



The Lok Sabha controversy highlights parliamentary privileges under Articles 105 and 194. It explains individual and collective privileges, breach procedures, disruption causes, and the codification debate. The Sita Soren (2024) ruling reshapes bribery law, highlighting the need to balance protest rights with legislative decorum.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: THE HINDU
Lok Sabha Speaker Om Birla is examining a notice submitted by a Member of Parliament (MP), alleging a breach of privilege and contempt of the House by some MPs, during the debate on the Viksit Bharat–Guarantee for Rozgar and Ajeevika Mission (Gramin) Bill, 2025.
|
Read all about: VB-G RAM G Bill to Replace MGNREGA |
Parliamentary privileges are a set of special rights, immunities, and exemptions enjoyed by the Houses of Parliament, their committees, and their members.
The primary purpose of these privileges is to ensure the independence and effectiveness of their actions, allowing them to discharge their legislative responsibilities without fear or favor.
These privileges are essential for maintaining the authority, dignity, and honor of Parliament.
Constitutional Basis
Article 105: Deals with the powers, privileges, and immunities of the Houses of Parliament, their members, and their committees.
Article 194: State Legislatures, members, and committees receive privileges and immunities similar to those in Article 105, at the state level.
Collective Privileges
These are the rights and immunities enjoyed by each House of Parliament as a collective body. Key collective privileges include:
Individual Privileges
These are the rights and immunities enjoyed by Members of Parliament in their individual capacity. They include:
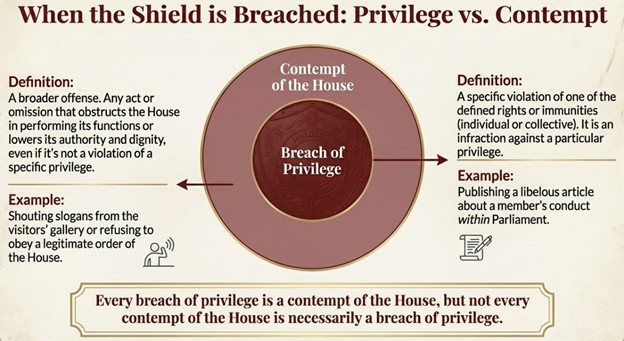
When any individual or authority disregards or attacks the rights and immunities of the House or its members, it is termed a 'breach of privilege' and is punishable by the House.
Actions that obstruct the House or its members from performing their duties or lower the dignity of the House are considered 'contempt of the House'.
Procedure for Addressing a Breach:
Lack of Codification
The absence of a specific law codifying privileges leads to ambiguity and potential for misuse, as Article 105's phrase "until so defined" suggests a law was intended but never enacted.
Conflict with Fundamental Rights
The central debate is whether parliamentary privileges outweigh Fundamental Rights; the Supreme Court urges a balance, especially regarding freedom of speech.
Misuse for Political Ends
Concerns exist that privileges may curb dissent and media freedom. Critics contend that self-adjudication breaches natural justice.
Immunity in Criminal Cases
The judiciary has consistently held that privileges do not grant immunity from criminal proceedings for actions unrelated to parliamentary duties.
Arguments for Codification
Arguments Against Codification
Parliamentary privileges are essential for the independent functioning of the legislature, but the absence of a codified law introduces ambiguity and potential conflicts with fundamental rights.
To strengthen democracy, the exercise of these privileges should be balanced with the principles of accountability, transparency, and the fundamental rights of citizens.
Source: THE HINDU
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. "While parliamentary privileges are essential for the independent functioning of the legislature, their frequent misuse and ambiguity call for a comprehensive review." Critically analyze. 250 words |
Parliamentary privileges are a set of special rights, immunities, and exemptions enjoyed by the Houses of Parliament, their committees, and their members. They are intended to secure the independence, authority, and dignity of Parliament, allowing members to perform their legislative duties without fear or obstruction.
A 'breach of privilege' is a violation of any of the specific rights and immunities of the House or its members. 'Contempt of the House' is a broader term for any act or omission that obstructs the House from performing its functions or lowers its authority and dignity, even if it is not a breach of any specific privilege.
A member, with the consent of the Speaker/Chairperson, can raise a notice of privilege. The Speaker/Chairperson can either decide on the matter or refer it to the Committee of Privileges. This committee investigates the case and submits a report with recommendations. The House then considers the report and takes a final decision on the matter and any potential punishment.



© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved