



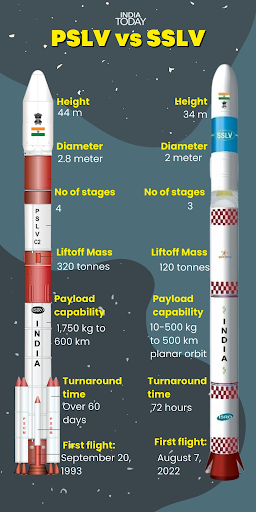
India's Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) is a response to global demand for rapid, cost-effective missions. Launched by ISRO, it features a liquid-based Velocity Trimming Module and a 72-hour turnaround time.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: NEWSONAIR
NewSpace India Limited (NSIL), the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe), and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) signed a Technology Transfer Agreement (ToT) to commercialize the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV).
It is a low-cost, and "launch-on-demand" rocket developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
It is specifically designed to meet the growing market demand for launching small satellites.
Key features
Significance: Provide a dedicated, cost effective, frequent, and flexible launch option for small satellites, empowering universities, startups, and developing nations to execute their space missions.
|
Read all about: India's Space Sector: $24 Billion GDP Contribution & Growth l India's Space Program: Achievements & Future Missions l SPACE TOURISM l Treaty to ensure peace & security in outer space |
Global Competition: SSLV faces tough competition from Rocket Lab’s Electron and SpaceX’s rideshare missions, which offer launches at $275,000 for a 50-kg satellite to sun-synchronous orbit (SSO). SSLV’s ₹30–35 crore cost must drop to compete effectively.
Funding Shortfalls: India’s space budget of $1.7 billion lags behind NASA’s $25.3 billion, limiting R&D and private investment due to high risks and long returns.
Regulatory Gaps: India lacks a comprehensive Space Activities Act, causing delays in approvals and uncertainty over private sector liabilities.
Technological Dependence: Importing components (₹2,114 crore in FY 2021-22) slows self-reliance. SSLV’s reliance on solid propellants limits reusability compared to SpaceX’s Falcon 9.
Space Debris Risks: Small satellite constellations increase orbital debris, risking collisions, and threaten long-term sustainability.
Enhance Cost Competitiveness: Reduce SSLV launch costs to rival SpaceX’s $2.75 million rideshare price.
Boost Private Investment: Launch a Space Component Indigenization Mission and expand Make in India schemes to cut reliance on imports and attract venture capital.
Enact Space Legislation: Pass an Indian Space Activities Act to clarify private sector roles, liability, and dispute resolution.
Tackle Space Debris: Mandate 5-year timelines and equip satellites with transponders for real-time tracking to reduce collision risks.
Strengthen Diplomacy: Leverage G20 platforms to promote SSLV launches, enhancing India’s role in the Global South.
Source: NEWSONAIR
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Analyze the strategic and economic significance of the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) in the context of India's growing ambition in the global commercial space market. 150 words |
The SSLV is a three-stage, solid-fuel launch vehicle developed by ISRO to provide cost-effective and on-demand launch services for small satellites into Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
SSLV can carry 500 kg to Low Earth Orbit (LEO) or 300 kg to Sun-Synchronous Polar Orbit (SSPO).
SSLV uses solid propulsion for its three main stages and a liquid propulsion-based velocity trimming module (VTM) for precision orbital insertion.







© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved