



In 2025, Indian Railways achieved 99.2% electrification, built the world’s highest arch bridge, expanded Vande Bharat and Amrit Bharat trains, cut accidents with AI-enabled Kavach, and became the second-largest freight carrier, advancing Aatmanirbhar Bharat and a Green Railway vision by 2030.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: sarkaritel
In 2025, the Ministry of Railways achieved record growth through massive capital investment and infrastructure modernization to align with the National Rail Plan 2030.
|
Read all about: INDIAN RAILWAYS SAFETY l INDIA'S FIRST HYDROGEN-POWERED COACH l LESSONS FROM RECENT TRANSPORT DISRUPTIONS l INDIA'S LONGEST RAIL TUNNEL |
Ministry of Railways Achievements/initiatives in 2025
Enhancing Passenger Experience & Services
Vande Bharat Express: Railways operates over 160 Vande Bharat semi-high-speed train services, with a Sleeper version expected to launch soon after advanced trials.
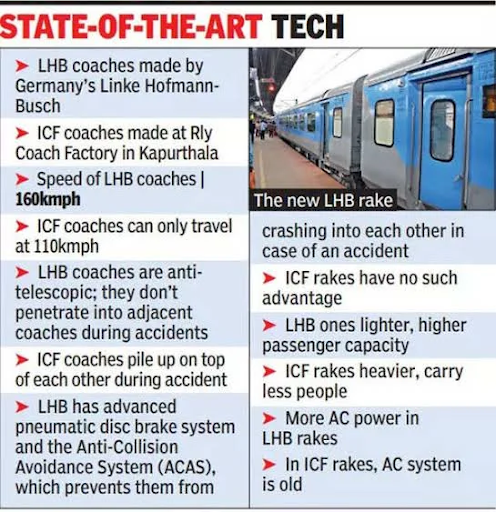
Amrit Bharat Trains: Trains utilize LHB push-pull technology for comfortable, affordable, non-AC travel with better acceleration, fewer jerks, and improved amenities.
Amrit Bharat Station Scheme (ABSS): Aims to redevelop major railway stations into modern, airport-like hubs.
Namo Bharat: IIndia's first Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS) is a high-speed electric train network in the National Capital Region (NCR), operating at 160 km/h to drastically cut the Delhi-Meerut travel time.
Infrastructure & Network Expansion
A strong focus has been placed on expanding and upgrading the core infrastructure to increase speed, safety, and capacity.
Track Commissioning
A record 5,522 km of new track was laid in FY 2023-24, averaging over 15 km per day. This includes new lines, doubling, and gauge conversion projects.
Electrification
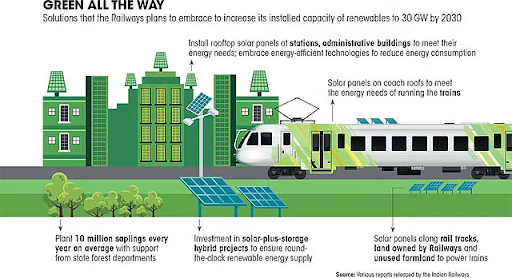
Over 95% of the Broad Gauge (BG) network has been electrified. Indian Railways aims to become the world's largest 100% green railway network.
Safety Infrastructure
Level Crossing gates are being eliminated by fast-tracking the construction of Road Over Bridges (ROBs) and Road Under Bridges (RUBs). 1,321 ROBs/RUBs were built in FY 2023-24.
Connectivity Projects
Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL): Provides all-weather connectivity to the Kashmir Valley. Its key features include:
New Pamban Bridge: India's first vertical-lift railway sea bridge connects Rameswaram to the mainland, replacing the old bridge. It is designed to allow ships to pass underneath.

Northeast Connectivity: The Bhairabi-Sairang new railway line to connect Mizoram's capital, Aizawl, to the Indian Railways network, enhancing regional trade and mobility.
Mumbai-Ahmedabad High-Speed Rail (MAHSR): The 'Bullet Train' project is under execution with technical and financial cooperation from Japan.
Enhancing Safety
Kavach - Automatic Train Protection (ATP) System: This indigenous system, a key part of Mission Raftaar, automatically applies brakes to prevent collisions if the loco pilot fails to act.
Accident Reduction: Railways achieved its lowest-ever level of train accidents, decreasing from 135 in 2014-15 to 31 in 2024-25, and further to only 10 by November in 2025-26 fiscal year.
Technological Aids
AI-based Systems: An AI-enabled system using Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) is being deployed in elephant corridors (especially in the Northeast Frontier Railway) to prevent collisions with wildlife.
Surveillance: CCTV cameras are being installed at stations and in coaches on a large scale to enhance passenger security.
Aatmanirbhar Bharat in Railways
The 'Make in India' initiative is at the core of Railways' manufacturing and procurement strategy.
|
Manufacturing Unit |
Product |
Partnership Model |
Key Highlights |
|
Madhepura, Bihar |
12,000 HP Electric Locomotives |
PPP with Alstom |
Manufacturing high-power locomotives for heavy freight haulage on DFCs. Over 500 locomotives were delivered. |
|
Marhowra, Bihar |
High HP Diesel Locomotives |
PPP with Wabtec |
Producing modern diesel locomotives, with a significant portion being exported, showcasing India's manufacturing prowess. |
|
Dahod, Gujarat |
9,000 HP Electric Locomotives |
Partnership with Siemens |
A new facility to produce 1,200 high-power electric locomotives over 11 years. |
|
LHB Coach Production |
Linke Hofmann Busch (LHB) Coaches |
In-house Production Units |
Production of safer, more comfortable LHB coaches has been ramped up, replacing conventional ICF coaches across the network. |
Source: PIB
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Regarding 'Amrit Bharat' trains, identify the correct statement: A) These are high-speed bullet trains connecting metros. B) They are fully non-AC trains designed for the common man with improved amenities. C) They consist only of AC-3 Tier and AC-2 Tier coaches. D) They are exclusively used for freight transport under Gati Shakti. Answer: B Explanation: The Amrit Bharat Express is an Indian Railways superfast, non-air-conditioned, low-cost long-distance service for the common man. |
The Amrit Bharat Station Scheme is an ambitious initiative by Indian Railways to redevelop 1,337 stations across India, aiming to provide modern, airport-like facilities and transform them into integrated transport hubs.
DFCs are separate railway lines for transporting goods, which decongest the main passenger network. This allows freight trains to run at higher speeds, drastically reducing transit times and logistics costs. For example, the Western DFC has reduced transit times from ports in Gujarat to the NCR, making Indian exports more competitive and helping lower logistics costs as a percentage of GDP.
'Kavach' is an indigenously developed Automatic Train Protection (ATP) system. It is designed to prevent accidents caused by human error, such as a train passing a signal at danger (SPAD) or over-speeding. By automatically applying brakes in such situations, it enhances the safety of train operations.



© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved