Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Tripoli, Nov 21 up to 662 illegal migrants were rescued off the coast of Libya in the past week, the International Organisation for Migration said.
About Libya
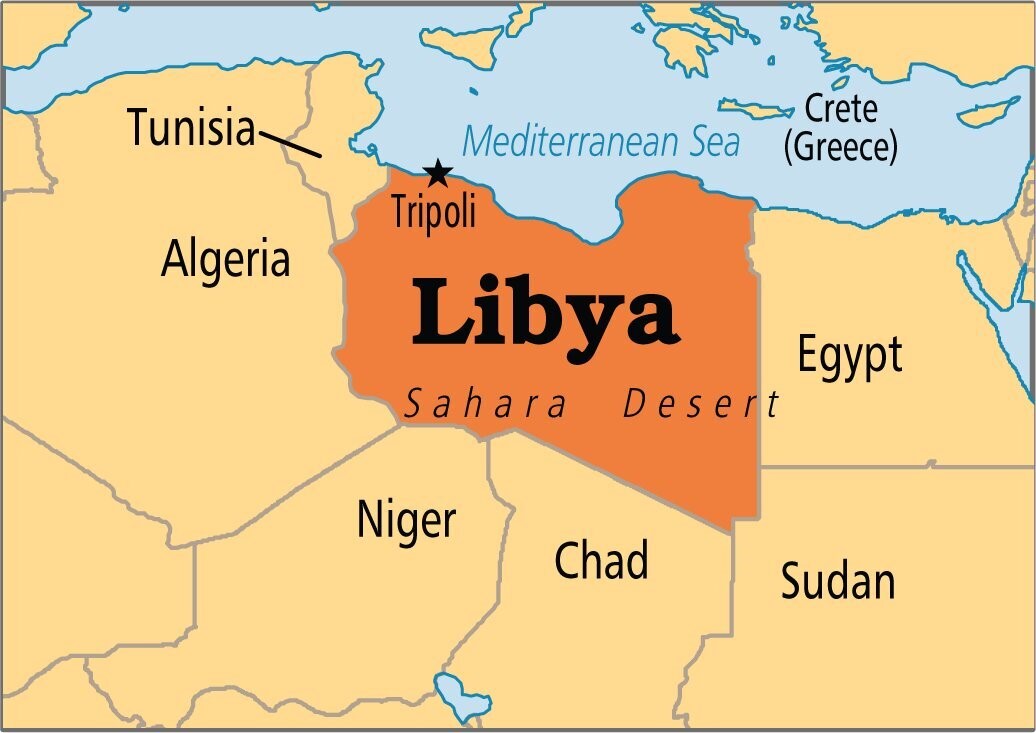
- Libya is a country located in North Africa, bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north.
- It is known for its rich history, diverse culture, and strategic geographical location.
Geography and Borders
- Libya shares its borders with several countries: Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, Algeria to the west, and Tunisia to the northwest.
- Its coastline along the Mediterranean Sea is significant, and many major cities are nearby.
Capital and Major Cities
- Libya's capital city is Tripoli, located on the country's northwestern coast.
- Other major cities include Benghazi, Misrata, and Sabha
Historical Significance
- Libya has a history dating back to ancient times, with notable civilizations like the Phoenicians, Greeks, Romans, and Byzantines having had an influence on the region.
- The city of Leptis Magna, a Roman archaeological site, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a testament to Libya's historical importance.
Colonial Influence and Independence
- Libya was under Ottoman rule for centuries and became an Italian colony in the early 20th century.
- After World War II, Libya gained independence in 1951 and became a monarchy under King Idris.
Gaddafi Era
- In 1969, Muammar Gaddafi led a coup that ousted King Idris and established a socialist government.
- Gaddafi's rule was characterized by authoritarianism, unconventional policies, and control over the country's vast oil resources.
- The country went through periods of international isolation and conflict during his rule.
.jpg)
Arab Spring and Civil Unrest
- In 2011, Libya became a focal point of the Arab Spring uprisings.
- Protests against Gaddafi's regime led to a violent conflict, with Western military intervention.
- Gaddafi was eventually captured and killed, leading to a power vacuum and ongoing instability.
Post-Gaddafi Challenges
- After Gaddafi's fall, Libya struggled with governance issues, the rise of militias, and tribal divisions.
- The country essentially split into multiple factions, with the internationally recognized Government of National Accord (GNA) in the west and the Libyan National Army (LNA) led by General Khalifa Haftar in the east.
Economy and Oil
- Libya possesses significant oil reserves, making oil exports a crucial component of its economy.
- However, political instability and conflicts have often disrupted oil production and exports.
Cultural Diversity
- Libya is home to diverse ethnic and tribal groups, including Arab-Berber
- Its cultural heritage includes traditional music, art, and festivals that reflect its history and regional influences.

The International Organisation for Migration (IOM):
- IOM, founded in 1951, is the world's premier intergovernmental organization in the field of migration.
- The International Organisation for Migration (IOM) defines the term migrant as "a person who moves away from his or her place of usual residence, whether within a country or across an international border, temporarily or permanently, and for a variety of reasons."
- It provides assistance to migrants, as well as internally displaced individuals, refugees, and other uprooted people, at the request of states, in the four general areas of migration and development, promoting migration, regulating migration, and combating forced migration.
- IOM seeks to foster international collaboration on migration issues by ensuring the orderly and compassionate management of migration.
- to aid in the search for realistic answers to migration challenges
- to give humanitarian help to migrants in need, including refugees and internally displaced individuals.
- In 2016, IOM entered into an agreement with the United Nations, becoming a related organization.
- IOM serves as coordinator of the United Nations network on migration, established by the Secretary-General in 2018.
- IOM is the UN agency in charge of labour mobility and migration in general.
- It currently has 172 member states and 8 states holding observer status.
- India is a member of IOM.
- Its headquarters are located in Geneva, Switzerland.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Examine the multifaceted dimensions of the Libya migration crisis, considering its historical roots, geopolitical implications, and the humanitarian challenges involved. Evaluate the role of international actors and organizations in addressing the crisis and propose sustainable strategies for mitigating the immediate and long-term effects on the affected populations and the global community.
|










