



India is advancing the democratisation of Artificial Intelligence by expanding affordable access to compute power, shared datasets, digital infrastructure and AI skills through initiatives like the IndiaAI Mission and AIKosh. With widespread 5G connectivity, growing data centre capacity and strong policy support, the approach aims to enable inclusive innovation, strengthen public service delivery, reduce regional disparities and position India as a global leader in equitable and development-focused AI.
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: PIB
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is emerging as a transformative force in India’s development journey, strengthening governance, improving service delivery and enabling scalable solutions across sectors.
|
Must Read: BASICS OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE l AI REGULATION ACROSS THE WORLD | AI IN GOVERNANCE | |
What is Democratisation of AI?
Democratisation of AI refers to making artificial intelligence accessible, affordable and usable for a broad range of users. It goes beyond ready-made applications and focuses on providing access to the core building blocks of AI like, compute power, datasets, models, infrastructure and skills. By expanding access to these foundational resources, India is enabling innovation beyond large technology firms and empowering startups, academic institutions and public agencies.
This inclusive approach also aims to widen economic opportunities. With over 6 million people employed in the technology ecosystem and nearly 490 million informal workers potentially benefiting through improved access to markets and services, AI is positioned as a tool for social and economic transformation.
Key highlights of India’s expanding AI ecosystem:
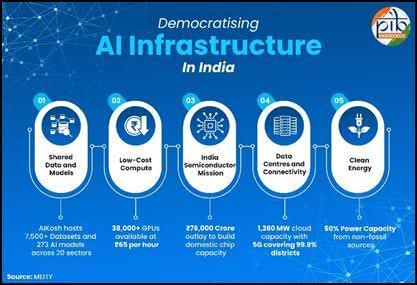
Affordable compute access: To reduce entry barriers for startups, researchers and institutions, the government has enabled access to over 38,000 high-end GPUs at subsidised rates of around ₹65 per hour, significantly lower than global costs. In addition, 1,050 Tensor Processing Units (TPUs) have been onboarded to support high-performance AI training and deployment.
Shared National data and model resources: Through the AIKosh platform, India is creating a common national repository that currently hosts 7,500+ datasets and over 270 AI models across multiple sectors. This shared ecosystem allows developers to build solutions faster without starting from scratch, promoting collaborative innovation.
Nationwide digital connectivity backbone: The rapid expansion of digital infrastructure has enabled 5G coverage in nearly all districts (99.9%), creating the network foundation required for real-time AI applications, cloud computing and edge-based services even in remote regions.
Public investment through IndiaAI Mission: The IndiaAI Mission, with an outlay of ₹10,371.92 crore over five years, serves as the central framework for expanding AI infrastructure, compute access, skilling, research support and responsible AI development across the country.
Key components of democratised AI infrastructure:
Global Cooperation and the India - AI Impact Summit 2026:
Significance for India:
Conclusion:
India’s approach to democratising AI reflects a commitment to making advanced technology accessible, affordable and inclusive. By expanding access to compute, data, infrastructure and skills, the country is enabling innovation across sectors while ensuring that the benefits of AI reach citizens, startups and public institutions alike. This balanced focus on scale, inclusion and self-reliance positions India to leverage AI as a key driver of sustainable growth and global leadership in the digital era.
Source: PIB
|
Practice Question Q. Democratisation of Artificial Intelligence is essential for inclusive development and technological self-reliance in India. Discuss. (250 words) |
Democratisation of AI refers to making artificial intelligence accessible, affordable and usable for a wide range of users by expanding access to core resources such as compute power, datasets, models, infrastructure and skills.
It helps reduce technological inequality, supports startups and innovation, improves public service delivery and ensures that the benefits of AI reach diverse sectors and regions, including rural and underserved areas.
The IndiaAI Mission is a government initiative aimed at strengthening AI infrastructure, providing subsidised compute access, enabling shared datasets and models, promoting research and building a skilled AI workforce.





© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved