



UNESCO added Himachal Pradesh’s Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve to the World Network of Biosphere Reserves, raising India’s tally to 13. Protecting snow leopards and supporting pastoralists, it exemplifies sustainable, community-led development in a fragile trans-Himalayan ecosystem.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: THE HINDU
The Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve (CDBR) in Himachal Pradesh has been officially included in UNESCO's World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR).
Location & Altitude: Located in the Trans-Himalayan region, covering the Spiti and Lahaul Forest Divisions of Himachal Pradesh. Altitudes range from 3,300 to 6,600 meters.
National Status: Declared a Biosphere Reserve (BR) in 2009, becoming India’s 16th and first high-altitude cold desert BR.
Biodiversity
Community Link: Around 12,000 residents practice traditional pastoralism (yak/goat herding) and small-scale farming, maintaining a harmonious human-environment coexistence. The region is a center for ancient Tibetan herbal medicine traditions (the Sowa-Rigpa or Amchi system).
A Biosphere Reserve is an international designation by UNESCO for landscapes that demonstrate a balanced relationship between people and nature. They are not just protected areas but are living laboratories for sustainable development.
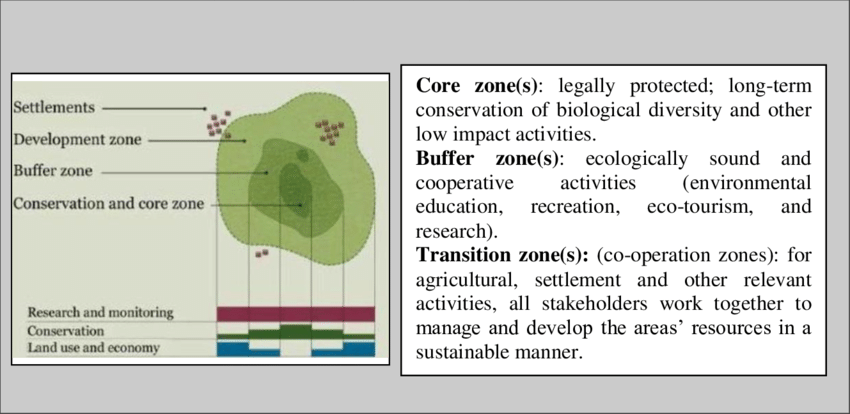
Three Core Functions:
Zonal Structure: BR is structured into three interconnected zones:
 World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR)
World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR)The WNBR is a global network operating under the UNESCO Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme.
Its objective is to promote international cooperation through the exchange of experiences, know-how, and best practices among Biosphere Reserves globally.
National Scheme: India launched its Biosphere Reserve scheme in 1986.
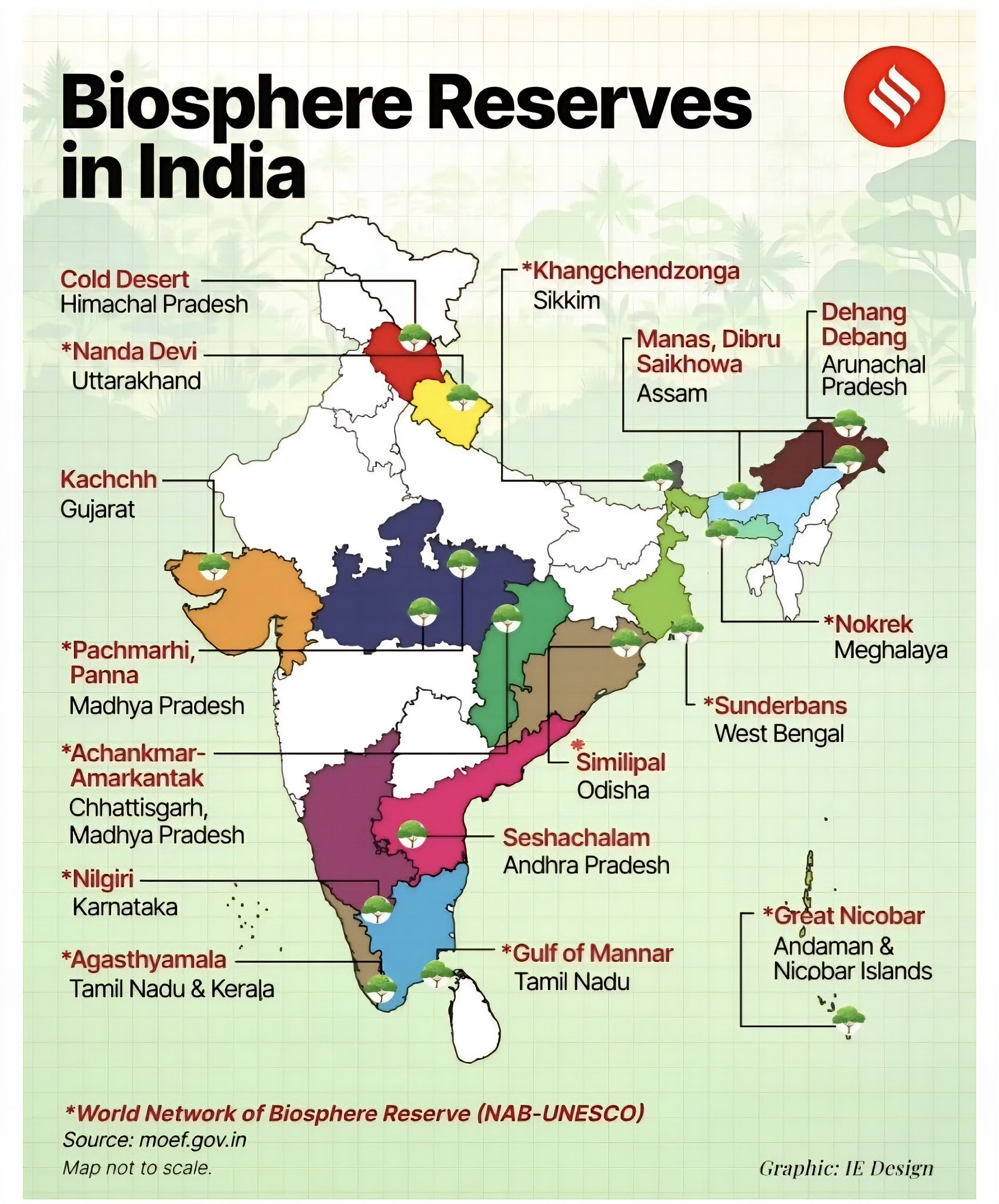
Total BRs: India currently has 18 designated Biosphere Reserves.
WNBR Sites: With the recent addition of the Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve, 13 of India's 18 BRs are now part of UNESCO's World Network of Biosphere Reserves.
Financial Assistance: Financial support is provided by the Central Government to the states at a 90:10 ratio for North Eastern and Himalayan states, and at a 60:40 ratio for other states.
Source: THE HINDU
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. What is the primary traditional medical system deeply rooted in the cultural heritage of the communities residing within the Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve? A) Unani Medicine B) Amchi system C) Ayurveda D) Siddha Medicine Answer: B Explanation: The traditional medical system is the Amchi system. It is also known as Sowa-Rigpa and is deeply rooted in the cultural heritage of the Cold Desert region's Tibetan Buddhist communities. |
A Biosphere Reserve is a protected area designated for conserving biodiversity and promoting sustainable development. These aim to balance the conservation of biological and cultural diversity with economic and social development. They are internationally recognized under UNESCO's Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme.
India has 18 designated Biosphere Reserves. Of these, 13 are part of UNESCO's World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR), including the recent addition of the Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve in 2025.
The largest Biosphere Reserve in India is the Great Rann of Kutch in Gujarat. The smallest is the Dibru-Saikhowa in Assam.





© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved