



India will build Maitri-II to replace the three-decade-old Maitri station, boosting polar and climate research. Equipped with advanced facilities and managed by NCPOR, it reinforces India’s Antarctic Treaty commitment, scientific leadership, and active role in global environmental monitoring and exploration.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: INDIANEXPRESS
The Ministry of Finance has granted approval for Maitri II, new research station in East Antarctica, expected to be operational by January 2029.
Purpose and Need
The original Maitri station, operational since 1989, has surpassed its design life of 10 years and faces challenges like flawed waste management.
Maitri II will serve as India's primary, year-round research hub, while the older Maitri station will be retained as a summer camp.
Nodal Agency
The project is being led by the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR), a Goa-based institution under the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
Key Features
A Natural Laboratory for Climate Science
Geopolitical and Strategic Significance
Provide Unique Scientific Research:
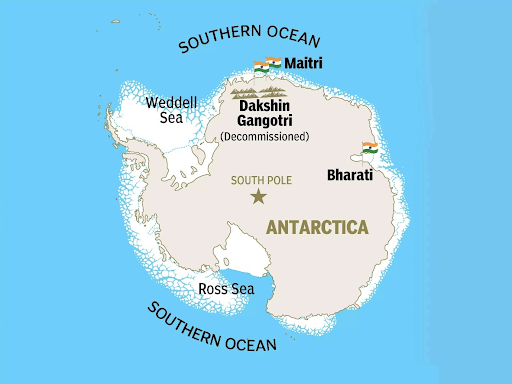
Dakshin Gangotri (1983): India's first scientific base in Antarctica, but was decommissioned in 1990 after being submerged in ice.
Maitri (1989): The second permanent research station and currently the oldest one in operation. Located in the Schirmacher Oasis,.
Bharati (2012): India's third and most modern research station.
Legal Framework: The Indian Antarctic Act, 2022, provides a domestic legal framework for activities on the continent, ensuring they are aligned with its obligations under the Antarctic Treaty.
Global Commitment: India's status as a Consultative Party to the Antarctic Treaty of 1959 binds it to the principles of using the continent for peaceful purposes, promoting scientific freedom, and protecting its unique environment.
India will construct Maitri-II to replace the old Maitri station, enhancing polar research, climate studies, and global environmental monitoring, while reinforcing its Antarctic Treaty commitment.
Source: INDIAN EXPRESS
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Discuss the key scientific objectives of India's Antarctic Programme. 150 words |
India’s Antarctic strategy aims to strengthen scientific research in polar sciences, assert India’s presence under the Antarctic Treaty System, and contribute to global climate change studies, resource security, and sustainable environment protection.
India operates two active Antarctic research stations—Maitri and Bharati—and plans to replace Maitri with the eco-friendly Maitri-II by January 2029..
The Indian Antarctic Act, 2022, provides a legal framework ensuring treaty compliance, environmental protection, and regulation of Indian activities, including research, tourism, waste disposal, and resource management in Antarctica.






© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved