



India, represented by the Surveyor General, has been elected Co-Chair of UN-GGIM-AP (2025–2028), marking its rising geospatial leadership. It will align regional strategies with the UN framework, promote data-driven governance, and advance initiatives like PM GatiShakti for sustainable digital transformation across Asia-Pacific.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: PIB
India has been elected as Co-Chair of the Regional Committee of the United Nations Global Geospatial Information Management for Asia and the Pacific (UN-GGIM-AP) for the 3 years term (2025 to 2028).
It is the inter-governmental body for making joint decisions and setting strategic directions on the use and management of geospatial information across the Asia-Pacific region.
Establishment
It was established in 2012, evolving from the former Permanent Committee on GIS Infrastructure for Asia and the Pacific (PCGIAP, 1995), to align with the global UN-GGIM framework.
Mandate & Objectives
It aims to maximize the economic, social, and environmental benefits of geospatial information through regional cooperation, capacity development, and shared solutions.
Membership
The committee represents the National Geospatial Information Authorities of 56 countries and economies in the Asia-Pacific.
Secretariat
The United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP) has served as its secretariat since 2018.
Geospatial information is any data linked to a location on Earth.
It combines physical coordinates (like latitude and longitude) with attribute data, such as the name, population, or land-use type for that location.
This allows for mapping, analysis, and visualization of geographic patterns.
Key components
Applications
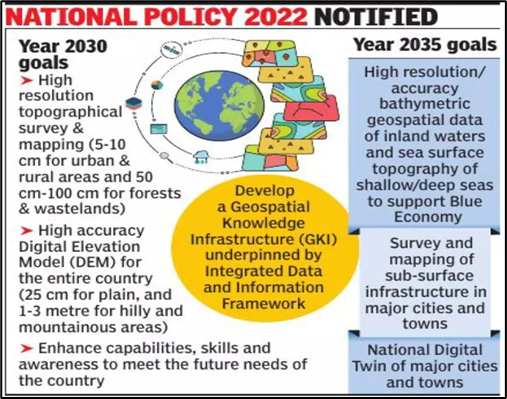
National Geospatial Policy (NGP) 2022
It liberalizes data acquisition and access, replacing the restrictive National Map Policy of 2005.
Its goal is to create a high-resolution topographical survey and mapping infrastructure for the entire country.
Integration with National Missions: Geospatial technology is the backbone of schemes like Digital India and the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan, which uses it for coordinated infrastructure development.
Global Engagement: India hosted the second United Nations World Geospatial Information Congress (UNWGIC) in Hyderabad in 2022, demonstrating its commitment to global collaboration.
Source: PIB
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Consider the following statements about the United Nations Global Geospatial Information Management (UN-GGIM):
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? A) 1 and 2 only B) 1 and 3 only C) 3 only D) 1, 2 and 3 Answer: B Statement 1 is correct: UN-GGIM was established by the UN Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) and is the apex intergovernmental body for setting directions on the use of geospatial information within national, regional, and global policy frameworks. Statement 2 is incorrect: UN-GGIM coordinates geospatial information for global challenges, especially Sustainable Development Goals, not solely post-conflict reconstruction. Statement 3 is correct: India, represented by Surveyor General Hitesh Kumar S. Makwana, was elected as Co-Chair of the UN-GGIM-AP for the term 2025–2028. |
The UN-GGIM-AP is the regional committee for Asia and the Pacific under the United Nations Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management (UN-GGIM). It is an inter-governmental body representing 56 national geospatial authorities in the region.
Key functions include promoting knowledge exchange and training, facilitating regional cooperation on cross-border initiatives, supporting the formulation of standards and policy frameworks, and aligning geospatial management with sustainable development goals (SDGs).
The UN Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UN-ESCAP) has served as the secretariat for UN-GGIM-AP since 2018, providing institutional and technical support.




© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved