



India encourages hybrid solar-wind-storage systems to ensure a steady clean energy supply, backed by government policies, despite challenges like high costs and land shortages. To achieve sustainable energy goals and become a global leader, India needs to focus on advanced storage solutions, smart grid development, and adaptable regulations.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: DOWNTOEARTH
India faces the dual challenge of increasing energy demand and transitioning to a sustainable, low-carbon future. Hybrid models, integrating solar, wind, and storage technologies, offer a solution by combining intermittent renewable energy with advanced storage.
It works by integrating solar panels, wind turbines, and a battery energy storage system (BESS) through smart control systems to provide a consistent and reliable power supply.
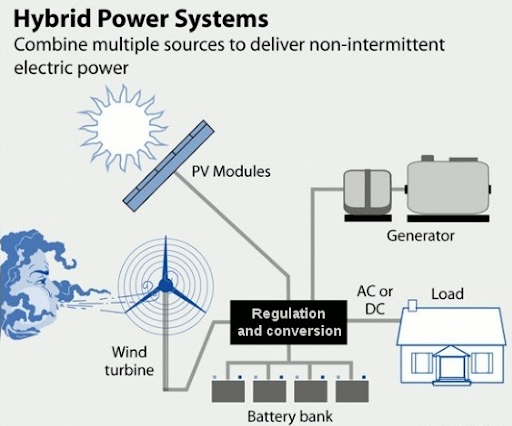
Role of Energy Storage Systems (ESS)
They store surplus energy generated during peak production hours and discharge it during periods of low generation or high demand.
The Central Electricity Authority (CEA) projects India will install 34 gigawatts (GW) or 136 gigawatt-hours (GWh) of battery energy storage by 2030.
India is projected to achieve the highest battery storage capacity globally by 2040, potentially reaching 140-200 gigawatts (GW), according to the International Energy Agency’s India Energy Outlook 2021.
Addressing Intermittency and Variability
Solar power peaks during daytime hours, while wind power generates more electricity at night or during specific seasons.
Hybrid systems create a more consistent and predictable power output, minimizing the fluctuations that destabilize the grid.
Optimizing Resource Utilization
Hybrid projects allow optimal utilization of land and shared transmission infrastructure, reducing overall land footprint and infrastructure costs.
This approach reduces land requirements and infrastructure costs; important in a densely populated country where land acquisition for large projects is challenging.
Enhancing Grid Stability and Reliability
Hybrid energy systems with integrated storage enhance grid stability and provide a continuous power supply by addressing the inconsistency of renewable energy sources; meeting peak demand when solar power is reduced.
National Wind-Solar Hybrid Policy (2018)
Launched by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) to provide a framework for promoting large grid-connected wind-solar PV hybrid systems.
Its objectives include efficient utilization of transmission infrastructure and land, reduction in renewable power generation variability, and enhanced grid stability.
It encourages battery storage integration to optimize output and reduce variability.
Viability Gap Funding (VGF) Scheme
Announced in 2023, this scheme allocates Rs 3,760 crore to develop 4,000 MWh of battery storage systems, offering financial support up to 40% of the project's capital cost. (Source: PIB)
Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme
Supports domestic manufacturing of Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) batteries, allocating ₹18,100 crore to achieve 50 GWh of battery capacities. (Source: PIB)
Energy Storage Obligations (ESO)
Applicable to distribution utilities, ESOs will gradually increase from 1% in 2023-24 to 4% by 2029-30, stimulating demand for storage solutions. (Source: Ministry of Power)
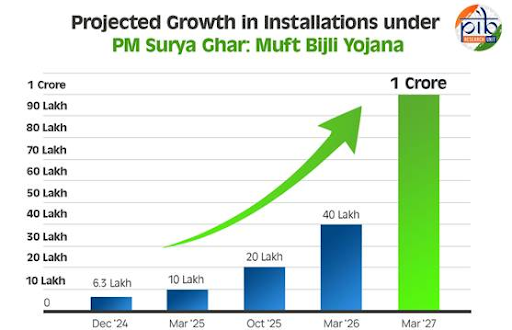
Launched in 2024, it targets installing rooftop solar in 1 crore households by March 2027, providing subsidies up to 40% (up to ₹78,000 for above 3kW systems). (Source: PIB)
Technical and Grid Integration Issue
Land and Resource Constraints
Financial Barriers
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities for Storage
Promote Indigenous Manufacturing of Storage
Accelerating the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme and investing in research and development for alternative battery chemistries to reduce dependency on imports and lower costs.
Streamline Policies and Regulatory Frameworks
Consistent and clear policies, along with faster clearances and a robust legal framework, are essential to attract investments and expedite project execution.
Invest in Transmission Infrastructure
Improve intrastate and interstate transmission networks to bring power from areas with high renewable energy generation to places that need it.
Technological Advancements
Encouraging innovation in energy storage technologies, smart grid solutions, and forecasting tools will enhance the efficiency and reliability of hybrid systems.
Address Financing Challenges
Exploring innovative financing mechanisms, de-risking projects, and ensuring competitive but sustainable tariff structures to attract more private capital.
Hybrid solar-wind-storage models stabilize renewable power by balancing intermittency. With strong policies, investments, and innovation, India drives a reliable clean energy transition and global green leadership..
Source: DOWNTOEARTH
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Critically analyze the role of the National Wind-Solar Hybrid Policy in achieving India's renewable energy targets. 150 words |
A wind-solar hybrid system combines wind turbines and solar photovoltaic (PV) panels to generate electricity from two different renewable sources. It leverages the complementary nature of wind and solar energy: wind blows more strongly at night and during certain seasons, while the sun shines only during the day.
The system consists of wind turbines and solar panels connected to a central controller or inverter. This device manages the power output from both sources, converts it to usable AC electricity, and directs it either to the grid, a battery bank for storage, or directly to the load (appliances/equipment).
It was launched in 2024 to promote rooftop solar installations in one crore households across India. The policy offers financial assistance and subsidies to beneficiaries, with the goal of providing up to 300 units of free electricity per month for these households.






© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved