Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- India Post Payments Bank (IPPB) wants to convert itself to a universal bank.
What is a Universal Bank?
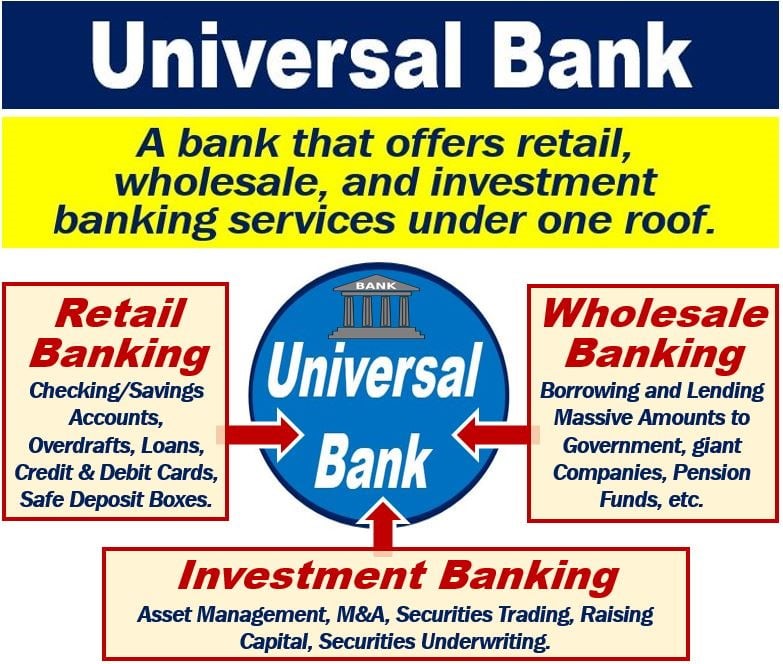
- A universal bank is a bank that combines the three main services of banking under one roof. The three services are wholesale banking, retail banking, and investment In other words, it is a retail bank, a wholesale bank, and also an investment bank.
Universal Bank Services
- Universal banks offer three main services:
Retail banking
- Retail banking services members of the publicand small and medium-size businesses. It focuses on looking after customers’ money as well as offering loans and mortgages.
- Retail banking includes the following services: savings accounts, checking accounts (UK: current accounts), overdrafts, personal loans, and mortgages.
- It also includes the provision of credit/debit cards, travelers’ checks, safe deposit boxes, and certificates of deposit.
.jpeg)
Wholesale banking
- Wholesale banking involves borrowing and lending money on a very large scale. Retail banks deal with relatively small amounts per customer. Wholesale banks, on the other hand, deal with massive amounts.
- Wholesale banks’ customers include pension funds, giant companies, governments, and other financial institutions.
Investment banking

Benefits of Universal Banks
- Investors' Trust: Universal banks hold stakes (equity shares) of many companies. These companies can easily get other investors to invest in their business. This is because other investors have full confidence and faith in the Universal banks. They know that the Universal banks will closely watch all the activities of the companies in which they hold a stake.
- Economics of Scale: Universal banking results in economic efficiency. That is, it results in lower costs, higher output and better products and services. In India, RBI is in favour of universal banking because it results in economies of scale.
- Resource Utilisation: Universal banks use their client's resources as per the client's ability to take a risk. If the client has a high risk taking capacity, then the universal bank will advise him to make risky investments and not safe investments. Similarly, clients with a low risk-taking capacity are advised to make safe investments. Today, universal banks invest their client's money in different types of Mutual funds and also directly into the share market. They also do equity research. So, they can also manage their client's portfolios (different investments) profitably.
- Profitable Diversification: Universal banks diversify their activities. So, they can use the same financial experts to provide different financial services. This saves cost for the universal bank. Even the day-to-day expenses will be saved because all financial services are provided under one roof, i.e. in the same office.
- Easy Marketing: Universal banks can easily market (sell) all their financial products and services through their many branches. They can ask their existing clients to buy their other products and services. This requires less marketing efforts because of their well-established brand name. For e.g. ICICI may ask their existing bank account holders in all their branches, to take house loans, insurance, to buy their Mutual funds, etc. This is done very easily because they use one brand name (ICICI) for all their financial products and services.
- One-stop Shopping: Universal banking offers all financial products and services under one roof. One-stop shopping saves a lot of time and transaction costs. It also increases the speed or flow of work. So, one-stop shopping gives benefits to both banks and their clients.
Limitations of Universal Banks
- Different Rules and Regulations: Universal banking offers all financial products and services under one roof. However, all these products and services have to follow different rules and regulations. This creates many problems. For e.g. Mutual Funds, Insurance, Home Loans, etc. have to follow different sets of rules and regulations, but they are provided by the same bank.
- Effect of failure on Banking System: Universal banking is done by very large banks. If these huge banks fail, then it will have a very big and bad effect on the banking system and the confidence of the public. For e.g. Recently, Lehman Brothers a very large universal bank failed. It had very bad effects in the USA, Europe and even in India.
- Monopoly: Universal banks are very large. So, they can easily get monopoly power in the market. This will have many harmful effects on the other banks and the public. This is also harmful to economic development of the country.
- Conflict of Interest: Combining commercial and investment banking can result in conflict of interest. That is, Commercial banking versus Investment banking. Some banks may give more importance to one type of banking and give less importance to the other type of banking. However, this does not make commercial sense.
IPPB
- India Post Payments Bank, abbreviated as IPPB, is a division of India Post which is under the ownership of the Department of Post, a department under Ministry of Communications.
- Opened in 2018 India Post Payments Bank is a 100% central government-owned entity.
- The Payment bank was started with the vision to build the most accessible, affordable and trusted bank for the common man in India.
- The main objective is to promote financial inclusion in a simple and secure manner at the customers' doorstep.
- It aims to utilize nearly 1,60,000 post offices as access points and 3 lakh postmen and Grameen Dak Sewaks to provide doorstep banking services.
- It delivers simple and affordable banking solutions through innovative interfaces available in 13 languages.

Services offered by the Bank
- It offers savings accounts, money transfers and insurances through the 3d parties, bill and utility payments.
- The Bank offers savings and current accounts up to a balance of ₹2 Lakh.
- Customers can use QR code payments eliminating the need to remember account numbers, PINs and Passwords.
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI)
- Immediate Payment Service
- National Electronic Funds Transfer
- Real-time gross settlement
- Bharat BillPay
- Direct Benefit Transfer
- RuPay Debit Card
- AEPS (Adhaar Enabled Payment Service)
Closing Remarks
- As a payment bank under the RBI, IPPB can extend services of deposits, remittances, internet banking and other specified services, but they cannot give loans or issue credit cards.
- Hence, India Post Payments Bank (IPPB) wants to convert itself to a universal bank as the vast network of post office branches would help in achieving financial inclusion.
Trivia

What is the difference between Universal Banks (UBs) and Small Finance Banks (SFBs)?
- UBs are financial entities like commercial banks, financial institutions, NBFCs, etc. that undertake multiple financial transactions.
- Small Finance Banks (SFBs) are focused financial institutions registered as a public limited company providing banking and credit services to unserved & unbanked regions of the country like marginal farmers, MSMEs, and other non-risk sharing financial activities with RBI’s prior approval.
- UBs were underscored as a development financial institution (DFI) by the Narsimham committee and the concept of SFBs was laid down in Raghuram Rajan
- On-tap bank licensing facility enables a window for making applications for bank licenses at the RBI throughout the year. This year-round window was introduced in 2016 with the view to further financial Inclusion and creation of more financing institutions. Prior to that, banking licenses were granted upon invitation of applications by RBI to prospective players. The last time RBI granted UB licenses was in 2015 to Bandhan Bank and IDFC Bank. It approved Unity SFB in 2021 to rescue the scam-hit Punjab & Maharashtra Cooperative Bank.
What is the selection process?
- UBs and SFBs are subject to Banking Regulation Act, RBI Act, and all statutes as applicable to banking entities. The specific guidelines for on-tap licensing of UBs and SFBs in the private sector were issued on August 1, 2016, and December 5, 2019, respectively.
- In the first stage, the applications are screened by RBI to ensure prima facie eligibility. Post-screening, it is forwarded to the Standing External Advisory Committee (SEAC) constituted of industry experts and eminent persons with experience in the BFSI sector, appointed for three years. SEAC’s recommendations shall then be examined by the Internal Screening Committee (ISC) consisting of Governor and Deputy Governors.
- ISC’s observations shall be forwarded to the Central Board (CB) of RBI which exercises the final discretion to grant in-principal approval for 18 months. Upon the culmination of this period, RBI shall on satisfaction with compliances grant the regular license for commencement of banking business.
Who can apply for UB, SFB, and UCB licenses?
- Any individual/entity with at least 10 years of experience in banking and finance at the senior level or private entities with 10 years of successful track record are eligible to apply for on-tap licensing as UBs. Secondly, aspiring entities ought to have assets of Rs. 5000 crore or above. Thirdly, the required net worth is Rs. 500 crore which has to be maintained at all times. However, large industrial houses are restricted to only invest in UBs up to 10% only.
- While the guidelines do not restrict applicants to only corporate entities, they vest discretion upon RBI to look for a strong promoter with significant experience and a proven track record. RBI emphasizes the entity’s track record in conforming to the best international and domestic standards of customer service, integrity, and efficiency. It implies that RBI would grant the licenses on the basis of discretional prudential factors, in addition to rule-based eligibility criteria.
- For an application for SFB, the individual entity must have 10 years of experience in the BFSI sector at the senior level. In the case of a corporate entity applicant, it must have at least 5 years of successful track record. Corporate applicants also encompass NBFCs, microfinance institutions, local banks and cooperative banks also. This aids such entities to expand their business on the liability side. Secondly, the minimum paid-up voting equity capital or net worth is Rs. 200cr., considering the size of operations and limited scope of activities.
- In the case of urban cooperative banks (UCBs) voluntarily transitioning as SFB shall have an initial net worth of Rs. 100 crore only but shall be increased to Rs 200 crores within five years from the commencement of business. However, this conversion model is plagued by ambiguities in promoter identification, investment plans and capital infusion by promoter groups.
- Summarily, there are five aspects that applicants ought to fulfill:
(i) financial inclusiveness,
(ii) soundness of business & technological model,
(iii) strong management track record,
(iv) sustainable governance, and
(v) adequate capital structure.
- The idea is that local players would be able to align themselves with respective target customer segments. Thus, it is imperative for the remainder and future applicants who fulfil the eligibility criteria they maintain sustainable financial principles.
|
PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. What do you understand by the concept of Universal Banking? What are its advantages and its limitations? Explain.
|

https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/industry/banking/finance/banking/india-post-payment-bank-wants-to-convert-itself-to-universal-bank-ceo/articleshow/98630770.cms













