



India’s foreign policy on the Israel-Palestine conflict masterfully balances historical solidarity with Palestine and strategic ties with Israel. This "de-hyphenated" approach protects national interests like energy security and counter-terrorism while advocating a two-state solution. India navigates this geopolitical tightrope with nuanced UN votes and a focus on peace and humanitarian aid.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: THE HINDU
India navigates a complicated balancing act, maintaining its historical support for a two-state solution and providing humanitarian aid to Palestinians, while strengthening strategic ties, including defense and technology, with Israel.
|
Read about Israel Palestine Conflict: http://iasgyan.in/ig-uploads/pdf/rstv_may3.pdf |
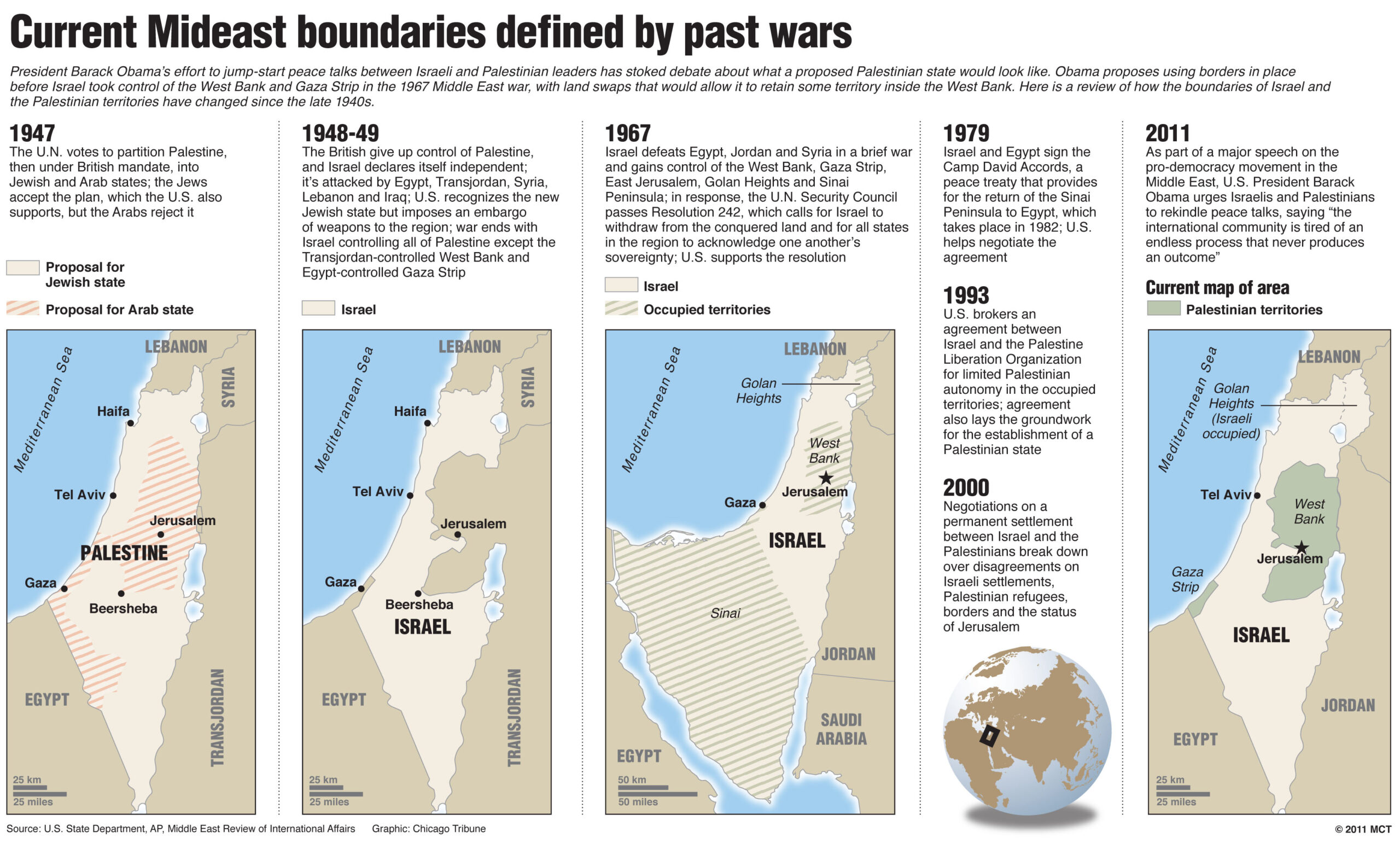
Modern history of Palestine is linked to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Balfour Declaration (1917): British pledge supported the establishment of a "national home" for the Jewish people in Palestine, igniting tensions between Arab and Jewish populations.
UN Partition Plan (1947): Proposed dividing Palestine into separate Arab and Jewish states, with Jerusalem internationalized. While Jewish leaders accepted the plan, Arab nations rejected it.
1948 Arab-Israeli War: Israel declared independence in 1948, then it was attacked by five Arab nations, as result Israel gain control of most of the territory, that led to the displacement of about 750,000 Palestinians, an event known as the Nakba (Catastrophe).
1967 Six-Day War: Israel occupied the West Bank and Gaza Strip, territories previously held by Jordan and Egypt respectively.
Oslo Accords (1993): Agreements established the Palestinian Authority (PA) as an interim body to govern parts of the West Bank and Gaza Strip, but failed to reach a permanent resolution.
Recent Conflicts and Challenges: Ongoing Gaza war, triggered by Hamas attacks in October 2023, has resulted in widespread destruction, humanitarian crises, and accusations of war crimes and potential genocide.
 Evolution of India-Palestinian Relations
Evolution of India-Palestinian Relations
Early Solidarity (Pre-1990s): India supported the Palestinian cause, viewing it through an anti-colonial lens.
Post-Cold War Shift and "De-hyphenation" (1990s-2010s): With the end of the Cold War and after the Oslo Accords, India started normalizing relations with Israel, established full diplomatic ties in 1992.
Deepening Engagement with Israel, Sustained Support for Palestine (2010s-Present): While economic and strategic ties with Israel have strengthened (bilateral trade reached nearly $11 billion in 2022-23, excluding defense). India continues to provide political and developmental assistance to Palestine, both are strategically important for India's Look West Policy.
Recent Stance (Post-October 2023): Following the Israel-Hamas conflict in October 2023, India condemned the Hamas attacks but also called for a sovereign, independent, and feasible State of Palestine within secure and recognized borders, living side-by-side with Israel in peace.
Historical Solidarity and Anti-Colonialism: India's foreign policy rooted in anti-colonialism and the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM), cultivated a strong solidarity with the Palestinian people and their cause for self-determination.
Multilateral Diplomacy and Global South Leadership: India supports the Palestinian cause in various international forums like the United Nations (UN), strengthens India's leadership aspirations within the Global South.
Developmental Cooperation: India provides various forms of assistance, including developmental projects, to Palestine. Examples include the National Printing Press at Ramallah.
Economic and Commercial Engagement: India-Palestine bilateral trade volume stood at USD 145.597 million in 2023. Although trade occurs through Israel, Indian exports to Palestine include marble, granite, basmati rice, coffee, sugar, and textiles.
Financial and Technical Aid: India Provide financial and technical assistance, funding various projects in Palestine, including infrastructure, education, and healthcare. For example, India built the "India-Palestine Centre for Excellence in IT" in Ramallah and contributed to the "India-Palestine Techno Park".
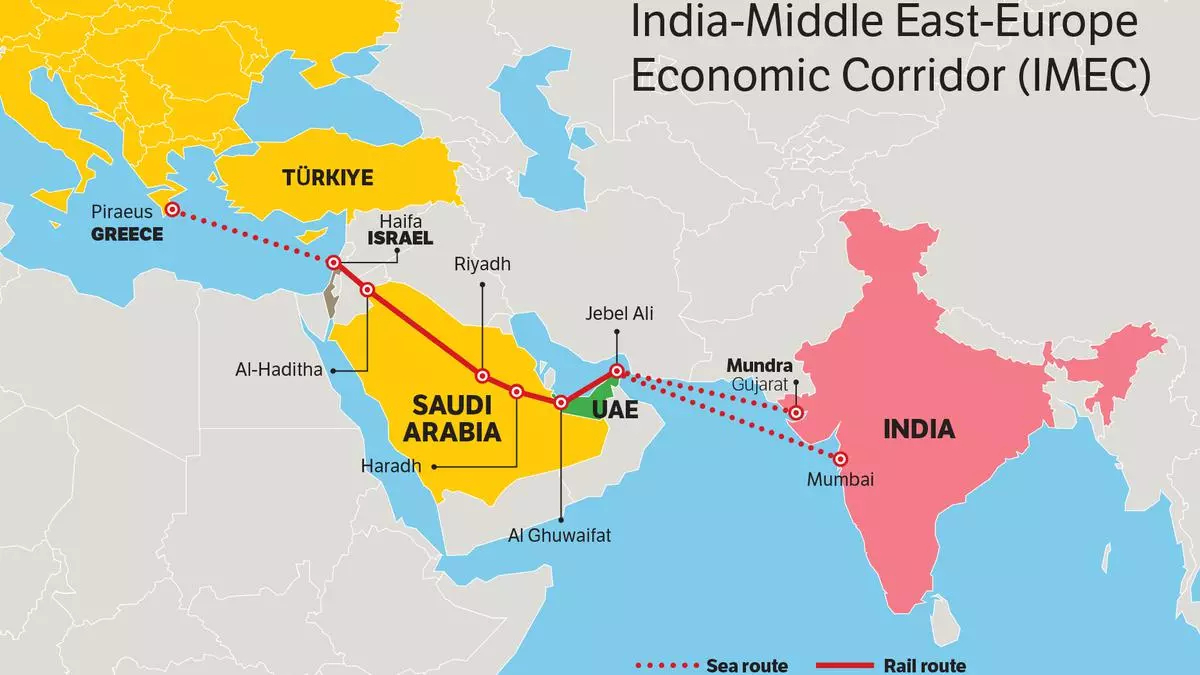
Regional Stability and Geopolitical Interests: Israel-Hamas conflict has raised concerns about geopolitical stability in West Asia and the potential impact on global oil prices, and delayed the progress of India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC). A stable resolution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict supports broader regional peace.
 Soft Power and International Credibility: Sustaining support for Palestine enhances India's credibility among Arab and Islamic nations, along with non-aligned countries.
Soft Power and International Credibility: Sustaining support for Palestine enhances India's credibility among Arab and Islamic nations, along with non-aligned countries.
Diaspora Concerns: A large Indian diaspora resides in Gulf countries. Maintaining good relations with Arab nations, strong supporters of Palestine, is vital for there safety and economic well-being.
Deepening Ties with Israel: India's growing strategic and economic partnership with Israel, especially in defense and technology, creates a perception of reduced solidarity with Palestine.
Shifting Global Dynamics: Abraham Accords (2020), which normalized relations between Israel and several Arab nations, have altered regional dynamics. This reduces pressure on India for exclusive alignment with the Palestinian cause.
Internal Political Pressures: India faces domestic pressure from groups advocating for stronger ties with Israel, and others demanding continued robust support for Palestine.
Declining Palestinian Leverage: Fragmented Palestinian leadership and continuous Israeli settlement expansion weaken the Palestinian position, making the two-state solution nearly impossible. This complicates India's support for a practical path forward.
Terrorism Narrative: India's strong stance against terrorism, complicates its traditional solidarity with the broader Palestinian movement, particularly after incidents like the October 2023 attack.
Limited Direct Influence: India has limited direct leverage to influence the core Israeli-Palestinian peace process. Its role remains primarily supportive and diplomatic.
US Influence: India's growing strategic partnership with the United States aligns with US policy in West Asia, which historically favors Israel.
Global Polarization: Israeli-Palestinian conflict polarizes international opinion. India must navigate this divide carefully, by avoiding aligning too closely with one side.
Reaffirm Two-State Solution: Consistently and vocally reaffirm its commitment to the Two-State Solution at all international forums. This includes supporting a sovereign Palestinian state based on pre-1967 borders with East Jerusalem as its capital.
Enhanced Developmental Partnership: Increase financial and technical assistance to Palestine, focus on impactful projects in education, healthcare, IT, and infrastructure that directly benefit the Palestinian people and build their capacity for statehood.
Support Palestinian Institutions: Provide training and capacity building for Palestinian administrative and security institutions, aiding their preparedness for effective governance.
Active Diplomacy: While maintaining the de-hyphenation policy, explore quiet diplomacy (or Track II diplomacy) to encourage a resumption of state dialogue, advocate more strongly for humanitarian access and civilian protection.
Clarify Narrative: Express stand more clearly on global platforms, explain how India's balanced approach supports stability and peace for both Israelis and Palestinians.
Address Humanitarian Concerns: Increase humanitarian aid to Palestine, especially in areas like Gaza that face severe humanitarian crises. Expand development cooperation projects in sectors such as healthcare, education, vocational training, and sustainable infrastructure.
Enhance Capacity Building and People-to-People Ties: Expand scholarship programs (e.g., ICCR scholarships) and technical assistance (ITEC) slots for Palestinian students and professionals, encouraging long-term human resource development.
Avoid Selective Condemnation: Adopt a consistent stance on human rights and international law, condemning violations by any party.
Leverage Multilateral Platforms: Utilize growing influence within multilateral bodies (e.g., G20, BRICS, Shanghai Cooperation Organisation) to build consensus for a peaceful resolution and to mobilize international support for Palestinian state-building efforts.
India must continue its principled yet pragmatic approach, strengthening developmental cooperation with Palestine and engaging all regional stakeholders to promote peace and stability in West Asia.
|
FOR MAINS: ISRAEL PALESTINE CONFLICT l ISRAEL HAMAS CONFLICT l ISRAEL'S GAZA REOCCUPATION PLAN l ISRAEL-IRAN CEASEFIRE AND FUTURE |
Source: THE HINDU
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. How does the ongoing Israel-Palestine conflict impact India's economic and energy security interests in the region? 250 words |
It is India's approach of treating its relationships with Israel and Palestine as separate and independent, without one affecting the other.
India has a Representative Office to the State of Palestine in Ramallah, not a full-fledged embassy.
It is a peace plan that proposes the creation of an independent Palestinian state alongside the state of Israel.




© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved