



India added Bihar’s Gokul Jalashay and Udaipur Jheel as Ramsar Sites, raising the total to 93, the highest in Asia. These oxbow lakes protect biodiversity, buffer Ganga floods, and enhance climate resilience for vulnerable communities under the “wise use” principle.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: HINDUSTANTIMES
India added two new wetlands in Bihar, Gokul Jalashay and Udaipur Jheel, to the global Ramsar list, increasing its total to 93 sites, the highest in Asia and third globally after the UK (176) and Mexico (144).
Gokul Jalashay, Buxar District (Bihar)
Type & Location: Oxbow lake situated on the southern edge of the Ganga River.
Ecological Role: Acts as a natural flood buffer for surrounding villages, mitigating the impact of monsoon flooding. During dry months it provides essential food and breeding habitats.
Biodiversity: Supports over 50 bird species.
Community Linkages: Local communities depend on the wetland for fishing, farming, and irrigation. The tradition of villagers cleaning the catchment annually during a festival highlights the site's social value.
Udaipur Jheel, West Champaran District (Bihar)
Type & Location: Oxbow lake, bordering the dense forest of the Udaipur Wildlife Sanctuary.
Biodiversity: Hosts over 280 plant species, including Alysicarpus roxburghianus, a perennial herb endemic to India.
Migratory Birds: Functions as an important wintering ground for around 35 migratory bird species, including the vulnerable common pochard (Aythya ferina).
Threats: Faces threats from illegal fishing and the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides from intensive agriculture in surrounding areas.
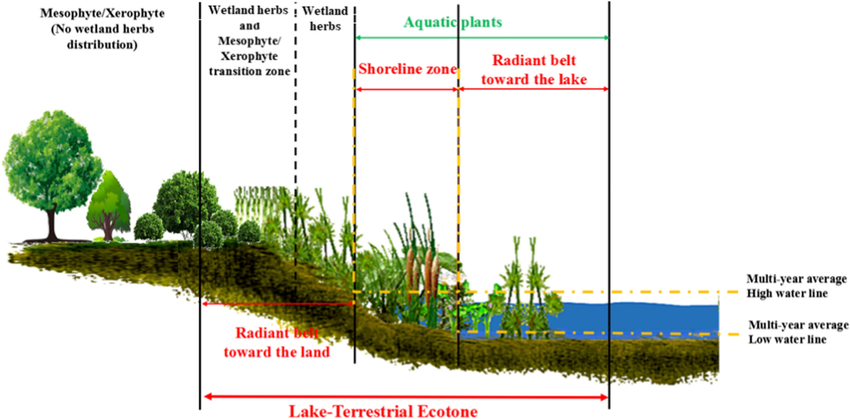
Wetlands are areas of marsh, fen, peatland, or water that are either natural or artificial, with water that is static or flowing.
They are defined as an ecotone—a transitional area between terrestrial (land) and aquatic (water) ecosystems. They include marine areas where the depth does not exceed six meters at low tide.
 About the Ramsar Convention
About the Ramsar ConventionObjective: Provides a global framework for the conservation and "wise use" of wetlands.
Adoption: Adopted in Ramsar, Iran, on 2nd February 1971 (India joined in 1982). February 2nd is celebrated as World Wetlands Day.
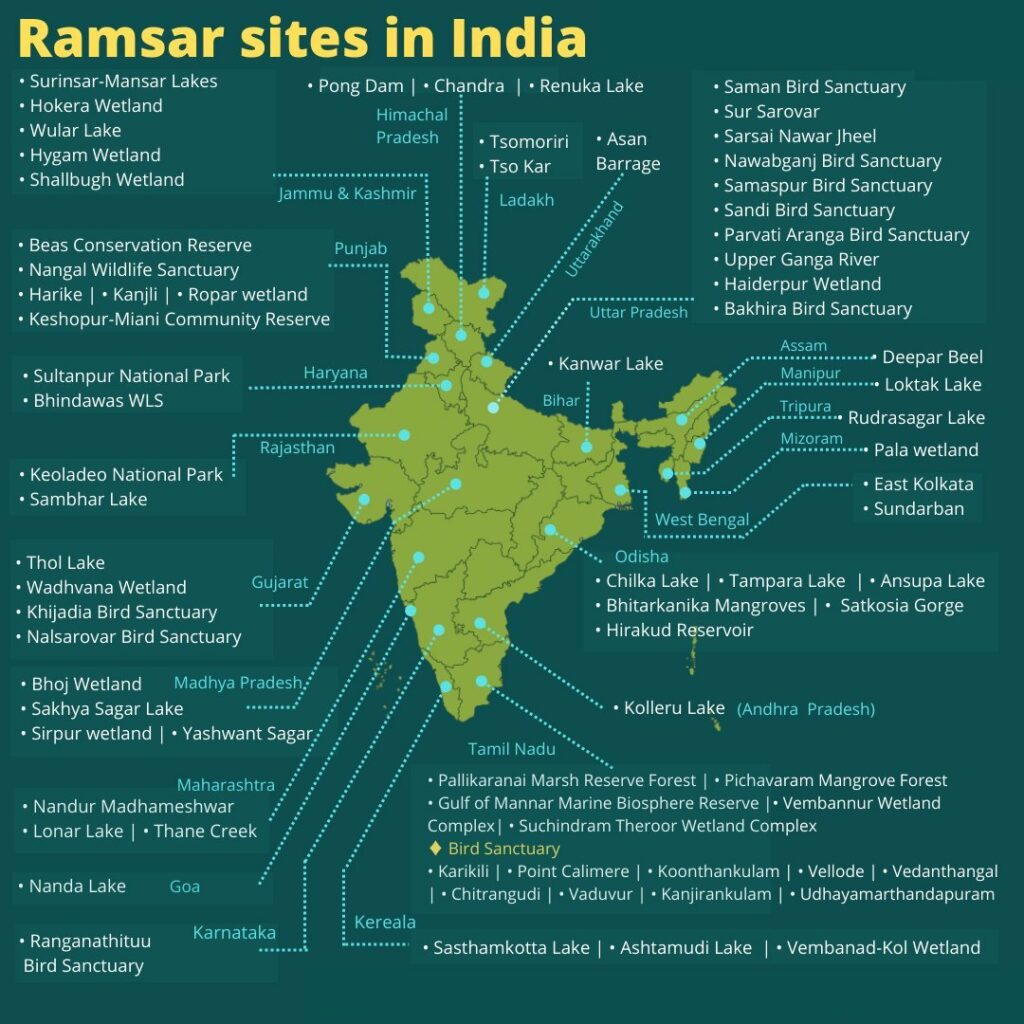
Global Status: India now has 93 Ramsar Sites, covering a total area of over 13.6 lakh hectares. Tamil Nadu (20) have the highest number of Sites.
The Montreux Record (Ramsar 'Threatened List')
The Montreux Record is a register of Ramsar sites where the ecological character has changed, is changing, or is likely to change due to human interference (e.g., pollution, technological developments).
Sites in India: India currently has two sites on the Montreux Record:
Removed Site: Chilika Lake, Odisha, was placed on the Record in 1993 due to siltation and removed in 2002 after successful conservation efforts—making it the first site from Asia to be removed.
 Source: HINDUSTANTIMES
Source: HINDUSTANTIMES
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Consider the following statements: 1. Loktak Lake in Manipur is the sole Indian wetland currently listed on the Montreux Record. 2. Kanwar Lake in Uttar Pradesh is Asia’s largest freshwater oxbow lake. Which of the above statements is/are correct? A) 1 only B) 2 only C) Both 1 and 2 D) Neither 1 nor 2 Answer: D Explanation: Statement 1 is incorrect: While Loktak Lake is on the Montreux Record, it is not the sole Indian wetland. Keoladeo National Park in Rajasthan is also currently listed on the Montreux Record, making a total of two Indian wetlands on the record. Statement 2 is incorrect: Kanwar Lake (also known as Kabartal Wetland) is located in Bihar's Begusarai district. It is Asia's largest freshwater oxbow lake. |
A wetland is an area of land that is either permanently or seasonally covered by water. This water can be fresh, brackish (a mix of fresh and salt), or saline (saltwater). The defining characteristics are waterlogged soil (known as hydric soil) and vegetation adapted to these saturated conditions (known as hydrophytes).
The Ramsar Convention, established in 1971, is an international treaty focused on the conservation and sustainable use of wetlands. Member countries work to manage their wetlands wisely and designate important sites as "Ramsar Sites".
The Montreux Record lists Ramsar Sites facing significant ecological changes due to human activity and requiring attention. India has two sites on this record: Loktak Lake in Manipur and Keoladeo National Park in Rajasthan.






© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved