



Trump’s 20-point Gaza plan offers ceasefire, relief, and reconstruction but depends on Hamas’s acceptance and strict enforcement. For India, it highlights West Asia’s centrality in energy, migration, and counter-terrorism. Its transformation into a credible two-state framework balancing security, equity, and justice is vital for lasting peace and India’s global role.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: THE HINDU
The Indian Prime Minister welcomed the U.S. President Donald Trump’s 20-point Gaza peace proposal, describing it as a “viable pathway to long-term and sustainable peace, security, and development” for Palestinians, Israelis, and the broader West Asian region.
|
Read all about: India Votes for Palestinian Statehood: UPSC Current Affairs l India Votes for Palestinian Statehood l Israel Palestine Conflict l India-Palestinian Relations |
Announced as a “Comprehensive Plan to End the Gaza Conflict,” the proposal outlines a diplomatic roadmap to end hostilities, secure hostages, dismantle Hamas’s military infrastructure, and rebuild Gaza as a demilitarized economic hub.
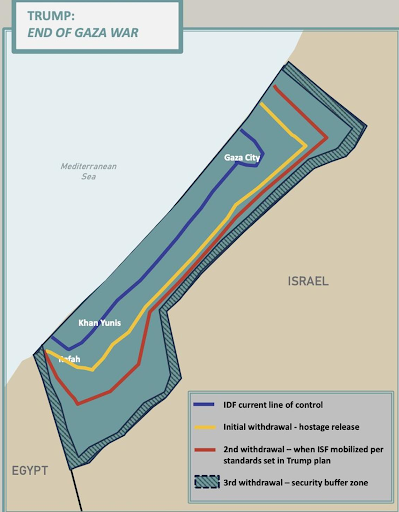
Immediate Security Measures
The plan calls for an immediate ceasefire, freezing the battle lines. It mandates the release of all hostages by Hamas within 72 hours, in exchange for Israel releasing over 1700 Palestinian detainees.
New Governance Framework
It excludes Hamas from any role in Gaza's future governance. An international "Board of Peace," co-led by prominent global figures, would oversee administration and reconstruction until Palestinian governance is reformed.
International Oversight
A multinational "International Stabilisation Force (ISF)" with participation from Arab states, would be deployed to maintain peace, secure borders, and train a new Palestinian police force.
Economic Reconstruction
The plan aims to transform Gaza into a "New Gaza" special economic zone, driven by international aid and preferential trade agreements to rebuild infrastructure and create economic opportunities.
Protection of Rights
A key provision ensures that Palestinians will not be forcibly displaced from Gaza, protecting their demographic and human rights.
Path to Statehood
It offers a "political horizon" for a Palestinian state, conditional on comprehensive reforms within the Palestinian Authority (PA) and security guarantees for Israel.
Immediate Humanitarian Relief: The ceasefire mechanism provides a direct and immediate halt to hostilities, preventing further civilian casualties and destruction.
Confidence-Building Measures: By prioritizing the hostage-prisoner exchange, the plan addresses emotionally charged issues, which can help build trust between the conflicting parties.
Multilateral Legitimacy: Backing of key regional powers, the EU, and India provides the plan with strong international legitimacy and increases the diplomatic pressure for compliance.
Economic Revival Focus: “New Gaza” vision prioritizes jobs and infrastructure, stabilizing the region and countering radicalization through opportunity.
Oversight Mechanisms: Trump-led Board and ISF ensure accountability, reducing bilateral mistrust via neutral international involvement.
The plan’s implementation depends on Hamas’s response, with mediators like Qatar and Egypt convening talks in Doha.
Acceptance by Key Actors
Success depends on acceptance from all sides. Radical factions within Hamas may refuse to disarm or be excluded from power. Israeli hardliners may reject the plan over security fears and doubts about the PA's capacity to govern.
Political Fragmentation
Deep-seated divisions between Hamas and the Fatah-led Palestinian Authority could paralyze any attempt to establish a unified and legitimate Palestinian governance structure in Gaza.
Ambiguity on Statehood
Plan's timeline and conditions for Palestinian statehood are not clearly defined, create long-term concern and could be seen as delaying sovereignty indefinitely.
Logistical Complexity
Implementing the plan on the ground—managing prisoner swaps, ensuring transparent aid distribution, and monitoring ceasefire compliance—is a complex task that requires coordination and a high degree of trust.
India’s acceptance reflects its balanced West Asia policy—strong Israel ties (defense, tech) alongside UN support for Palestinian statehood.
Key Concerns for India:
Opportunities for India: The plan’s multilateralism offers India a platform to contribute via UN or QUAD+ formats, enhancing its Global South voice on humanitarian issues.
The Gaza peace plan offers a comprehensive framework combining ceasefire, hostage exchange, reconstruction, and international oversight to end the Israel-Hamas conflict. While it provides humanitarian relief and a pathway to statehood, challenges remain in acceptance, governance, and implementation. Its success depends on mutual compliance and a credible two-state solution.
Source: THE HINDU
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. India's engagement in West Asia is guided by the principle of balancing ties with both Israel and the Arab world. Critically Analyze. 250 words |
The "Board of Peace" is a new international transitional body proposed to oversee Gaza's governance and reconstruction. Donald Trump and former British Prime Minister Tony Blair would co-chair this body, which would include other international leaders and handle funding.
This is a mini-lateral grouping of India, Israel, the UAE, and the USA, formed in 2021. It focuses on joint investments in key sectors like water, energy, transportation, space, and food security, signifying a new geo-economic alignment.
Geopolitical instability and maritime security are major concerns. Events like the Red Sea crisis, caused by Houthi rebel attacks on shipping, and regional conflicts threaten vital sea lanes and supply chains crucial for India's trade and energy flows.




© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved