
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- The U.S. has emerged as India's biggest trading partner in 2022-23 – [Provisional data, Commerce Ministry].
Highlights of the Provisional Data
Bilateral Trade
- Bilateral trade between India and the U.S. has increased by 7.65% to $128.55 in 2022-23 as against $119.5 billion in 2021-22. It was $80.51 billion in 2020-21.
Exports to US [Trend]
- Exports to the US rose by 2.81 percent to $78.31 billion in 2022-23 as against $76.18 billion in 2021-22.
Import to U.S. [Trend]
- Imports grew by about 16 percent to $50.24 billion, the data showed.
Major Export Items to U.S.
- Major export items from India to the U.S. include petroleum, polished diamonds, pharmaceutical products, jewellery, light oils and petroleum, frozen shrimp, made ups etc
Increase in exports of certain goods to U.S.
- Increasing exports of goods such pharmaceuticals, gems and jewellery were helping India to push its shipments to America.
Major Import Items from U.S.
- Major imports from the U.S. include petroleum, rough diamonds, liquified natural gas, gold, coal, waste and scrap, almonds etc.
Trade Surplus Trends
- America is one of the few countries with which India has a trade surplus.
- In 2022-23, India had a trade surplus of $28 billion with the U.S.
- China was India's top trading partner from 2013-14 till 2017-18 and also in 2020-21.
- Before China, the UAE was the country's largest trading partner.
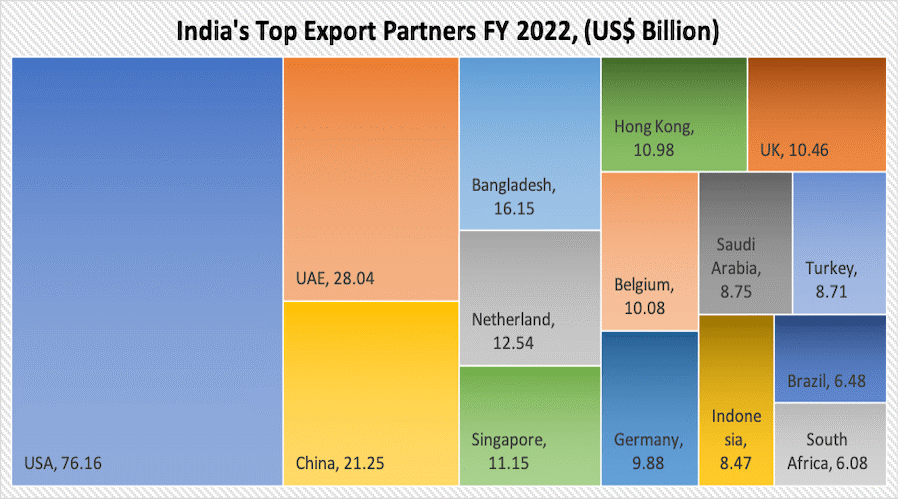
- In 2022-23, the UAE with $76.16 billion, was the third largest trading partner of India.
- It was followed by Saudi Arabia ($52.72 billion), and Singapore ($35.55 billion).
Note: India records trade surpluses with countries like US, United Arab Emirates, Hong Kong, United Kingdom and Vietnam.
.jpeg)
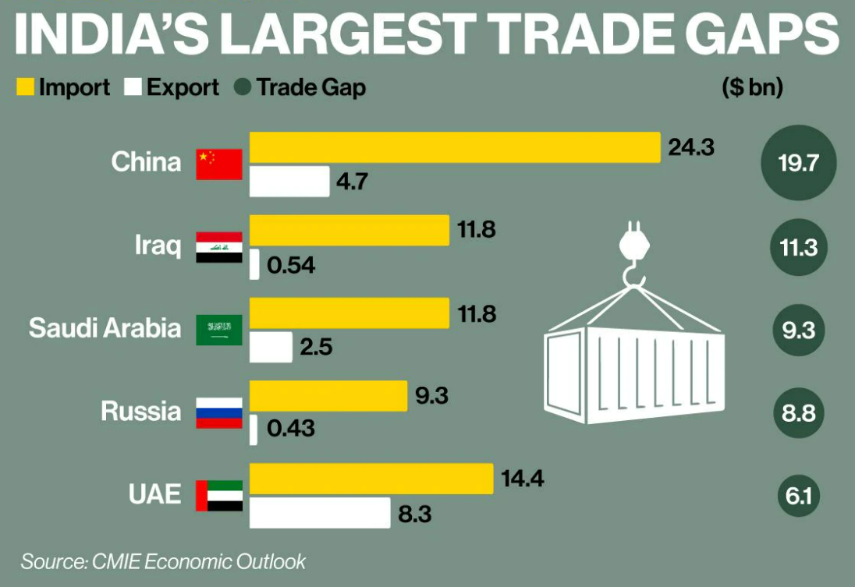
Trade Trends with China
- While China has been one of the top trading partners, India's deficit has widened over the years.
- Exports to China dipped by about 28 percent to $15.32 billion in 2022-23, while imports rose by 4.16 percent to $98.51 billion in the last fiscal.
- Between April 2022 and March 2023, India's trade with China declined 1.5 percent to reach $113.83 billion. But the trade deficit widened from $72.91 billion dollars in 2021-22 to $83.2 billion in the last fiscal.
A trade deficit is said to happen when a country's imports are higher than its exports. Trade deficit puts a strain on a country's foreign exchange and contributes to the balance of payments problem.
- Note: Though, India’s exports to China fell China is India’s second-largest trade partner.
Indo- U.S. Trade Trend: Last 20 years
- Over the years, India’s trade ties with the US have strengthened steadily.
- In the 20 years between 1999 and 2019, bilateral trade grew 787% from $16 billion to $142 billion.
- So, basically Indo-US trade rose nearly 800% between 1999 and 2019.
READ: INDIA-US TRADE RELATIONS: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/india-us-trade-relations
Silver Lining
- Experts believe that the trend of increasing bilateral trade between India and the US will continue in the coming years as both countries aim to strengthen their economic ties further.
Trivia
India’s Export Outlook
- Over the past few years, exports from India have soared tremendously on the back of robust manufacturing in several sectors and an enabling policy landscape.
- In the financial year (FY) 2022, India’s merchandise exports soared to a record high of US$417.81 billion, surpassing the government’s target of US$400 billion.
- The export growth was mainly driven by a surge in demand for products like petroleum, cotton yarn, textiles, chemicals, and engineering goods.
- The government estimates that India will achieve an export target of US$450 billion during FY 2023.
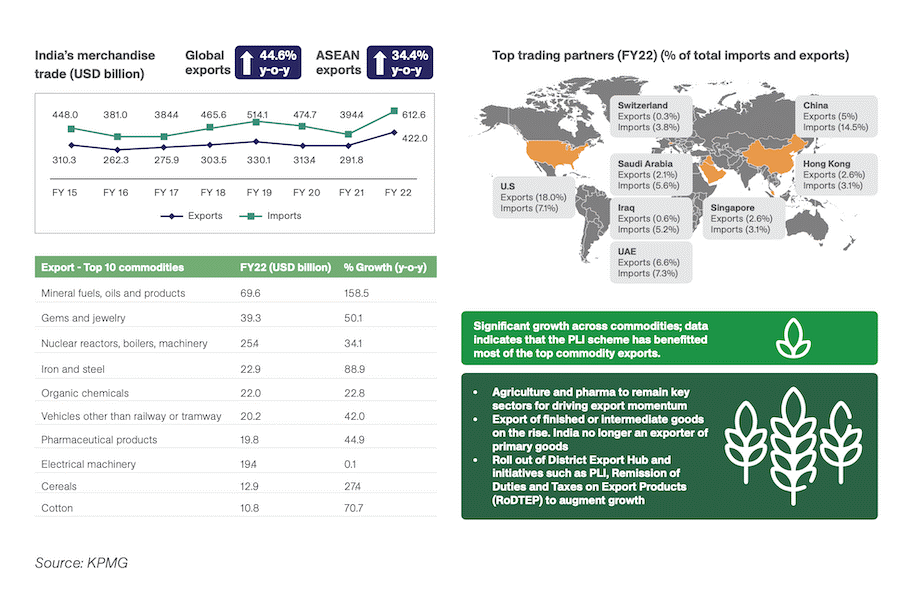
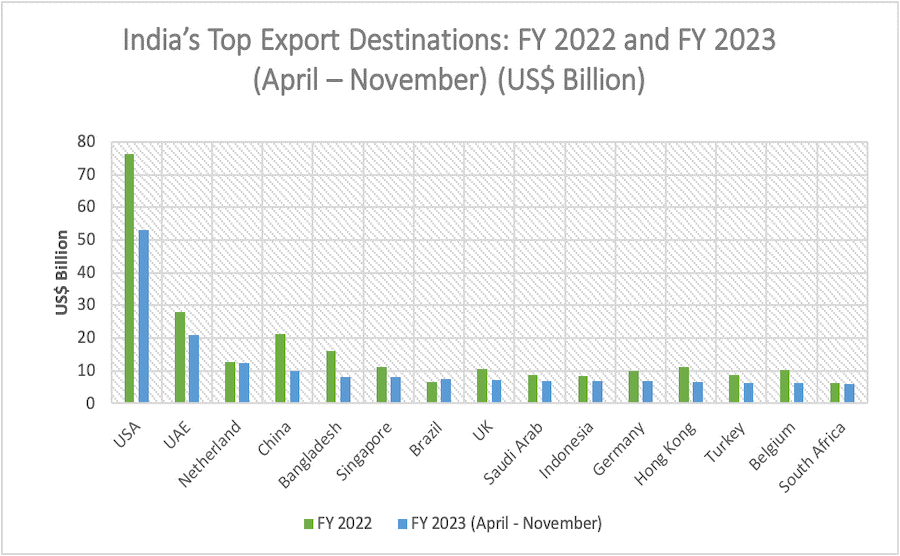
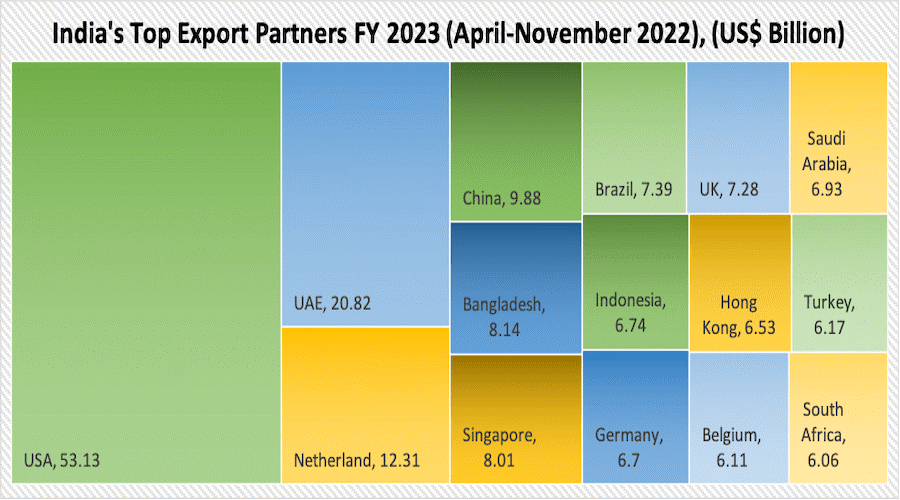
- The US, UAE, Netherlands, China, Bangladesh, Singapore, Brazil, UK, Saudi Arabia, Indonesia, Germany, Hong Kong, etc. are among India’s leading export destinations.
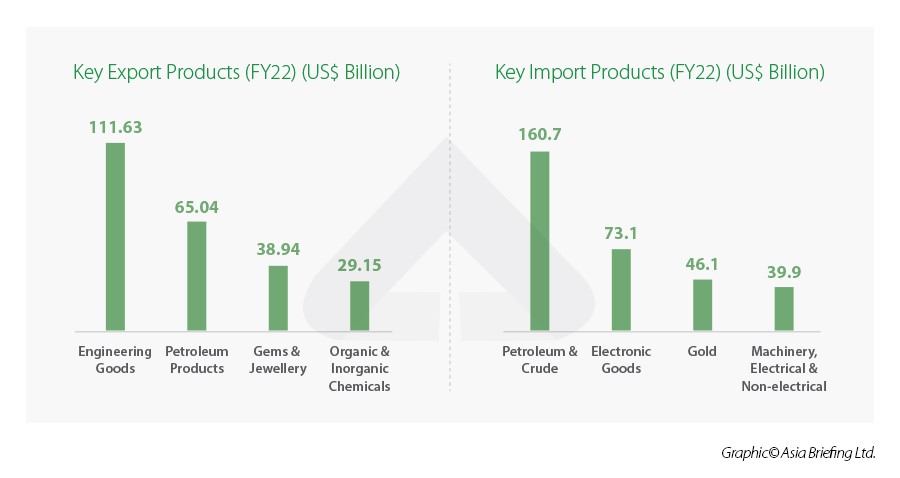
India’s top exports
- The top exports of India are engineering goods, gems and jewelry, petroleum products, drugs and pharmaceuticals, organic chemicals, electronic goods, etc.
- India’s import basket primarily comprises petroleum and crude products, electronic goods, gold, machinery and electrical appliances, pearls, stones and semi-precious metals, transport equipment, etc.
Export promotion measures by the government
Foreign Trade Policy (FTP)
- It envisages outlining the roadmap for attaining US$2 trillion in exports (goods and services) by 2030.
- It would also concentrate on a variety of other new and developing trade-related fields, such as exports from e-commerce.
Interest equalization scheme (IES) on pre- and post-shipment rupee export credit:
- Under this scheme, an eligible exporter has to submit a certification from the external auditor to the concerned bank to claim this benefit.
- Banks provide IES benefits to the eligible exporters and claim a reimbursement from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) based on the external auditor certification furnished by the exporter.
- The scheme helps the identified export sectors to be internationally competitive and to achieve a higher level of export performance.
Trade Infrastructure for Export Scheme (TIES):
- This scheme aims to assist Federal and State government agencies in the creation of appropriate infrastructure for the growth of exports.
- The scheme can be availed by States through their implementing agencies, for infrastructure projects with significant export linkages like border haats, land customs stations, quality testing and certification labs, cold chains, trade promotion centres, export warehousing and packaging, special economic zones (SEZs) and ports/airports cargo terminuses.
Market Access Initiatives (MAI) scheme
- It is an export promotion scheme envisaged to act as a catalyst to promote India’s exports on a sustained basis.
- The scheme is formulated on a focus product-focus country approach to evolve specific markets and specific products through market studies/surveys.
Rebate of State and Central Levies and Taxes (RoSCTL) scheme
- This scheme has been implemented since March, 2019 to promote labour-oriented textile export.
Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP) scheme
- It is a tax neutralization scheme that will refund the central, state, and local duties or taxes to exporters who do not benefit from pre-existing rebates or refund schemes.
- This scheme replaces the previous Merchandise Export from India Scheme (MEIS), which was not considered compliant with World Trade Organization (WTO) rules.

Common Digital Platform for Certificate of Origin (CoI)
- The common digital platform is a single point access for certificates of origin for all FTAs and preferential trade agreements (PTAs) for all agencies and all products.
- It is designed to facilitate exporters through a secure, electronic, paperless CoI issuance process. All designated CoI issuing agencies are required to work through this portal.
Champion Service Sectors
- Identification of 12 champion services sectors for promoting and diversifying services exports by pursuing specific action plans.
- These include –
- Information technology (IT) and information technology-enabled services (ITES),
- Tourism and hospitality services,
- Medical value travel,
- Transport and logistics services,
- Accounting and finance services,
- Audio-visual services,
- Legal services,
- Communication services,
- Construction and related engineering services,
- Environmental services,
- Financial services and
- Education services.
Districts as Export Hubs:
- Under this initiative, products and services (including GI products, agricultural clusters, toy clusters, etc.) with export potential are identified in all districts of the country.
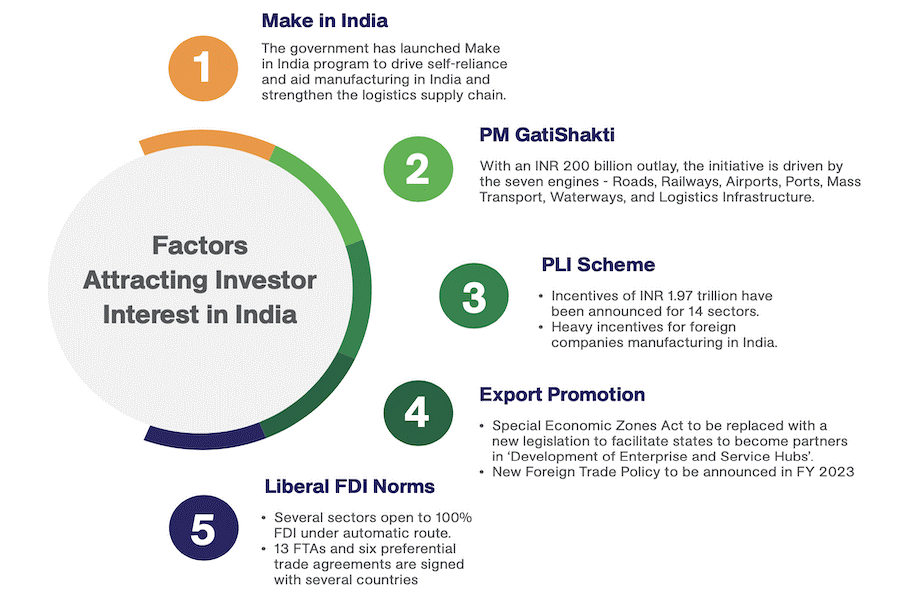
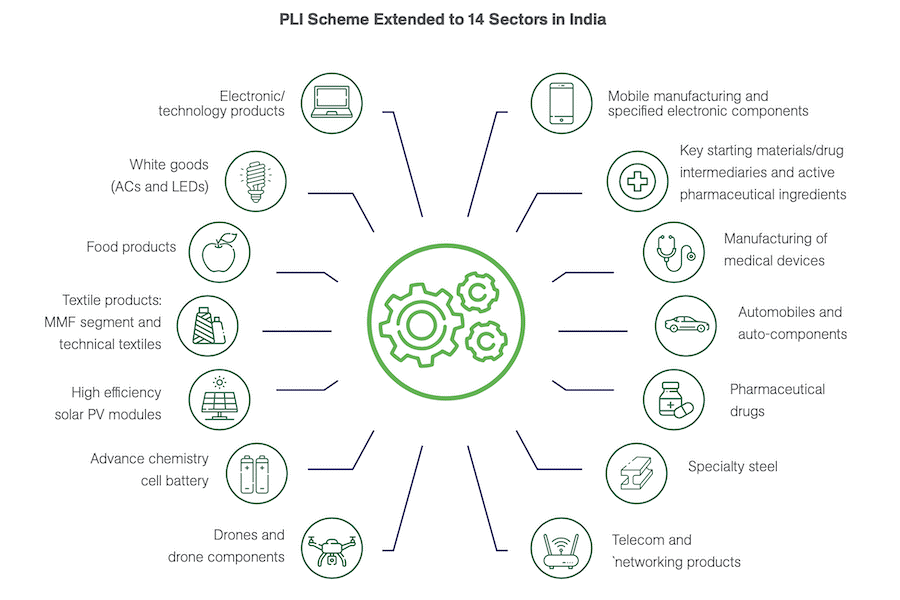
Production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme
- To develop India into a global manufacturing hub and speed up job creation, the government has rolled out PLI schemesin 14 sectors since 2020, with incentives amounting to INR 1.97 trillion (US$23.81 billion).
- The scheme, which is in tune with the “Make in India” program, is intended to boost domestic manufacturing and simultaneously catapult India’s export sector.
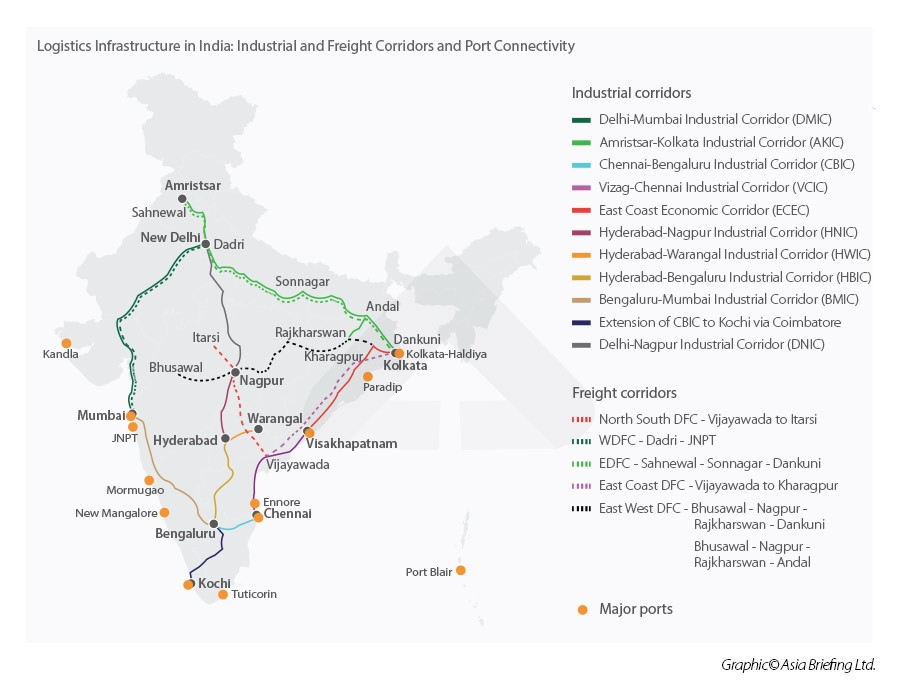
National Logistics Policy (NLP)
- To make Indian exports globally more competitive, India also recently released the National Logistics Policy.
- This Policy provides for the seamless integration of multiple modes of transportation by leveraging technology, processes, and skilled manpower.
- The policy, which is in line with PM GatiShakti National Master Plan, will give a massive boost to India’s US$200 billion logistics sector, thereby enabling the smooth movement of goods both domestically and internationally.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) policy
- Within the ambit of this policy, the federal government has approved 100 percent FDI under an automatic route in many sectors in order to give a thrust to Indian exports.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. India has proven its resilience as a trading nation in recent times. Discuss the major trends India's foreign trade. Also, shed light on the Export promotion measures taken by the government to promote trade and exports.
|

https://www.thehindu.com/business/Economy/us-emerges-as-indias-biggest-trading-partner-in-fy23-at-12855-billion-china-at-second-position/article66743587.ece


















