



India's foreign policy evolved from Cold War non-alignment to multi-alignment with the West. Economic ties (US trade $146B, EU €115B), strategic alignment (Quad, defense deals), and democratic values drive this. Challenges include Russian oil purchases, trade disputes (US tariffs), and domestic policy critiques. Deepening economic ties and direct dialogue are key for future collaboration.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: BEHORIZON
The foreign policy of India has shifted from traditional non-alignment to a dynamic, multi-aligned approach that seeks closer ties with Western countries, particularly the United States and Europe.
'The West,' includes the USA, EU, UK, Canada, and Australia, refers to a group of economically advanced, with historical, cultural, and political connections. These nations favor market economies, democratic systems, and individual liberties.
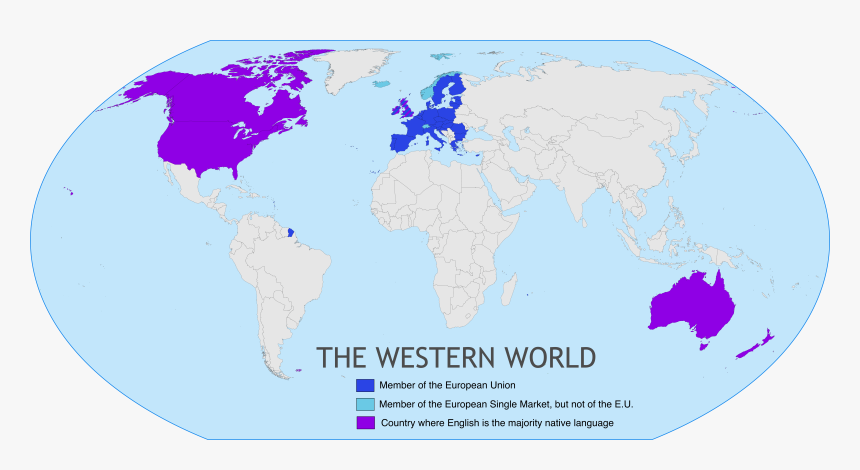 Economic Influence: The US has the world's largest economy, with a 2025 GDP of over $30 trillion.
Economic Influence: The US has the world's largest economy, with a 2025 GDP of over $30 trillion.
Democratic Governance: All functions under democratic systems, supporting representative government and political freedom.
Shared History & Alliances: Many share a history as former British colonies, resulted similarity in legal and political systems.
Cold war era(1947-1991)
Policy of non-alignment: India refused to formally ally with either the US-led Western bloc or the Soviet-led Eastern bloc, to preserve its sovereignty and decisional autonomy in foreign affairs.
Engagement with the US: Relations with the US were strained due to conflicting ideologies and US alliances with Pakistan. However, India received economic and food aid from the US.
Engagement with European nations: India maintained friendly relations with European nations, such as the UK and France, engaging in defense cooperation and receiving development assistance.
Post-cold war transformation (1990s onwards)
Economic Liberalization (1991): India's economic reforms opened up its economy, increasing foreign direct investment from Western countries. FDI inflows from Western countries rose significantly after liberalization, reaching $5.3 billion by 2000.
Deepening Bilateral Ties: Key moments like the 2005 US-India Civil Nuclear Agreement signaled a shift towards a closer partnership.
Strategic Dialogue and Cooperation: High-level dialogues and ministerial meetings have developed stronger bilateral relations.
Strategic Autonomy and Multi-Alignment: India's current foreign policy underlines strategic autonomy and a multi-aligned approach.
Economic cooperation
Strategic alignment
Democratic values
Geopolitical tensions: India’s purchase of Russian oil, draws Western criticism amid sanctions over the Ukraine war.
Trade disputes: Protectionist policies lead to conflict. The US imposed a 25% tariff on Indian goods in August 2025, impacting $2 billion in trade.
Domestic policy criticism: West critiques India’s internal policies, including hate speech against minorities, internet shutdowns, which restrict trade and raise human rights concerns.
China’s influence: India's rivalry with China complicates Western engagement.
Digital Challenges: Concerns about India's digital governance originate from the high prevalence of cyberbullying. 85% of Indian children report experiencing online harassment, impacts India’s global image.
Strengthen economic ties: Finalizing FTAs with the EU and UK, including streamlining regulations and lowering tariffs on imports.
Balance strategic partnerships: Enhance Quad cooperation through joint initiatives and exercises.
Address domestic concerns: Implement transparent digital laws to curb cyberbullying, aligning with Western standards.
Counter geopolitical pressures: Communicate multi-alignment strategy, emphasizing energy security needs, particularly concerning Russian oil imports.
Promote democratic dialogue: Annual democracy summits with Western partners to show success of electoral process and address criticisms regarding domestic policies through open channels.
|
For Mains: India-US Relation Under Trump 2.0 l India and U.S to Lower Tariffs l INDIA EUROPEAN UNION RELATIONS l India-Europe Bilateral Relations l India-UK FTA 2025 |
Source: THE HINDU
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. India's foreign policy is a delicate balancing act between its strategic autonomy and the demands of its key partners." Critically analyze. 250 words |
The Quad (India, US, Australia, Japan) promotes a free and open Indo-Pacific and enhances maritime security.
iCET (2023) deepens collaboration in AI, semiconductors, and defense co-production between India and the US.
85% of Indian children report experiencing online harassment.




© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved