



The UNSC’s late-2025 adoption of a US plan for Gaza shifts from immediate statehood to a security-first, economy-driven roadmap with temporary administration, demilitarization-linked aid, and expanded Abraham Accords. India must balance its two-state stance with strategic ties. Success depends on Palestinian consent, security, and sustained global backing.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: REUTERS
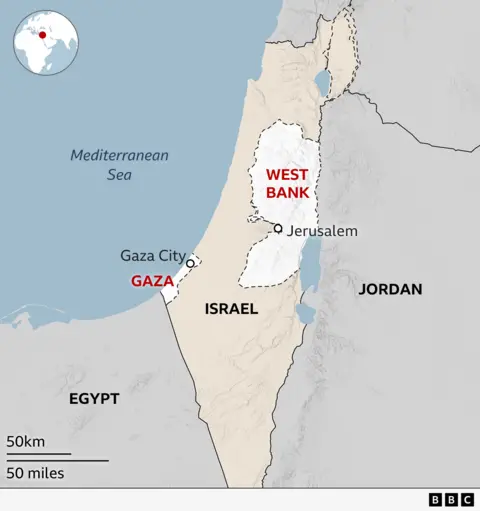
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) has passed a resolution to endorse a comprehensive plan proposed by the United States for a permanent ceasefire and reconstruction in Gaza.
|
Read all about: India Votes for Palestinian Statehood: UPSC Current Affairs l India Votes for Palestinian Statehood l Israel Palestine Conflict l India-Palestinian Relations |
Immediate Security: Calls for an immediate ceasefire, freezing battle lines, and a hostage-detainee exchange (Hamas releases all hostages within 72 hours for Israel to release over 1700 Palestinian detainees).
New Governance: Excludes Hamas. An international "Board of Peace," co-led by global figures, will oversee administration and reconstruction until Palestinian governance reforms.
Oversight: A multinational "International Stabilisation Force (ISF)," including Arab states, will maintain peace, secure borders, and train a new Palestinian police force.
Economy: Aims to create a "New Gaza" special economic zone with international aid and preferential trade for reconstruction and job creation.
Rights: Guarantees Palestinians will not be forcibly displaced.
Statehood: Offers a "political horizon" for a Palestinian state, conditional on comprehensive Palestinian Authority (PA) reforms and Israeli security guarantees.
Firm Support for a Two-State Solution
India advocates for a negotiated two-state solution, resulting in a sovereign, independent, and viable State of Palestine coexisting peacefully and securely alongside Israel.
Condemnation of Terrorism and Civilian Deaths
India maintains a "zero-tolerance" anti-terrorism policy, condemning the attacks on Israel while stressing deep concern for civilian casualties and demanding adherence to international humanitarian law.
Humanitarian Assistance
India, as a first responder, sent crucial humanitarian aid (food, medical supplies, disaster relief) to Palestine's civilian population. India increased its annual financial assistance to the United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA) to $5 million.
Strategic Balancing
India maintains strong, independent relationships with regional powers, balancing strategic partnerships with Israel (defence, tech, agriculture), the US, and key Arab nations like the UAE and Saudi Arabia (energy, trade, I2U2) through careful diplomacy.
Despite UNSC endorsement, the plan faces obstacles that could prevent its successful implementation.
The current "security-first, economy-led" proposal for the Gaza conflict is insufficient for long-term peace because it avoids the core issue of Palestinian sovereignty. Enduring peace requires the framework to lead to a political settlement that includes Palestinian self-determination.
Source: REUTERS
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. How does India balance its historical support for Palestine with its growing strategic partnership with Israel? 150 words |
The plan faces several major hurdles: gaining acceptance from key Palestinian factions like Hamas and the Palestinian Authority; the task of successfully demilitarizing Gaza and establishing an effective security force; securing and sustaining over $50 billion in reconstruction funds; and maintaining the long-term political will of all international and regional actors.
The plan diverges by postponing negotiations on a sovereign Palestinian state based on 1967 borders. Instead, it proposes a long-term vision of enhanced Palestinian autonomy and economic prosperity, contingent on the success of the initial security and economic phases.
The plan faces several major hurdles: gaining acceptance from key Palestinian factions like Hamas and the Palestinian Authority; the task of successfully demilitarizing Gaza and establishing an effective security force; securing and sustaining over $50 billion in reconstruction funds; and maintaining the long-term political will of all international and regional actors.




© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved