Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- India’s first homegrown mRNA vaccine against coronavirus are aiming to roll out before April.
Understanding mRNA Vaccines
Traditional Vaccines
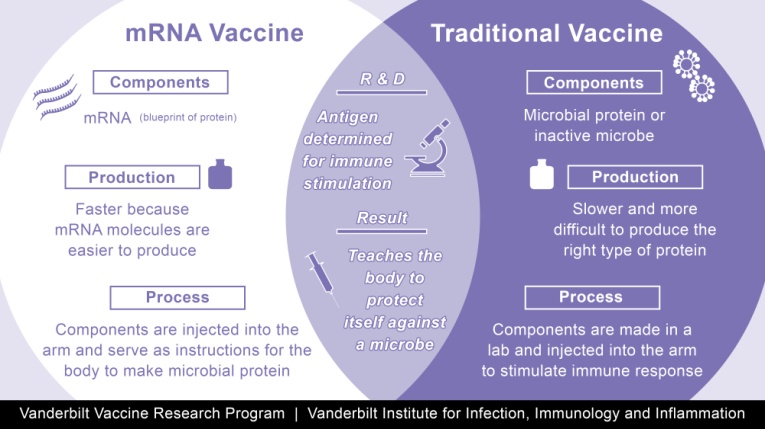
- Vaccines help prepare the body to fight foreign invaders (pathogens such as bacteria or viruses), to prevent infection.
- All vaccines introduce into the body a harmless piece of a particular bacteria or virus, triggering an immune response.
- Most vaccines contain a weakened or dead bacteria or virus.
mRNA Vaccines
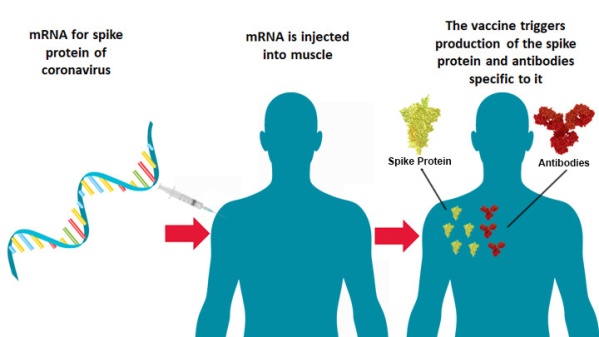
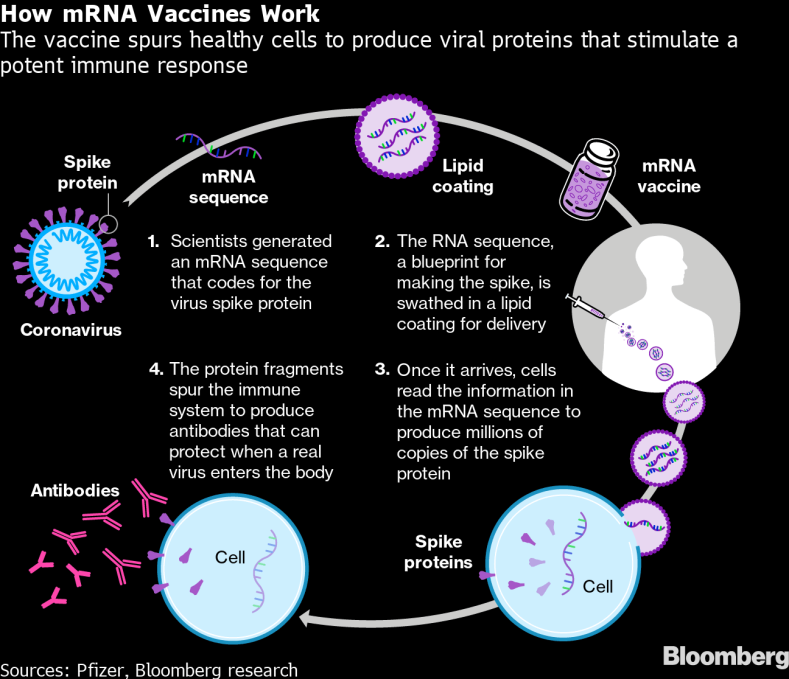
- Scientists have developed a new type of vaccine that uses a molecule called messenger RNA (or mRNA for short) rather than part of an actual bacteria or virus.
- Messenger RNA is a type of RNA that is necessary for protein production in our body. In cells, mRNA uses the information in genes to create a blueprint for making proteins. Once cells finish making a protein, they quickly break down the mRNA.
- mRNA from vaccines does not enter the nucleus and does not alter DNA.
- mRNA vaccines work by introducing a piece of mRNA that corresponds to a viral protein, usually a small piece of a protein found on the virus’s outer membrane. (Individuals who get an mRNA vaccine are not exposed to the virus, nor can they become infected by the vaccine.)
- Using this mRNA blueprint, cells produce the viral protein.
- As part of a normal immune response, the immune system recognizes that the protein is foreign and produces specialized proteins called antibodies.
- Antibodies help protect the body against infection by recognizing individual viruses or other pathogens, attaching to them, and marking the pathogens for destruction.
- Once produced, antibodies remain in the body, even after the body has rid itself of the pathogen, so that the immune system can quickly respond if exposed again.
- If a person is exposed to a virus after receiving mRNA vaccination for it, antibodies can quickly recognize it, attach to it, and mark it for destruction before it can cause serious illness.
https://epaper.thehindu.com/Home/ShareArticle?OrgId=G509FU8AM.1&imageview=0