Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: REUTERS
Context
India and the Philippines have elevated their bilateral relations to a strategic partnership during a recent meeting between the Indian Prime Minister and the Philippines President in New Delhi.
What are the main outcomes of the recent India-Philippines bilateral talk?
Strategic relation
Defence cooperation
- Naval Exercises: In August 2025, for the first time, Indian Navy participated in exercises in the Philippines.
- Defence Procurement: Discussions on defence acquisitions, including the BrahMos missile system.
- Maritime Domain Awareness: India invited the Philippines to participate in the Information Fusion Centre – Indian Ocean Region (IFC-IOR).
Economic partnership
- Trade Liberalization: India to the review of the India-ASEAN Free Trade Agreement (FTA) and agreed to work towards a bilateral Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA).
- Digital Economy: India offered to support a pilot project for the Philippines' Sovereign Data Cloud Infrastructure.
- Development Projects: India committed to increase the number of Quick Impact Projects (QIPs) in the Philippines.
- Quick Impact Projects (QIPs) initiative, provide grant assistance for small-scale, community-based development projects in the Philippines.
- 9 Pacts Signed: Nine agreements were signed, including on strategic partnership, defence, space, and a cultural exchange program.
People-to-people ties
Evolution of India-Philippines Relations
Early engagement (1949-early 1990s)
- Diplomatic relations were established in 1949.
- Both countries shared democratic ideals and a commitment to anti-colonialism and South-South cooperation.
- Philippines opened its embassy in New Delhi in 1959, India open embassy in Manila in 1962.
- A Treaty of Friendship was signed in 1952.
- Limited high-level interaction during the Cold War era due to differing foreign policy alignments.
Deepening engagement (Post 1990s)
- India's "Look East" policy (initiated in 1992) and "Act East" policy (since 2014) boosted engagement with ASEAN nations, including the Philippines.
- India became a Sectoral Dialogue Partner of ASEAN in 1995.
- The Agreement on Expansion of Trade was signed in 1996.
- The ASEAN–India Free Trade Area agreement, signed in 2009, also included the Philippines.
- In 2022, India and the Philippines signed a $ 375 million agreement for BrahMos supersonic cruise missile system.
- August 2025 meeting elevated ties to a Strategic Partnership.
Why is the strategic value of Philippines for India?
Geopolitical positioning and Indo-Pacific vision
Counterbalancing China's assertiveness
- Shared Concerns: Both nation have experienced challenges with China's assertive actions in their maritime and land borders. India's military cooperation with countries like the Philippines can serve as a reciprocal pressure point for China.
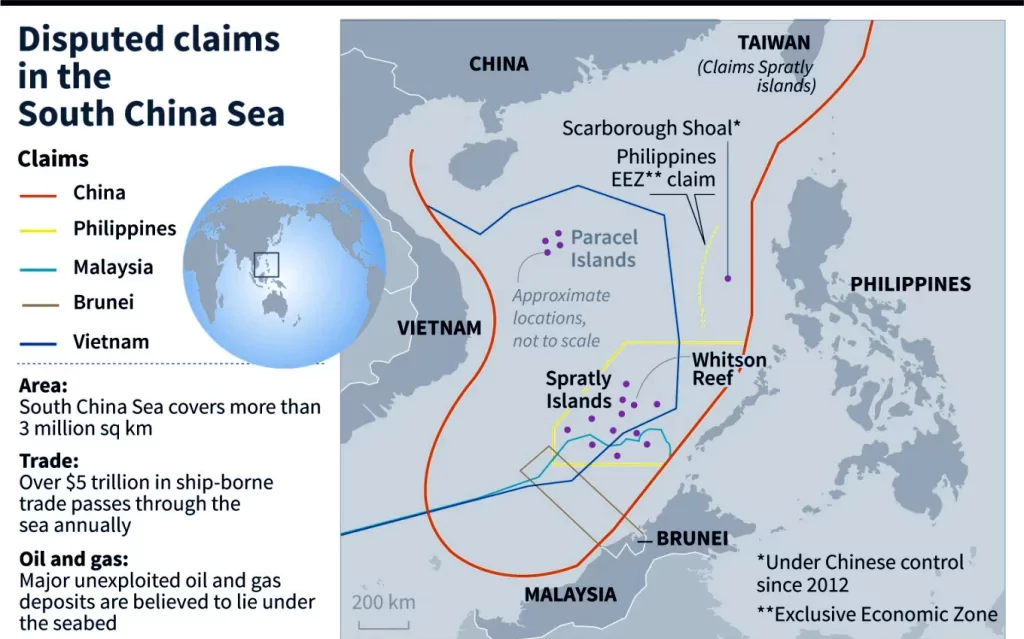
- South China Sea (SCS) Disputes: The Philippines' ongoing territorial disputes with China in the SCS, including the West Philippine Sea, make it a natural partner for India, which also faces border issues with China.
- Naval Cooperation: Both conducted their first-ever joint naval exercises in the South China Sea, near the disputed Scarborough Shoal, in August 2025.
 Defence and security cooperation
Defence and security cooperation
- BrahMos Missile Deal: The deal for the BrahMos missile system marks India's first major defense export.
- Maritime Domain Awareness (MDA): India's invitation to the Philippines to join the Information Fusion Centre – Indian Ocean Region (IFC-IOR) aims to improve MDA in the region.
- Joint Defence Production: Strategic Partnership encourages co-development and co-production of defence equipment, promoting self-reliance and encouraging investments in defence R&D and supply chain ecosystems.
Economic opportunities
- Growing Bilateral Trade: Bilateral trade between India and the Philippines reached USD 3.53 billion in 2023-24. India's exported $350 million, and imported $92.3 million.
- Major Indian Exports: India mostly exports engineering goods, automobile parts, petroleum products, iron and steel products, and pharmaceuticals to the Philippines.
- Indian pharmaceutical products alone made up nearly 16% of total Philippine pharmaceutical imports in 2023.
- Major Indian Imports: India imports electrical machinery, semiconductors, ores, copper, lead, plastics, and precious stones from the Philippines.
Expanding Partnership
- India is the largest supplier of pharma products to the Philippines, accounting for about 12% of its total pharmaceutical imports.
- Both countries recognize Fintech as a key growth sector and have an agreement to cooperate.
- Philippines was the first ASEAN country to approve Bharat Biotech's Covaxin for emergency use during COVID-19 pandemic.
|
How does India support capacity building and humanitarian efforts in the Philippines?
- Capacity Building (ITEC Program): Under Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) program, over 1000 Filipino professionals have received training in areas like electoral technology, renewable energy, and public health management.
- Humanitarian Assistance: India consistently offers aid during natural disasters and crises.
- 2006: Sent relief materials and contributed $250,000 after Typhoon Reming/Durian.
- 2012: Provided $200,000 for disaster relief after Typhoon Pablo/Bopha.
- 2013: Grant $100,000 after an earthquake in Bohol and sent 15 tons of relief supplies after Super Typhoon Haiyan.
- 2020: Provided nearly US$ 250,000 worth of face masks to COVID-19 frontline workers.
|
What are the challenges in India-Philippines Relations?
China's Influence: Both India and the Philippines have direct or indirect concerns about China's growing influence and assertive actions in the Indo-Pacific.
- Philippines: Directly faces territorial disputes in the South China Sea, where China claims vast areas, including the Spratly Islands and Scarborough Shoal, based on historical claims and the "nine-dash line".
- The 2016 Permanent Court of Arbitration ruling rejected China's claims, but China dismissed.
- India: Faces land border disputes with China. India supports a rules-based order, however, it must balance its own strategic interests when engaging in security cooperation that might be seen as directly challenging China.
Economic Imbalance: Indian companies have invested an estimated US$ 5 billion in the Philippines, mainly in IT & IT-enabled services (BPO), pharmaceuticals, healthcare, and manufacturing.
- Philippine investments in India have been more modest, suggests untapped potential and a need for greater reciprocal economic engagement.
Connectivity: Lack of direct flight connectivity, with passengers currently relying on transit hubs like Singapore and Kuala Lumpur, impacts business and people-to-people ties.
Defence Cooperation: Translating the BrahMos missile deal into broader, sustained defence cooperation, remains a key challenge.
Limited Awareness of Mutual Opportunities: Despite cultural and historical ties, a lack of awareness about the business and investment opportunities in both countries hinders the full exploitation of the economic potential.
Way Forward for India to strengthen its relations with the Philippines?
Strategic Integration
- Strategic Dialogues: Establish regular "2+2" dialogues (Foreign and Defense Ministers) to ensure continuous, high-level strategic alignment on regional security issues, especially concerning the Indo-Pacific.
- Defense partnership: India should promote "Make in India" defense exports to the Philippines, this includes patrol vessels, surveillance systems, and other defense equipment.
- Defense cooperation should expand beyond missile sales to include joint training, intelligence sharing, and maritime domain awareness initiatives, establishing a dedicated maritime security dialogue.
- Capacity Building: Expand training programs for Filipino armed forces in specialized areas like cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, and naval tactics, sharing India's expertise.
Boost Economic Ties
- Negotiate a bilateral Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA) or Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA), to reduce trade barriers and open new market access.
- Diversification of trade baskets and promotion of two-way investments in sunrise sectors like renewable energy, digital economy, and start-ups should be prioritized.
- Investment promotion and offering tax breaks to Philippine companies investing in India can encourage balanced growth.
- Initiatives like sector-specific trade missions can diversify trade. Investing in infrastructure projects, such as ports, roads, and warehousing, and harmonizing regulations will mitigate logistical barriers.
Promote People-to-People Connections
- Promote Indian culture through festivals, art exhibitions, and yoga initiatives in the Philippines.
- Expand scholarships and exchange programs for students and researchers in diverse fields.
- Over 70,000 people of Indian origin live in the Philippines.
Strengthen Multilateral Cooperation
- Strategically, both nations must enhance multilateral engagement within forums such as ASEAN, and the East Asia Summit, advocating for a free, open, and inclusive Indo-Pacific based on international law.
- Collaborate on shared global challenges such as climate change, disaster management, food security, and public health.
- As the Philippines takes on the role of Country Coordinator for ASEAN-India Dialogue Relations (2024–2027), India needs to engage with the broader ASEAN framework to ensure its strategic and economic initiatives align with regional.
Source: REUTERS
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Discuss the role of India and the Philippines in promoting maritime security and freedom of navigation in the Indo-Pacific. 150 words
|
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
It is India's foreign policy to deepen its engagement with Southeast Asian nations, including the Philippines, for mutual economic, strategic, and cultural benefits.
Bilateral trade reached US$ 3.5 billion in the financial year 2023-24.
It stands for "Mutual and Holistic Advancement for Security and Growth Across Regions," a key framework for India's maritime cooperation.





 Defence and security cooperation
Defence and security cooperation


