



Coal gasification is a process that converts coal into cleaner syngas, reducing India's energy dependence. Despite challenges like high ash content and water usage, government initiatives like the National Coal Gasification Mission and financial incentives are paving the way for energy transition.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: BUSINESS-STANDARD
The Ministry of Coal organized a roadshow in Mumbai to promote coal gasification technologies, highlighting its potential to drive India’s self-reliance and clean energy transition.
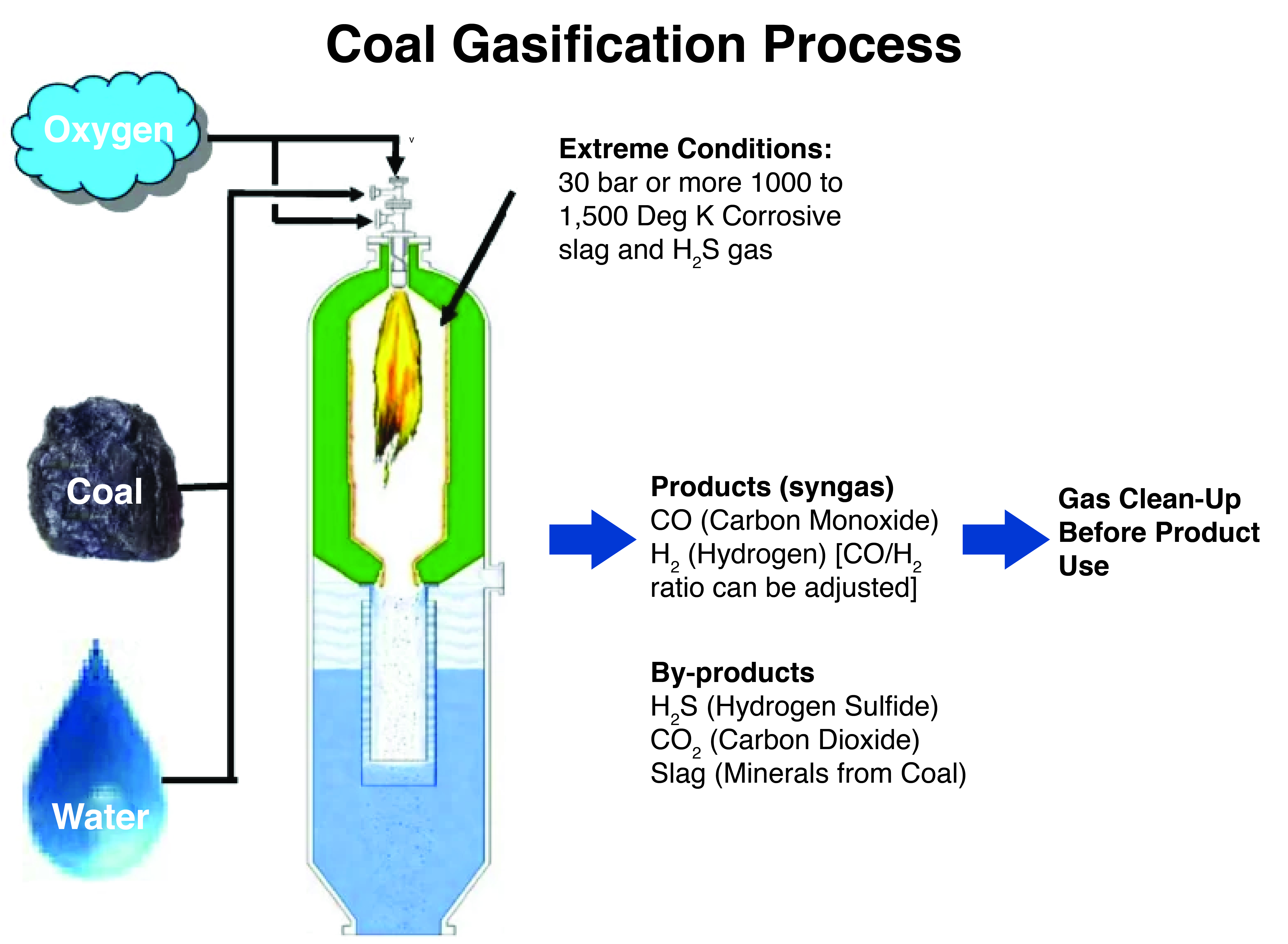
It is a thermo-chemical process that converts coal into syngas (synthetic gas), a mixture of carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H₂), carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), and water vapour (H₂O).
The process involves reacting coal at high temperatures with controlled amounts of oxygen and steam.
|
Read all about: Coal Gasification |
Preparation: Coal is crushed into fine powder to increase surface area for efficient chemical reactions.
Gasification Reactor: Powdered coal is fed into a high-temperature, high-pressure reactor with limited oxygen/air and steam.
Chemical Reactions: Partial oxidation breaks down coal into syngas components.
Gas Cleaning: Impurities like tar, sulfur, and dust are removed to produce clean syngas.
|
Ex-situ vs In-situ Gasification |
||
|
Ex-situ Gasification |
In-situ Gasification |
|
|
Location |
Above ground in controlled gasifiers |
Underground in coal seams |
|
Process |
Coal is mined and gasified in reactors |
Oxygen and steam injected into coal seams to produce syngas |
|
Application |
Suitable for shallow reserves |
Ideal for deep, unmineable coal seams |
|
Efficiency |
Energy-intensive due to mining |
More energy-efficient for deeper deposits |
Cleaner Alternative: Produces fewer emissions than direct coal combustion; pollutants are captured before use.
Versatile Syngas: Used for electricity, clean fuels (e.g., hydrogen, methanol), and chemicals (e.g., ammonia, fertilizers).
Resource Utilization: Taps unmineable coal reserves, reducing import dependency.
Abundant Reserves: India has the fourth-largest coal reserves globally (378 billion tonnes). Top 3 Coal Reserves: US, Russia and Australia.
Energy Security: With coal production crossing 1 billion tonnes in FY 2024, gasification reduces reliance on imported oil, gas, and fertilizers.
Economic Growth: Supports India’s goal to become the third-largest economy by 2028 by boosting new industries (chemicals, fertilizers, clean fuels).
Sustainable Transition: Aligns with India’s clean energy goals by offering a cleaner alternative to coal combustion, supporting net-zero ambitions.
Global Relevance: Coal remains a key global energy source (26% of primary energy, 37% of electricity), and gasification enhances its sustainability.
|
Case Study United States: Pioneer in coal gasification, with projects like the Great Plains Synfuels Plant producing syngas for power and chemicals since the 1980s. China: Leads in coal-to-chemicals, produces more than 90% of its ammonia through coal gasification South Africa: Sasol’s coal-to-liquid (CTL) technology produces synthetic fuels, reducing oil import dependency. |
High Capital Costs: Setting up gasification plants requires significant investment (estimated ₹4 lakh crore for India’s 100 MT target). (Source: PIB)
Technological Barriers: Limited indigenous technology for in-situ gasification; reliance on imported expertise increases costs.
Environmental Concerns: Despite being cleaner, gasification emits CO₂; scaling carbon capture and storage (CCS) is critical but expensive.
Competition with Renewables: Rapid growth in solar and wind energy divert investment from coal-based technologies.
Coal Gasification Incentive Scheme (2024): ₹8,500 crore outlay to promote public and private sector participation in achieving 100 MT gasification by 2030.
Long-Term Coal Linkages: Provides stable supply for gasification projects, encouraging investment.
Revenue Sharing Discounts: Coal mine owners using coal for gasification receive concessions, boosting project viability.
Production Targets: Coal and lignite production reached 1 billion tonnes in FY 2024, with a target of 1.08 billion tonnes for FY 2025.
Policy Support: Streamlined clearances and investor-friendly policies to create a robust gasification ecosystem.
Technology Development: Invest in indigenous R&D for in-situ gasification and CCS to reduce costs and dependency on foreign expertise.
Public-Private Partnerships: Encourage private sector participation through incentives, risk-sharing, and transparent bidding processes.
Carbon Management: Scale up CCS and explore syngas-based hydrogen production to align with India’s net-zero goals.
Regional Cooperation: Learn from global leaders like China and South Africa to adapt best practices for India’s context.
Balanced Energy Mix: Integrate coal gasification with renewables to ensure energy security while transitioning to cleaner fuels.
Coal gasification can transform India’s energy landscape by converting vast coal reserves into cleaner fuels, driving energy security, industrial growth, and sustainability while advancing towards the 100 MT target by 2030.
Source: THE HINDU
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Discuss the meaning and process of coal gasification. How does it contribute to India's energy self-reliance and clean energy goals? (150 words) |
It is a thermo-chemical process that converts coal into synthesis gas or syngas, a cleaner fuel.
Coal is partially oxidized by steam, air, or oxygen under controlled conditions to produce a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen.
Emissions are trapped at the gasification stage, making the combustion of syngas more efficient and less polluting.






© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved