



The 20th East Asia Summit in Kuala Lumpur offers India a platform to advance its Act East Policy and Indo-Pacific vision. By supporting ASEAN Centrality and maritime security under UNCLOS, India seeks stronger economic, digital, and security cooperation amid rising geopolitical tensions and supply chain challenges.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: NEWSONAIR
The External Affairs Minister represented India at the 20th East Asia Summit (EAS) in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia under the theme of "Inclusivity and Sustainability."
Reinforcing Regional Architecture
The East Asia Summit (EAS) remains the primary forum for strategic dialogue in the Indo-Pacific, with ASEAN's central role and the ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific (AOIP) as the guiding framework.Economic Integration and Resilience
The summit focused on strengthening regional economic integration, trade, and investment, emphasizing supply chain resilience, digitalization, renewable energy, and green growth.
Maritime Security and Cooperation
Leaders discussed maritime security, freedom of navigation, and overflight in line with international law, stressing cooperation in disaster management, the blue economy, and combating transnational crimes.Addressing Regional and Global Challenges
Leaders discussed major regional and global issues like the South China Sea, Myanmar, Middle East, Ukraine, and the Korean Peninsula, emphasizing dispute resolution through dialogue and international law.
Membership and Partnerships
Timor-Leste officially joined as the 11th ASEAN member state.
India designated 2026 as the 'ASEAN-India Year of Maritime Cooperation'.
Initiated in 2005 in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, to promote peace, stability, and economic prosperity across East Asia.
Membership
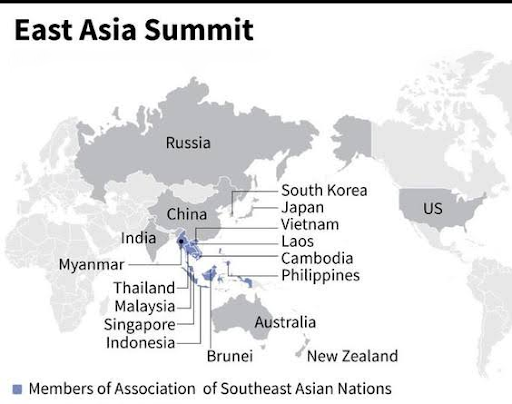
The EAS comprises 18 member states.
ASEAN Centrality: ASEAN leads the EAS, with its member states annually rotating the chairmanship, ensuring the forum reflects the region's collective interests.
Source: NEWSONAIR
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Consider the following countries:
Which of the above countries are members of the East Asia Summit (EAS)? A) 1, 2, 3 and 4 only B) 1, 3 and 4 only C) 1, 3, 4 and 5 only D) 2 and 5 only Answer: B Explanation: The East Asia Summit comprises the 10 ASEAN Member States and eight dialogue partners: Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, the Republic of Korea, the Russian Federation, and the United States. Canada and the United Kingdom are not members of the EAS. |
The EAS is a leaders-led forum for strategic dialogue in the Indo-Pacific, established in 2005 as an ASEAN initiative. It includes 18 countries discussing political, security, and economic issues.
The EAS comprises the 10 ASEAN countries (Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam) and 8 dialogue partners (Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, the Republic of Korea, Russia, and the United States).
The Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI), launched by India at the 2019 East Asia Summit, is a non-treaty framework promoting cooperation for a rules-based and sustainable maritime domain. It aligns with India's SAGAR vision and is structured around seven pillars, including maritime security and resource management.




© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved