



The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor, launched at the 2023 G20 Summit, aims to enhance trade and integration via a multimodal route, offering a strategic alternative to China’s BRI. Its success depends on overcoming Middle East geopolitical instability through collaborative, transparent efforts, ensuring sustainable connectivity and mutual economic growth across regions.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: INDIAN EXPRESS
Amid recent US tariffs, India is diversifying its trade relationships, strengthening domestic industries, and leveraging initiatives like the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) to reduce dependence on single markets.
It was launched in 2023, during the G20 New Delhi Summit. Leaders from India, the United States, the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, France, Germany, Italy, and the European Union signed Memorandum of Understanding (MoU).
It includes two main segments:
Goods would move by rail from the UAE through Saudi Arabia and Jordan to Israel's Haifa port, then by ship to European ports like Piraeus (Greece), Messina (Italy), and Marseille (France), for onward transmission by European rail networks.
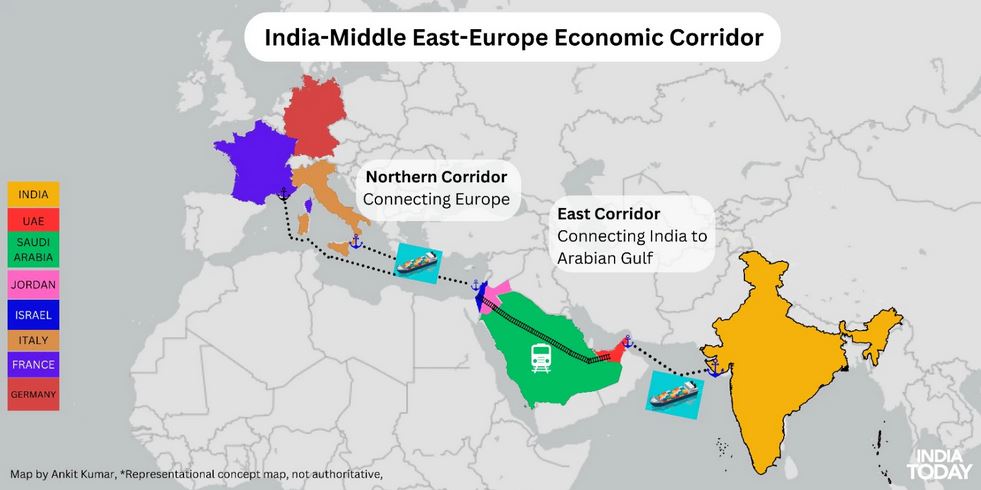
Current progress of the IMEC
The eastern section of the IMEC, which links the UAE and India, is progressing rapidly due to strong economic ties between India and the UAE. The Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) has boosted trade.
The Northern section of the IMEC faces challenges due to the ongoing Israel-Palestine conflict, which has disrupted plans and affected the participation of Saudi Arabia and Jordan, as they need to collaborate with Israel on the project.
Reduce Logistics Costs and Time: IMEC will reduce transportation time between India and Europe by 40% and logistics costs by 30% compared to the Suez Canal route. This boosts the competitiveness of Indian exports in European markets.
Enhanced market access: Direct market access in the Middle East and Europe. The European Union already serves as India's largest trading partner, with bilateral trade reached $137.41 billion in FY 2023-24. The corridor specifically boosts India's engineering exports.
Supply chain resilience and diversification: Reduces India's dependence on the Suez Canal, a vulnerable single point that handles the majority of India's exports to Europe and the US.
Green energy hub: Encourage the development of green hydrogen and green ammonia production hubs along Indian coasts for export to the Middle East and Europe, aligns with India's "One Sun, One World, One Grid" initiative, facilitating the transfer of renewable energy across regions and promoting a greener energy transition.
Digital connectivity: IMEC includes a secure, high-speed data pipeline, to challenge the Chinese dominance in the data cable market and enhance India's digital footprint. It also promises high-speed, secure information and data flow for regional integration.
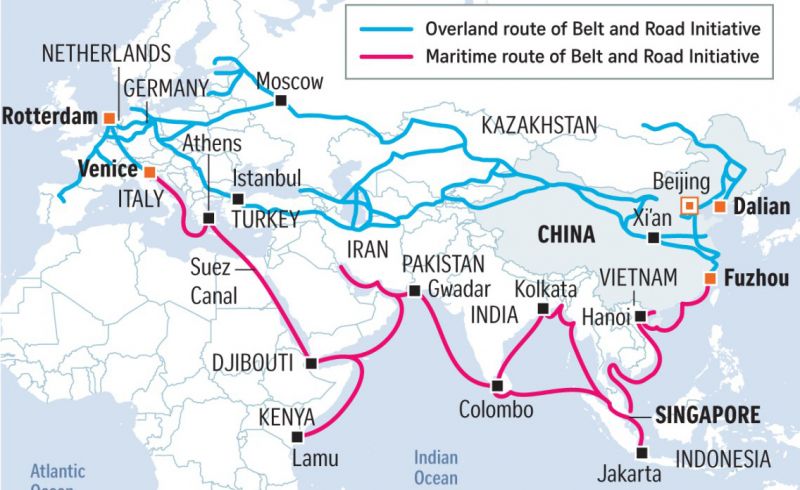
Countering China's BRI: IMEC serves as a counter to China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) by offering a transparent, sustainable, and debt-free infrastructure alternative.
 Strategic partnerships and geopolitical influence: Strengthens India's strategic alliances with key global players like the US, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and European nations.
Strategic partnerships and geopolitical influence: Strengthens India's strategic alliances with key global players like the US, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and European nations.
Development of Infrastructure: Encourage investments in port modernization, railway upgrades, road networks, and digital infrastructure (e.g., high-speed data cables and clean hydrogen pipelines) across the corridor.
Opportunities for Investment and Job Creation: Creates opportunities for Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in sectors like infrastructure, logistics, green energy, and digital technologies in India, leading to job creation.
|
Other Efforts Taken for Expanding and Strengthening Trade Routes by India
|
Geopolitical Instability: Ongoing conflicts, including the Israel-Hamas war, create security and political instability, disrupting cooperation between regional partners. For example, strikes on commercial vessels in the Red Sea have forced shipping companies to reroute via the Cape of Good Hope, adding a week to transit times and approximately $1 million in fuel costs per voyage.
Financial Commitment and Viability: IMEC requires estimated costs for infrastructure development between $3 billion to $8 billion per route. Securing the funding on a risky route, and ensuring the economic viability of a multi-modal route compared to existing sea routes remains a challenge.
Coordination and Regulation: Building a multimodal transport corridor across multiple nations with diverse legal systems, policies, and regulations demands a complex level of coordination and policy harmonization among participating countries. For example, differences in emissions standards between the EU and India create operational difficulties and logistical friction.
Security Risks: Corridor crosses regions sensitive to security threats like piracy, terrorism, and cyberattacks, requiring robust security measures including joint naval patrols, advanced cargo security systems, and a comprehensive, multi-layered security framework.
Exclusion of Key Regional Players: Exclusion of major regional economies like Egypt and Turkey from IMEC, limit its geopolitical and economic reach.
Competition with Existing Routes: Established and efficient Suez Canal route poses a challenge to IMEC's competitiveness, requiring the corridor to offer provable benefits in terms of cost and speed to attract traffic.
Sovereignty Concerns and Differing Interests: Negotiating the national interests, priorities, and bureaucratic processes of around twenty countries, including the US, EU members, and nations in the Middle East.
Technological Integration and Standardization: Digital infrastructure, including undersea data cables and smart port technology, faces integration challenges due to differences in technological standards and cyberattack risks, require seamless connectivity and robust security measures.
Prioritize Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Involve the private sector in planning, implementation, and financing, to utilize their expertise, enhance efficiency, and ensure financial viability.
Harmonize Regulatory Frameworks and Digital Connectivity: Align trade processes, customs procedures, and paperwork among participating nations.
Enhance Energy Cooperation: Focus on interconnected grids and green hydrogen to address energy transition challenges.
Engage Stakeholders: Engage industry bodies, trade associations, think tanks, and academia to identify bottlenecks, promote best practices, contribute innovative solutions, and assist in capacity-building along the corridor.
Strategically Expand Membership: Expand membership to other interested countries like Turkey and Egypt to enhance IMEC's geopolitical and economic reach.
Address Geopolitical Realities: Strategically navigate regional tensions, such as the Israel-Palestine conflict, which directly impacts cooperation and implementation timelines.
Ensure Holistic Development: Extend IMEC beyond infrastructure to promote cooperation, collaboration, and cultural bridging. This includes creating skill corridors and encouraging university collaborations to develop human resources in areas like ports, energy, and digital infrastructure.
Success of the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) depends on India's strategic focus on the Eastern Leg, streamlined regulatory harmonization and innovative Public-Private Partnership financing, ensuring security and regional inclusivity, and leveraging digital and green energy infrastructure to overcome obstacles and realize its potential as a transformative trade route connecting Asia, the Middle East, and Europe.
|
For Mains: BELT AND ROAD INITIATIVE (BRI) l USA PRESSURE TACTIC FOR TRADE CONCESSION |
Source: INDIAN EXPRESS
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Analyze the geopolitical and geoeconomic significance of the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) for India. 250 words |
IMEC is a planned multimodal connectivity project linking India, the Middle East, and Europe through sea lanes and railways.
India, the USA, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, the EU, France, Germany, and Italy are the key signatories.
Its main goal is to boost trade, reduce transport costs, and create a more efficient and reliable trade route.




© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved