



Flash floods caused by heavy rainfall have wreaked havoc along the Kheer Ganga river in Uttarkashi district, Uttarakhand. The floods that ravaged Dharali, a renowned tourist destination 8,600 feet above sea level, killed several people and left many more missing.

Copyright infringement not intended
Source: The guardian
A committee has been formed to look into the reasons for the Dharali tragedy in Uttarakhand, which occurred on August 5, 2025. The team, which includes geologists, will present a report within a week. Rescue activities are hampered by deep debris and damaged roadways, and the death toll remains undetermined, with only one confirmed fatality.
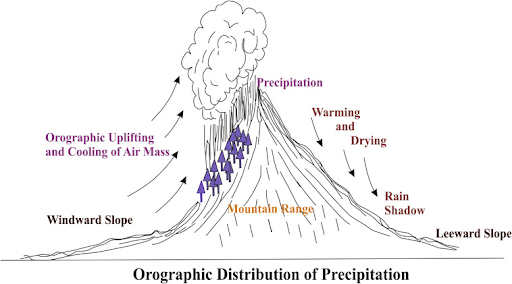
Copyright infringement not intended
Source: Sciencedirect
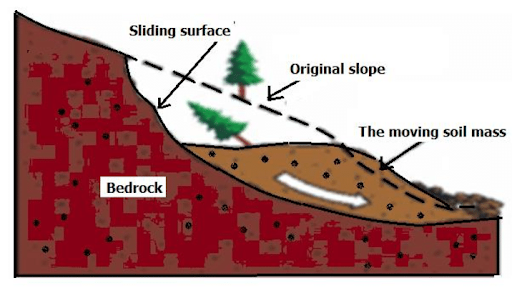
Copyright infringement not intended
Source: Researchgate
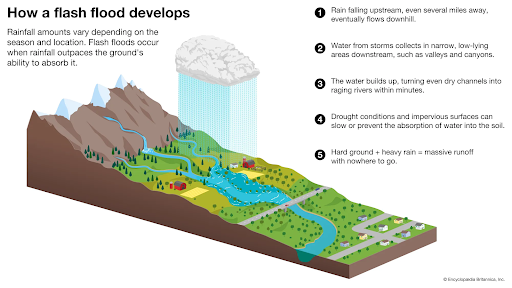
Copyright infringement not intended
Source: Britannica
|
What is NDMA? NDMA, in the context of disaster management in India, stands for the National Disaster Management Authority. It is the apex body in India responsible for disaster management. NDMA is headed by the Prime Minister of India and is tasked with laying down policies, plans, and guidelines for disaster management. It was established under the Disaster Management Act of 2005. |
|
What is GLOF?
|
|
For Prelims: CORAL BLEACHING | DORJILUNG HYDROPOWER PROJECT For Mains: MOUNT CLIO | BAITARANI RIVER | FLASH FLOODS |
Source: Downtoearth
|
Practice Question Q. Which of the following factors primarily increases the risk of landslides in hilly regions? Answer: A |
A cloudburst is a sudden, intense rainfall exceeding 10 cm in less than an hour over a small area (~10 km²), commonly occurring in mountainous regions like the Himalayas.
Intense rainfall from a cloudburst saturates slopes and river catchments, causing soil instability (landslides) and rapid water accumulation leading to flash floods.
Landslides are caused by heavy rainfall, earthquakes, slope erosion, deforestation, and unstable geological formations that weaken slope stability.
Flash floods occur suddenly within 6 hours of heavy rainfall or triggers like dam breaches, characterized by rapid water rise and short duration, unlike regular floods which develop slowly.
Mountainous regions like the Himalayas (Uttarakhand, Himachal), Western Ghats, Northeast India, and urban areas with poor drainage systems are most vulnerable to cloudbursts, landslides, and flash floods.





© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved