the right people efficiently.



© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved