Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Forest officials experiment to learn that the tree indeed stores water, particularly in the summer, as claimed by the konda reddy tribe
Details
About the tribe
- It is one of the most backward tribal groups in the states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
- Konda Reddis have also been recognized as Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups.
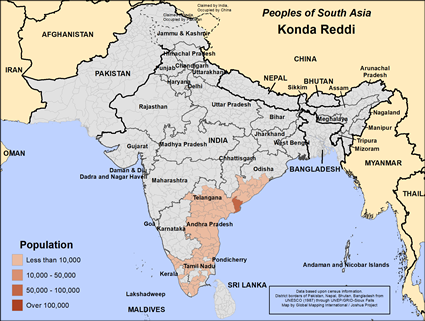
Distribution
- They can also be found in Tamil Nadu, Pondicherry, Karnataka, Kerala, Orissa and Maharashtra.
- They inhabit on both the banks of the Godavari River (East and West Godavari districts), in the hilly-forest region of Khammam (Telangana) and Srikakulam (Andhra Pradesh).

Food and occupation
- The majority of the Reddy communities are non-vegetarian, and all the communities take rice as their staple cereals. Jowar, wheat, bajra and ragi are the other cereals for them.
- The traditional occupation of most of the Reddy groups is settled cultivation, followed by animal husbandry and labour.
- The Konda Reddis are known for their eco-friendly practices such as use of household articles made of bamboo, bottle gourd, and seed.
Society
- Traditionally the Reddy belong to the fourth of the Hindu Varnas, Sudra. One section of the Reddy is called Kapu which means guardian.
- The Reddy community has social divisions such as clans, lineage, subcastes and sects. These social divisions regulate marital alliances.
- They speak the Kannada and Telugu languages. Among the Reddy people, cross-cousin marriages of both types are allowed.
- Widow Remarriage is not permitted. Being a dominant community, the Reddy have been primarily landlords and landholders. Social control is regulated through traditional caste and village councils.
Religious belief
- They are Hindu by faith and worship many deities. Their main festivals are Ugadi, Akshade and Dussehra.
Recent News
- Andhra Pradesh Forest Department’s recent experiment in Papikonda National Park confirmed the indigenous knowledge of the Konda Reddi tribe. By cutting bark from Indian laurel trees (Terminalia tomentosa), authorities confirmed the tribe’s claim that these trees store natural water, particularly during summer.
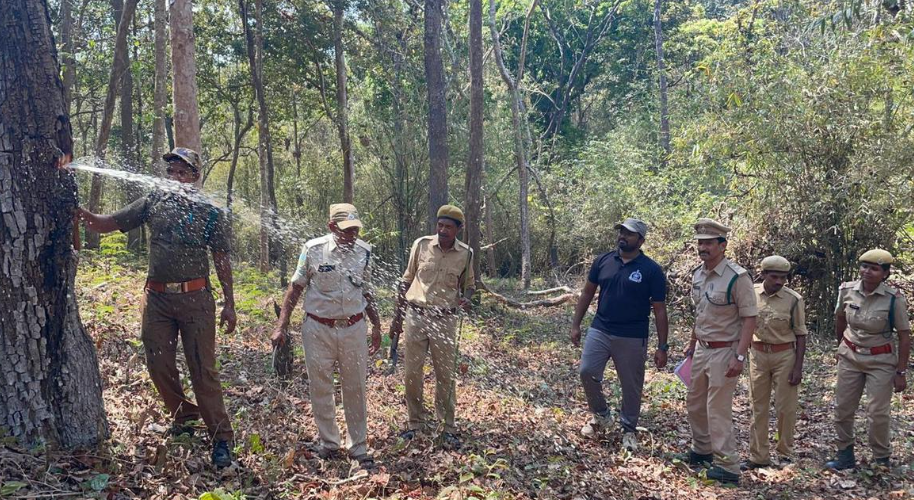

Indian Laurel tree
- The Indian Laurel tree, scientifically known as Ficus microcarpa, is a tropical or subtropical tree found primarily in several parts of Asia, Western Pacific Islands and Australia.
- As an ornamental tree, it provides a dense canopy and has a smooth light-gray bark, and shiny green lanceolate leaves.
- Its thick foliage creates excellent habitat for various bird species, and its small round figs serve as food for birds.
- The holds significant commercial value owing to its timber.
|
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Papikond anational park located in which of the following state?
- Karnataka
- Tamil Nadu
- Kerala
- Andhra Pradesh
Answer D
|











