Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Oil tanker breakdown in the Suez Canal, a major global waterway, which disrupted traffic and temporarily halted the transit of other vessels.
Details
Incident Details:
- A tanker carrying crude oil, named Seavigour, experienced a mechanical malfunction at the 12-kilometer mark of the Suez Canal.
- The incident occurred in a single-lane section of the canal, disrupting the transit of eight other vessels in the north convoy.
Response and Towing:
- The Suez Canal Authority deployed three tugboats to tow the stranded tanker away from the single-lane area.
- The goal was to move the tanker to a double-lane section at the 17-kilometer mark, allowing other vessels to continue their transit.
Vessel Information:
- The Seavigour is a Malta-flagged tanker built in 2016.
- It measures 274 meters (899 feet) in length and 48.63 meters (159 feet) in width, according to MarineTraffic.
Previous Incidents in the Suez Canal:
- Over the past few years, there have been several cases of vessels running aground or experiencing breakdowns in the Suez Canal.
- Notable incidents include a Hong Kong-flagged ship blocking the canal on May 25 and a Liberia-flagged ship running aground in March 2022. Both were refloated later.

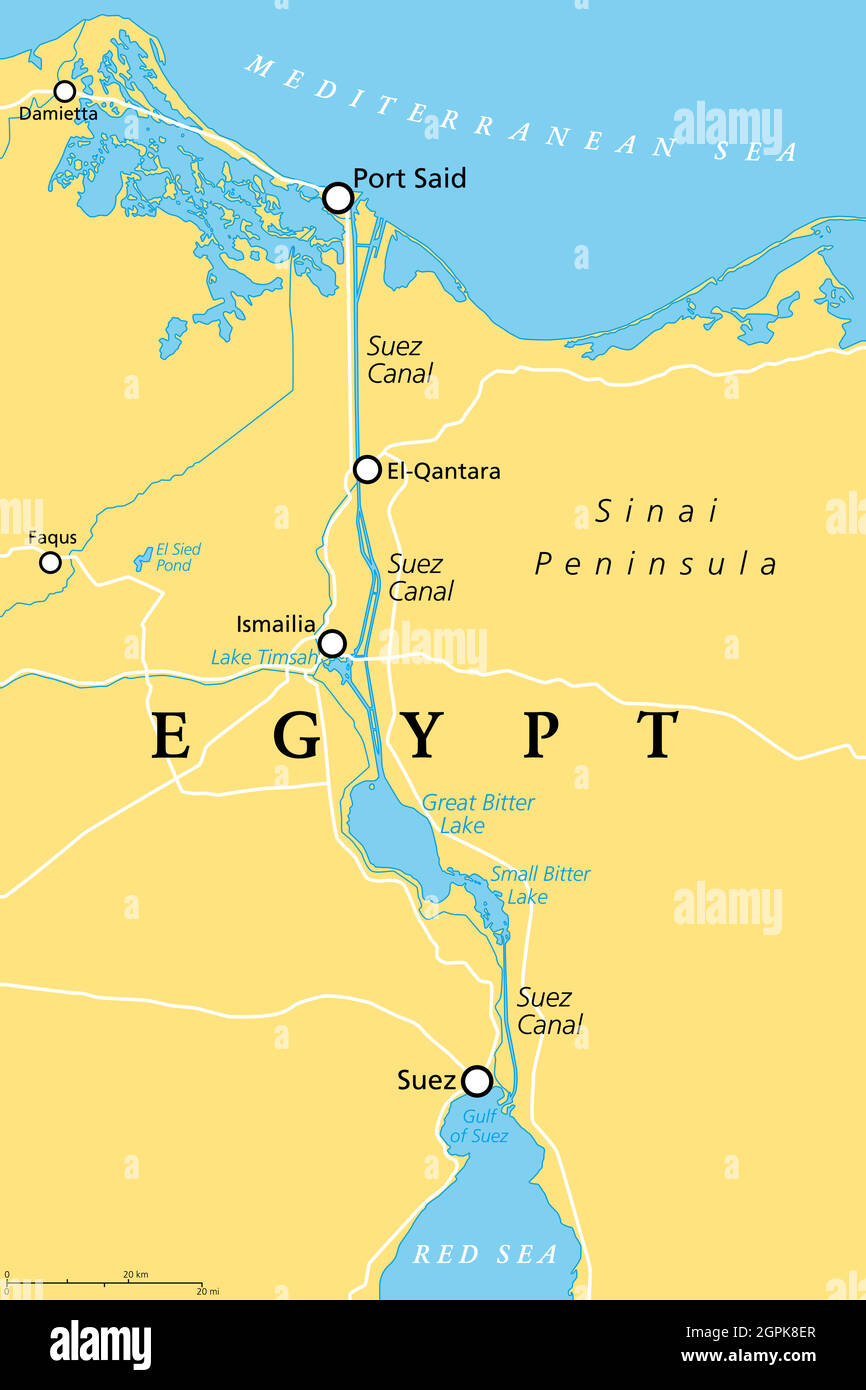
About Suez Canal
- The Suez Canal is a strategically important waterway connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea.
- It serves as a crucial link for international trade, facilitating the transportation of goods, oil, and natural gas.
- Managed by the Suez Canal Authority, the canal has a significant impact on global maritime commerce.
Historical Significance:
- The Suez Canal was opened in 1869 after years of construction efforts led by Ferdinand de Lesseps.
- It provided a direct shipping route between Europe and Asia, reducing the journey time and costs for vessels.
Geographic and Technical Details:
- Located in Egypt, the Suez Canal stretches for approximately 193 kilometers (120 miles).
- It includes multiple sections, including single-lane and double-lane parts, allowing for the passage of vessels in both directions.
- The canal is supported by a network of ports, terminals, and infrastructure along its route.
Role in Global Trade:
- The Suez Canal is a critical artery for international trade, handling around 10% of global maritime traffic.
- It offers a shorter route for ships traveling between Europe, Asia, and the Middle East, saving time and fuel costs.
- The canal is vital for transporting goods, including manufactured products, raw materials, and energy resources.
Economic Importance:
- The Suez Canal serves as a major source of revenue for Egypt, contributing significantly to its economy.
- Fees and tolls collected from vessels passing through the canal contribute to the country's foreign currency reserves.
- The revenue generated by the canal plays a crucial role in funding infrastructure projects and supporting national development.
Challenges and Disruptions:
- The Suez Canal occasionally faces challenges such as vessel breakdowns, grounding incidents, or congestion.
- These incidents can temporarily disrupt traffic and result in delays for ships transiting through the waterway.
- Notable disruptions include the grounding of the Ever Given in 2021, which blocked the canal for six days, causing significant disruptions to global trade.
Continuous maintenance, infrastructure development, and effective management are essential to ensure the smooth and efficient operation of the Suez Canal.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Which countries border the Suez Canal?
(A) Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Jordan
(B) Egypt, Sudan, Yemen
(C) Egypt, Israel, Cyprus
(D) Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Jordan, Israel
Answer: A) Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Jordan
|
https://www.moneycontrol.com/news/world/oil-tanker-breaks-down-in-egypts-suez-canal-disrupting-traffic-in-the-global-waterway-10739511.html









