



In February 2026, India and the GCC finalized the ToR for an FTA under the Act West policy, aiming to expand ties beyond energy into renewables, investment, and diaspora welfare. Backed by $178.56 billion trade, it supports IMEC and targets $300 billion trade by 2030.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: newsonair
India and the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) initiated the process for negotiating a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) by signing the Terms of Reference (ToR).
|
Read all about: GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL l INDIA-GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL |
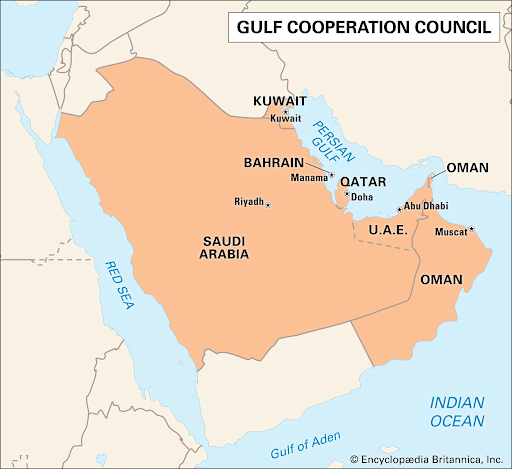
It is a regional political and economic union of six Arab countries located in the Arabian Peninsula.
Established in 1981, the alliance focuses on achieving unity and coordination among its member states through shared cultural, religious, and economic ties.
Member States
The GCC comprises six monarchies that border the Persian Gulf:
Key Objectives
The council was formed to address shared security challenges, such as threats from the Iran-Iraq war at the time of its founding, and to promote regional integration. Its core goals include:
Organizational Structure
The GCC operates through three main bodies:
|
What is Free Trade Agreement (FTA)? It is a legally binding treaty between two or more countries aimed at reducing or eliminating barriers to the exchange of goods and services. While traditional FTAs focused on reducing tariffs (import duties), modern agreements often include provisions for investment, intellectual property (IP), and regulatory standards. How FTAs Work?
|
The FTA seeks to evolve the relationship beyond a traditional energy buyer-seller dynamic into a comprehensive and strategic economic partnership.
Trade and Investment
Massive Trade Volume
In FY 2024-25, bilateral trade reached USD 178.56 billion, representing 15.42% of India’s total global trade. The FTA aims to boost Indian exports to address the existing trade deficit. (Source: Ministry of Commerce & Industry)
Energy Security & Diversification
While India imports about 35% of its crude oil and 70% of natural gas imports from the GCC, the FTA will promote joint ventures in petrochemicals and renewable energy, especially Green Hydrogen. (Source: Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas)
Key Source of FDI
The GCC is a major source of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) for India, with cumulative investments surpassing USD 31.14 billion by September 2025. (Source: PIB)
Diaspora and Remittances
Large Indian Community: The GCC hosts a vibrant community of over 10 million Indians, the largest Indian diaspora globally.
Remittance Powerhouse: India received nearly 38% of remittance originating from the GCC region, an FTA will help create a more stable environment for Indian workers and facilitate smoother financial flows. (Source: RBI)
Strategic Importance and 'Act West' Policy
Regional Stabilizer
In a region facing geopolitical uncertainties, a formal economic framework with India provides stability and strengthens India's role as a reliable partner.
Connectivity & Counterbalance
The FTA will provide the soft infrastructure needed for major connectivity projects like the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC).
Proven Success Model
The FTA negotiations are expected to draw lessons from the successful India-UAE Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) of 2022, which led to a 14% increase in India's non-oil exports to the UAE within two years. (Source: Ministry of Commerce Report)
While the potential benefits are immense, negotiators must navigate several complex challenges to finalize a balanced agreement.
Divergent Economic Interests
Individual GCC members have different priorities. For example, Saudi Arabia's "Saudization" (Nitaqat) policy restricts foreign labor, which conflicts with India’s demand for easier access for its professionals and service providers.
Protecting Domestic Industry
Indian industries, particularly the chemical sector, are concerned about the potential dumping of cheap petrochemicals from the GCC, where feedstock costs are very low. The FTA must include adequate safeguard measures.
Rules of Origin (ROO)
Strict ROO are essential to prevent third countries (like China) from using a GCC country as a transit hub to export goods to India at lower tariff rates.
Labor Standards
Balancing modern trade agreement norms on labor rights with the GCC's distinct labor laws, including ongoing reforms to the Kafala system, will require careful diplomatic negotiation.
Shift from Defensive to Offensive
Move beyond protecting sectors like agriculture and focus on securing market access for India’s strengths, such as Services (Fintech, IT, Healthcare) and high-value manufacturing.
Forge an Energy Transition Partnership
Agreement should include provisions for green energy collaboration, including interconnecting power grids under the One Sun One World One Grid (OSOWOG) initiative and joint exploration for critical minerals.
Implement a Skill Mobility Partnership
India should negotiate a framework for skill harmonization, ensuring Indian workers are trained for the high-tech jobs emerging from the Gulf's economic diversification plans like Saudi Vision 2030.
Lessons from Global Best Practices
India can draw valuable lessons from other successful trade agreements to structure an effective India-GCC FTA.
The India-GCC FTA has the potential to create a robust US$ 300 billion trade corridor by 2030. Its successful conclusion will not only boost economic growth but also solidify a lasting strategic partnership, anchoring India's interests in the West Asian region.
Source: PIB
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Critically examine the challenges associated with finalizing the Free Trade Agreement between India and the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC). 150 words |
The Terms of Reference (ToR) is a document signed by India and the GCC that establishes the framework, scope, and modalities for the negotiations of the Free Trade Agreement. It sets the ground rules for how the trade deal will be discussed and finalized.
The GCC is a regional intergovernmental political and economic union comprising six countries: Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
Key challenges include divergent economic interests among GCC members, "Saudization" labor policies restricting Indian workers, fears of petrochemical dumping in India, and the need for strict Rules of Origin to prevent third-party goods from bypassing tariffs.





© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved