Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement is not intended.
Context:
- Over 50% of the world's mangroves are at risk of collapse due to human activities and climate change.
Major drivers mangrove decline:
- Human Activities: Deforestation, development, pollution, and dam construction are major threats.
- Climate Change: Increased storm frequency and sea-level rise increase the risks.

Impacts of mangroves destruction:
- Geographical Impact: Mangroves in South India, Sri Lanka, Maldives, and the North West Atlantic are critically endangered.
- Economic Impact: Loss of mangroves could cost $13 billion in carbon market value. If current trends continue, 7,000 km² of mangroves will be lost, and 23,672 km² will be submerged by 2050.
- Loss of Biodiversity: Mangroves support diverse species, providing critical habitat and breeding grounds.
- Increased Carbon Emissions: Mangroves store large amounts of carbon; their destruction releases this carbon, contributing to climate change.
- Coastal Erosion and Flooding: Mangroves protect coastlines from erosion and reduce the impact of storm surges and floods.
- Impact on Fisheries: Mangroves support fish populations, essential for local fisheries and livelihoods.
- Economic Losses: The ecosystem services provided by mangroves, such as tourism and fisheries, are economically valuable.
Importance of mangroves:
- Mangroves store 11 billion tonnes of carbon, protect 15.4 million people, and support 126 million fishing days annually.
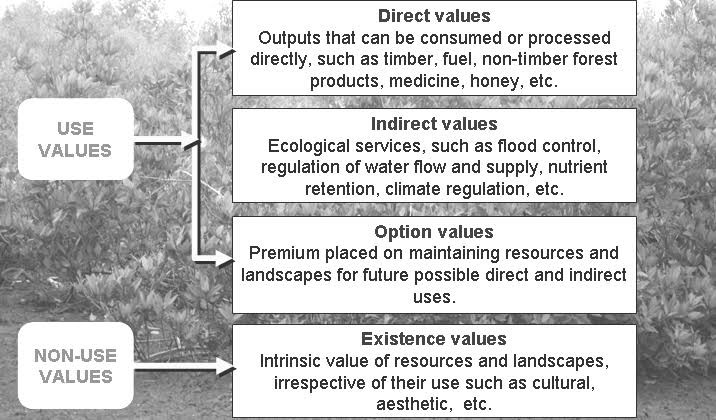
Conclusion:
- There is urgent need for protection and restoration to mitigate climate change impacts and support biodiversity.
Source:
https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/wildlife-biodiversity/over-half-of-world-s-mangroves-face-collapse-due-to-human-actions-and-climate-change-96311
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Mangroves play a critical role in coastal ecosystems and provide numerous ecological, economic, and social benefits. Discuss the importance of mangroves in mitigating climate change and protecting coastal communities. ( 250 words)
|













