



India and Qatar have strengthened their Strategic Partnership, advancing energy security, trade diversification, and digital collaboration. By leveraging LNG supplies, expanding non-hydrocarbon sectors, and engaging the Indian diaspora, both nations drive mutual economic growth and investment.
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: NDTV
The official visit of India's Union Minister of Commerce and Industry, Shri Piyush Goyal, to Doha in October 2025 for the India-Qatar Joint Commission meeting marks a significant milestone in a rapidly evolving bilateral relationship.
Early Phase (1970s-1990s)
After establishing diplomatic ties in 1973, the relationship was friendly but limited. The main connection was the growing community of Indian workers in Qatar.
The Energy Era (Post-2000)
As India's economy grew, so did its need for energy. Qatar, as the one of the world's top Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) exporter, became a vital partner. The signing of long-term LNG supply agreements made energy security the core of the relationship.
Strategic Diversification (Post-2014)
High-level visits broadened the partnership beyond energy. The focus expanded to include investments, food security, and defense cooperation. This phase culminated in the decision to elevate the relationship to a strategic partnership.
Qatar is a crucial partner for India, central to its 'Link West' foreign policy for several key reasons.
Energy Security
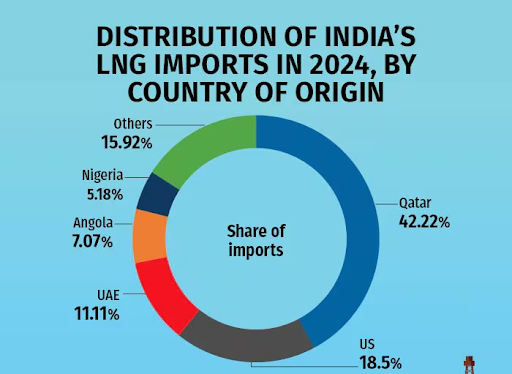
Qatar is India's largest supplier of LNG (over 42%), making it essential for India's energy stability and its goal of moving towards a cleaner, gas-based economy. A long-term agreement ensures India receives 7.5 million tonnes of LNG per year from 2028.
The Indian Diaspora
Over 800,000 Indians live and work in Qatar, making them the largest expatriate community. They act as a vital "human bridge," contribute to Qatar's economy, and send billions of dollars in remittances back to India.
The recent launch of the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) in Qatar makes digital transactions easier for this community.
Economic and Investment Partnership
Trade: In FY 2024-25, India's bilateral trade with Qatar stood at $14.14 billion; India’s export was $1.68 billion and imports $12.46 billion. Both aim to double bilateral trade by 2030.
Investment: Qatar has one of the world's largest sovereign wealth funds, the Qatar Investment Authority (QIA) has committed a $10 billion investment in India. India seeks more Qatari investment in its infrastructure, technology, and manufacturing sectors to support its vision of becoming a Viksit Bharat (Developed India) by 2047.
Geopolitical Stability
Qatar plays an important role as a diplomatic mediator in the Gulf region. Its unique position makes it a valuable partner for India in navigating regional complexities and ensuring peace and stability.
Beyond a Buyer-Seller Relationship
India aims to move past a simple energy trade relationship. It seeks joint ventures, technology transfer, and co-investment, especially in high-growth areas like solar energy.
Balancing Trade
India's imports from Qatar (mostly LNG) are much larger than its exports. The Indian Commerce Minister's visit highlighted sectors like electronics, automobiles, pharmaceuticals, textiles, and IT where India can increase its exports.
Deepening Economic Ties
India is pursuing an India–Qatar Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) to create a formal structure to lower trade barriers and encourage more investment between the two countries.
Strengthening People-to-People Connections
The launch of UPI and regular meetings of the Joint Business Council are concrete steps to bring the people and businesses of both nations closer.
Trade Imbalance: The trade relationship is heavily tilted in Qatar's favor due to India's LNG imports. Correcting this requires a sustained effort from India to boost its exports.
Regional Instability: The Gulf region is subject to geopolitical tensions. India must carefully manage its relationships with all countries in the region to protect its interests.
Diaspora Welfare: The large Indian community is a strength, but any issues related to labor rights or legal matters involving Indian nationals can become sensitive diplomatic challenges.
Finalize the CEPA: Fast-tracking the negotiations for the economic partnership agreement to provide a solid foundation for boosting trade and investment.
Establish a Joint Investment Fund: Creating a dedicated fund, co-financed by India's National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF) and Qatar's QIA, would help channel investments into priority sectors like renewable energy and technology startups in India.
Boost Food and Healthcare Security: India can be a reliable partner for Qatar's food and healthcare needs. Long-term supply agreements for food products and joint ventures in pharmaceutical manufacturing can strengthen this cooperation.
Expand Security Dialogue: Broaden cooperation to include counter-terrorism, maritime security, and intelligence sharing to address shared security concerns.
Leverage the Digital Partnership: Build on the successful launch of UPI to explore more collaborations in FinTech and digital governance, promoting India's digital public infrastructure.
India and Qatar have transformed their energy-based ties into a strategic partnership. By leveraging trade, investment, and digital cooperation, they can convert political commitment into tangible economic and strategic outcomes, strengthening regional stability and shared prosperity.
Source: PIB
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Analyze the challenges in the India-Qatar relationship, and suggest way forwards to further strengthen the bilateral ties? 150 words |
India and Qatar elevated their relationship to a "Strategic Partnership" in February 2025 during the visit of the Amir of Qatar, Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani, to India. The partnership covers diverse areas including energy, trade, investment, technology, and security.
In the financial year 2024–25, the bilateral trade between India and Qatar stood at around $14 billion
Beyond liquefied natural gas (LNG), India's imports from Qatar include liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), petroleum crude, plastics, organic and inorganic chemicals, fertilizers, and aluminum articles.




© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved