Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: Invest India
Context:
The National Technical Textiles Mission (NTTM), an initiative by the Ministry of Textiles has successfully supported the development of 03 indigenous instruments for testing Convective, Radiant, and Contact (Conductive) Heat Resistance of protective textiles.
What are Technical Textiles?
Technical textiles are textile products designed primarily for functionality and performance rather than aesthetics or fashion. They are engineered to meet specific technical requirements and solve practical problems across diverse sectors, from healthcare and agriculture to defense, construction, and transportation. Unlike conventional textiles, which focus on comfort, style, or decoration, technical textiles are valued for their durability, safety, efficiency, and specialized properties.
Key Characteristics
- Purpose-driven:Manufactured to serve a clear functional need, such as protection, reinforcement, or filtration.
- High-performance materials:Often incorporate advanced fibers, composites, or coatings to enhance strength, heat resistance, water repellency, or biodegradability.
- Industry-specific applications:Each category is tailored to solve problems in a particular sector.
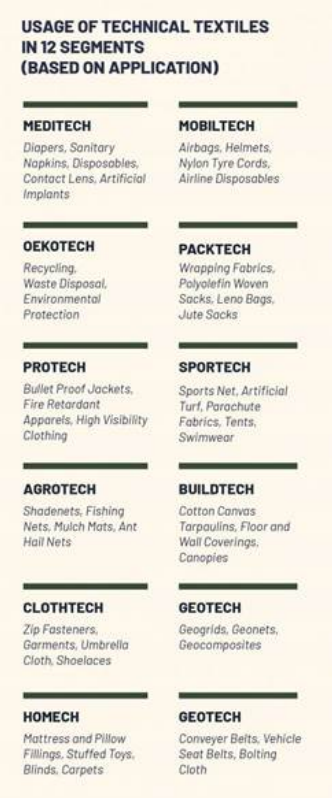
Classification (Based on End Use)
- Agrotech:Enhances agricultural productivity (shade nets, crop covers, mulching films).
- Medtech:Improves healthcare outcomes (surgical sutures, implants, wound care products).
- Mobiltech:Supports transport and mobility (airbags, seat belts, automotive upholstery).
- Buildtech / Geotech:Strengthens infrastructure (roofing materials, geotextiles for soil stabilization).
- Protective / Safety textiles:Ensures safety in hazardous environments (fire-resistant clothing, bulletproof vests).
- Sportech / Hometech:Enhances lifestyle and recreation (sports gear, tents, ropes, carpets).
- Indutech:Industrial and manufacturing uses (filtration fabrics, conveyor belts, insulation).
Current findings in India’s technical textiles industry:
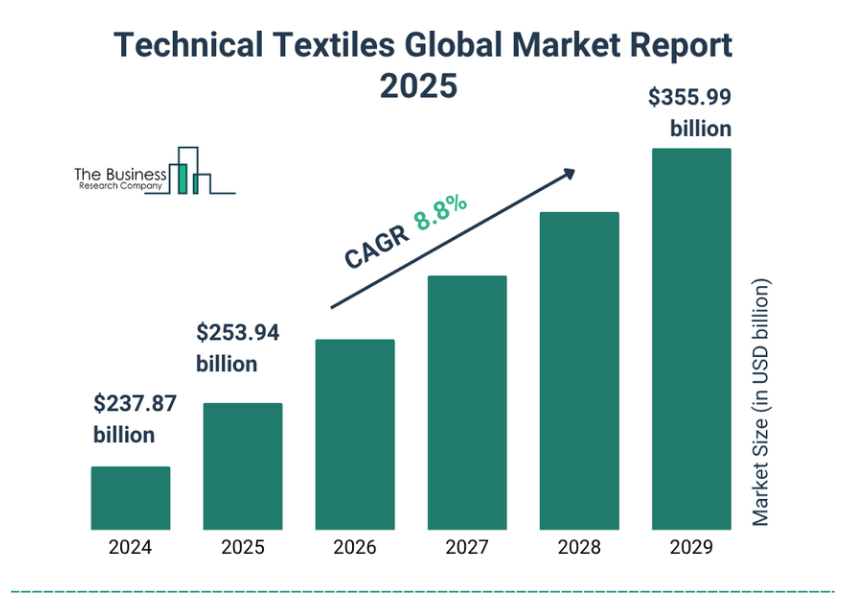
- The Indian technical textiles market is growing strongly. It was valued at around US $29 billion in 2024and is projected to reach US $45 billion by 2026.
- Growth rate:The sector is growing at approximately 10 % + per annum, with some segments accelerating faster.
- Export momentum:India’s exports of technical textiles are rising. For FY25, exports stood at around ₹24,732.68 crore, showing a strong yearonyear growth.
- Innovation and highvalue segments are gaining traction:Smart textiles (fabrics with embedded sensors), advanced materials (e.g., composites, specialty fibres) are emerging in sectors like defence, automotive, medical, infrastructure.
- Government policy support: Thegovernment has mapped out the sector through measures such as quality control orders (QCOs) for technical textile products, Harmonized System of Nomenclature (HSN) code classification to improve tracking & regulation, and programmes under the National Technical Textiles Mission.
- Importdependency still a concern: Although the domestic market is growing, India remains dependent on imported specialty fibres and hightech inputs in certain advanced segments.
Picture Courtesy: Business Research Company
National Technical Textile Mission (NTTM):
The National Technical Textile Mission (NTTM) is an ambitious initiative by the Government of India to promote the growth, research, and application of technical textiles across industries. Launched with a multi-year vision, it aims to position India as a global hub for high-performance textiles while supporting economic growth, employment, and innovation.
Significance
- Industrial Growth:Technical textiles are critical for sectors like automotive, defense, healthcare, and construction, driving high-value industrial output.
- Economic & Export Potential:With a strong domestic base and export promotion, NTTM contributes to foreign exchange earnings and reduces import dependence.
- Innovation & R&D:Encourages development of advanced fibers, composites, and smart fabrics, positioning India as a knowledge-driven manufacturing hub.
- Employment & Skill Development:Supports job creation and upskilling in textiles and allied sectors.
- Sustainability:Encourages eco-friendly materials and sustainable production processes aligned with global green trends.
Objectives
- Enhance production and usageof technical textiles in India.
- Promote research and developmentin high-value, specialized technical textiles.
- Encourage domestic manufacturingto reduce import dependency.
- Support industrial applicationin sectors like healthcare, agriculture, infrastructure, defense, and automotive.
- Create skilled manpowerfor innovation, production, and quality control.
Key Components
- Research, Innovation & Development:
- Funding R&D projects in technical textiles.
- Developing specialized fibres, composites, and smart textiles.
- Promotion & Market Development:
- Encouraging adoption across industries such as agriculture (aggrotech), medical (MedTech), and construction (build tech).
- Creating awareness about the benefits of technical textiles.
- Export Promotion & Import Substitution:
- Strengthening domestic capacity to manufacture high-value products currently imported.
- Targeting global export markets to enhance India’s share in the $250+ billion global technical textiles industry.
- Skill Development & Infrastructure:
- Establishing training centres for technical textile manufacturing and R&D.
- Supporting incubation centres for startups and small businesses in technical textiles.
- Standards & Quality Assurance:
- Developing certification and quality standards to ensure global competitiveness.
- Facilitating compliance with international norms for exports.
New Development in Technical Textile:
Convective Heat Resistance Tester
- Measures the fabric’s ability to resist heat transfer through moving air.
- Essential for designing garments that protect against flames, hot gases, or industrial ovens.
Radiant Heat Resistance Tester
- Evaluates how well textiles withstand heat radiationfrom flames, molten metal, or hot surfaces.
- Critical for firefighters’ suits and molten-metal handling apparel.
Contact (Conductive) Heat Resistance Tester
- Tests the fabric’s ability to resist direct heat transfer from a hot surface.
- Important for industrial and laboratory protective clothing.

Picture Courtesy: PIB
Significance of such developments:
- Self-reliance: India now has domestic capabilityto test high-performance protective fabrics, reducing dependence on imported machines.
- Cost & Time Efficiency: Indigenous instruments reduce testing costs and turnaround time, making safety certification more accessible.
- Global Standards Alignment: These instruments comply with ISO and Indian Standards, enabling India-made protective textiles to meet international quality requirements.
- Support for Innovation: With faster and affordable testing, Indian manufacturers can experiment, innovate, and produce advanced protective fabricsfor diverse applications.
- Strategic Value: Enhances India’s capability in critical sectors like defence, infrastructure, and healthcare, where safety and protection are paramount.
What are the challenges in technical textiles?
Technological and Innovation Challenges
- Limited indigenous R&D: Many high-performance fibres, composites, and smart textiles still rely on imported technology.
- Slow adoption of advanced manufacturing: Automated and precision manufacturing for technical textiles is not widespread.
Market and Demand Challenges
- Low awareness among end-users: Many sectors, including agriculture, healthcare, and construction, are yet to fully adopt technical textiles.
- Price sensitivity: High-performance fabrics are costlier than conventional textiles, making adoption slow in price-sensitive markets. For e.g. Protective and industrial textiles have global demand, but domestic manufacturers often struggle to scale up production competitively.
Financial and Policy Challenges
- High capital investment: Production of advanced fibers, composites, and smart textiles requires significant upfront investment.
- Limited access to credit and subsidies: Small and medium enterprises face difficulty securing funding for technical textile projects.
Global Context: Countries like Germany, Japan, and the USA provide extensive subsidies, tax incentives, and R&D grants for technical textiles, giving them a competitive edge.
Skill and Human Resource Challenges
- Shortage of skilled manpower: Specialized training in high-performance textile manufacturing, testing, and R&D is limited.
- Need for interdisciplinary expertise: Technical textiles often require knowledge of polymer science, nanotechnology, and engineering, which is scarce in the workforce.
Other Government initiatives for Technical Textiles:
|
Initiative
|
Purpose
|
Conceptual Idea
|
Impact / Outcome
|
|
Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme
|
Promote large-scale domestic manufacturing of technical textiles and high-value textile products
|
Encourages technology-driven production, reduces import dependence
|
Attracts investment, boosts competitiveness, promotes exports
|
|
PM MITRA Parks Scheme
|
Establish integrated textile parks covering the full value chain
|
Provides an ecosystem for manufacturing, innovation, and scaling up technical textiles
|
Supports clustering, improves efficiency, enhances global competitiveness
|
|
HSN Codes & Standardization
|
Assign 207 specific codes for technical textile products
|
Enhances regulatory clarity and policy visibility
|
Facilitates monitoring, tracking, and better policy implementation
|
|
Quality Control Orders (QCOs) & BIS Standards
|
Mandate quality and safety standards for certain technical textiles
|
Builds credibility and trust in domestic products
|
Improves export-readiness, ensures safety, strengthens global competitiveness
|
|
Startup & Innovation Support under NTTM
|
Provide grants and support for R&D and startups
|
Encourages innovation, new applications (smart textiles, MedTech, protective gear), and self-reliance
|
Boosts domestic innovation ecosystem and high-value product development
|
|
Skill Development & Capacity Building
|
Train manpower in advanced textile manufacturing and R&D
|
Addresses skill gaps and prepares workforce for advanced manufacturing
|
Ensures sustainable growth and long-term sectoral development
|
What we can do more?
Strengthen R&D and Innovation
- Promote indigenous development of fibres, composites, smart textiles, and protective fabrics.
- Encourage collaboration between industry, startups, and academic institutions for new technologies.
Modernize Manufacturing & Infrastructure
- Expand advanced production facilities, textile clusters, and PM MITRA Parks.
- Promote automation, precision manufacturing, and technology adoption to improve global competitiveness.
Skill Development & Human Resource Capacity
- Train specialized workforce in polymer science, nanotechnology, material engineering, and textile design.
- Integrate technical textile courses into higher education, vocational training, and industry programs.
Market Development & Export Promotion
- Increase adoption across sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, defense, and construction.
- Encourage exports, import substitution, and value addition to boost India’s presence in the global market.
Conclusion:
India’s technical textiles sector has enormous growth potential. With strong R&D, modern infrastructure, skilled workforce, policy support, and global market integration, India can become a global leader in high-value, innovative, and sustainable technical textile products, reducing import dependence and driving economic growth.
Source: PIB
|
Practice Question
Q. Examine the challenges and opportunities in the technical textiles sector in India. How can policy initiatives like PLI schemes, PM MITRA Parks, and quality standardization contribute to sectoral growth? (250 words)
|
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Technical textiles are materials and products manufactured primarily for their functional properties rather than aesthetics. They are used in industries like healthcare, defense, construction, agriculture, automotive, and protective equipment. Examples include geotextiles, agrotextiles, medical textiles, and protective fabrics.
Launched by the Government of India, NTTM is a 4-year mission (2020–2024) aimed at promoting R&D, innovation, manufacturing, and export of technical textiles. It supports startups, MSMEs, skill development, and quality standards.
India aims to:
- Reduce import dependence in high-value technical textiles.
- Develop domestic manufacturing and innovation.
- Enhance exports and global competitiveness.
Create employment and skill development opportunities.













