



Researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay have developed a gentler method to recover lab-grown T-cells, a crucial step in CAR T-cell therapy. Using the mild enzyme Accutase instead of harsher alternatives helps improve cell survival and preserve immune function. The approach enhances the reliability and efficiency of immunotherapy production, supports cost reduction, and strengthens India’s efforts to make advanced cancer treatments more affordable and accessible.
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: Indian Express
Context:
Researchers at Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, led by Prof. Prakriti Tayalia, tested recovery methods for cell recovery for cancer immunotherapy, particularly CAR T-cell therapy.
|
Must Read: CAR T-CELL THERAPY | NexCAR19 | |
What are T-cells?
T-cells are specialised white blood cells that form a crucial part of the body’s adaptive immune system. They continuously circulate through the blood and tissues, scanning for pathogens, infected cells, or abnormal cells such as cancer.
When a threat is identified, some T-cells directly kill the diseased cells, while others release chemical signals that activate and coordinate the broader immune response. Their ability to recognise specific targets and remember them makes T-cells central to modern immunotherapy.
Functions of T-cells
Because they can specifically recognise abnormal cells, T-cells play a central role in modern cancer immunotherapy.
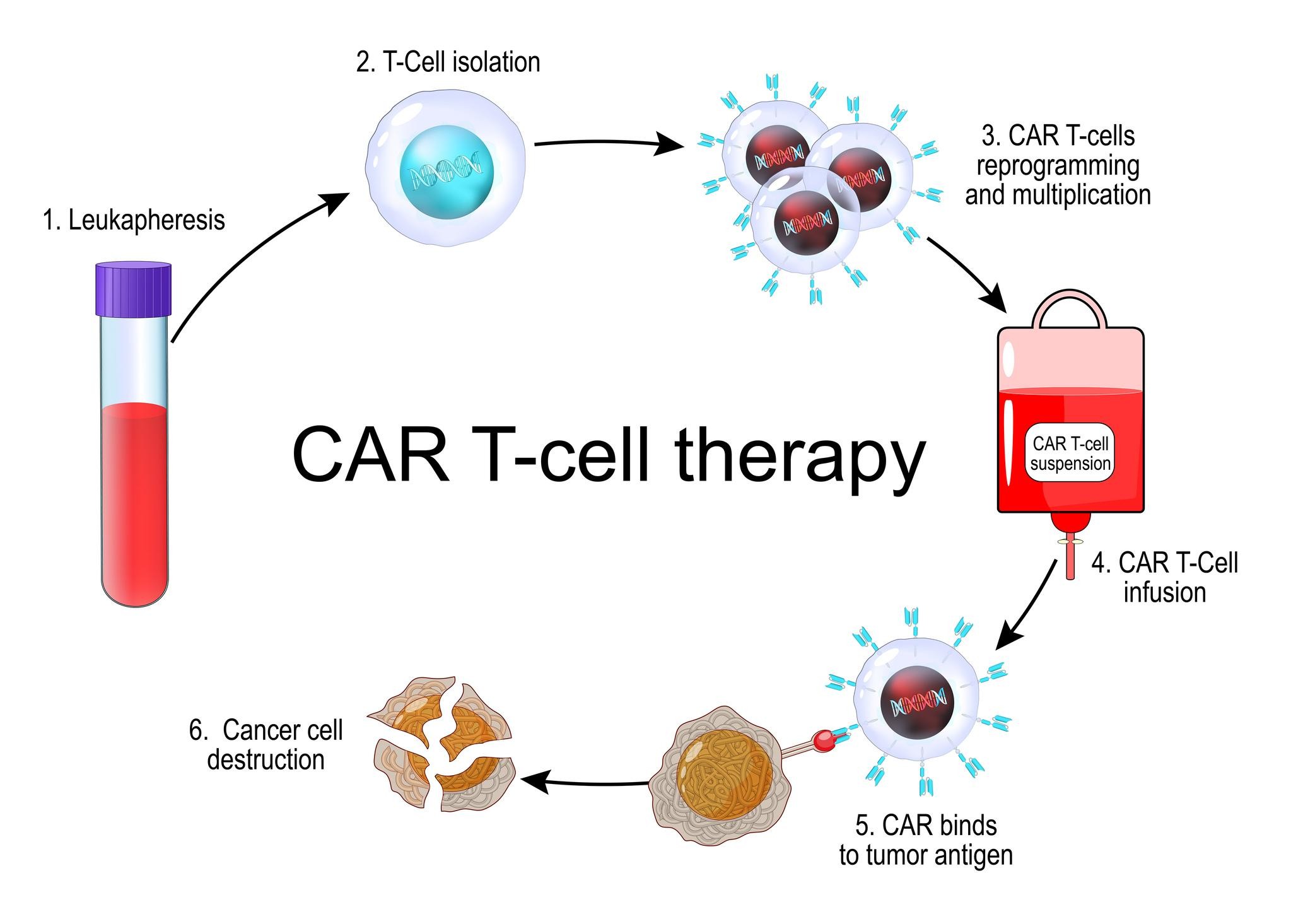
What is CAR T-cell Therapy?
CAR T-cell therapy is an advanced form of personalised cancer treatment that enhances the patient’s own immune cells. In this process, T-cells are extracted from the patient and genetically modified in a laboratory.
Scientists insert a gene that enables the cells to produce Chimeric Antigen Receptors (CARs) engineered molecules that help T-cells identify and attach to specific proteins present on cancer cells.
The modified cells are then multiplied in large numbers and infused back into the patient, where they actively seek out and destroy cancer cells.
This therapy is currently approved for certain blood cancers, particularly leukemia and lymphoma, and is being explored for other cancer types.
Working mechanism:
In 2023, NexCAR19 became India’s first domestically developed CAR T-cell therapy. It was created through a collaboration between the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Tata Memorial Centre, and ImmunoACT.
Designed to be significantly more affordable than global alternatives, NexCAR19 marks a major step toward accessible advanced cancer treatment and strengthens India’s presence in the field of cell and gene therapy.
Key highlights of IIT Bombay study on CAR T-cell therapy:
Importance of the IIT Bombay study:
Conclusion:
The IIT Bombay study shows that small improvements in cell-processing techniques can significantly enhance the quality, reliability, and affordability of CAR T-cell therapy. By enabling gentle recovery and better survival of therapeutic T-cells, the research strengthens India’s efforts to develop cost-effective, accessible, and globally competitive advanced cancer treatments.
Source: Indian Express
|
Practice Question Q. CAR T-cell therapy represents a major advancement in cancer treatment, but its large-scale adoption faces technical and cost-related challenges. In this context, discuss the significance of process innovations such as improved T-cell recovery techniques for strengthening India’s immunotherapy ecosystem. (150 words) |
CAR T-cell therapy is a form of personalised immunotherapy in which a patient’s T-cells are genetically modified to recognise and destroy specific cancer cells before being infused back into the body.
After expansion in the laboratory, T-cells must be collected without damage. Gentle recovery ensures high cell survival and preserved immune function, which is critical for treatment effectiveness.
India has developed its first indigenous therapy, NexCAR19, through efforts by the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Tata Memorial Centre, and ImmunoACT, aiming to make advanced cancer treatment more affordable and accessible.







© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved