





Source: NDTV
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Contxt
Details
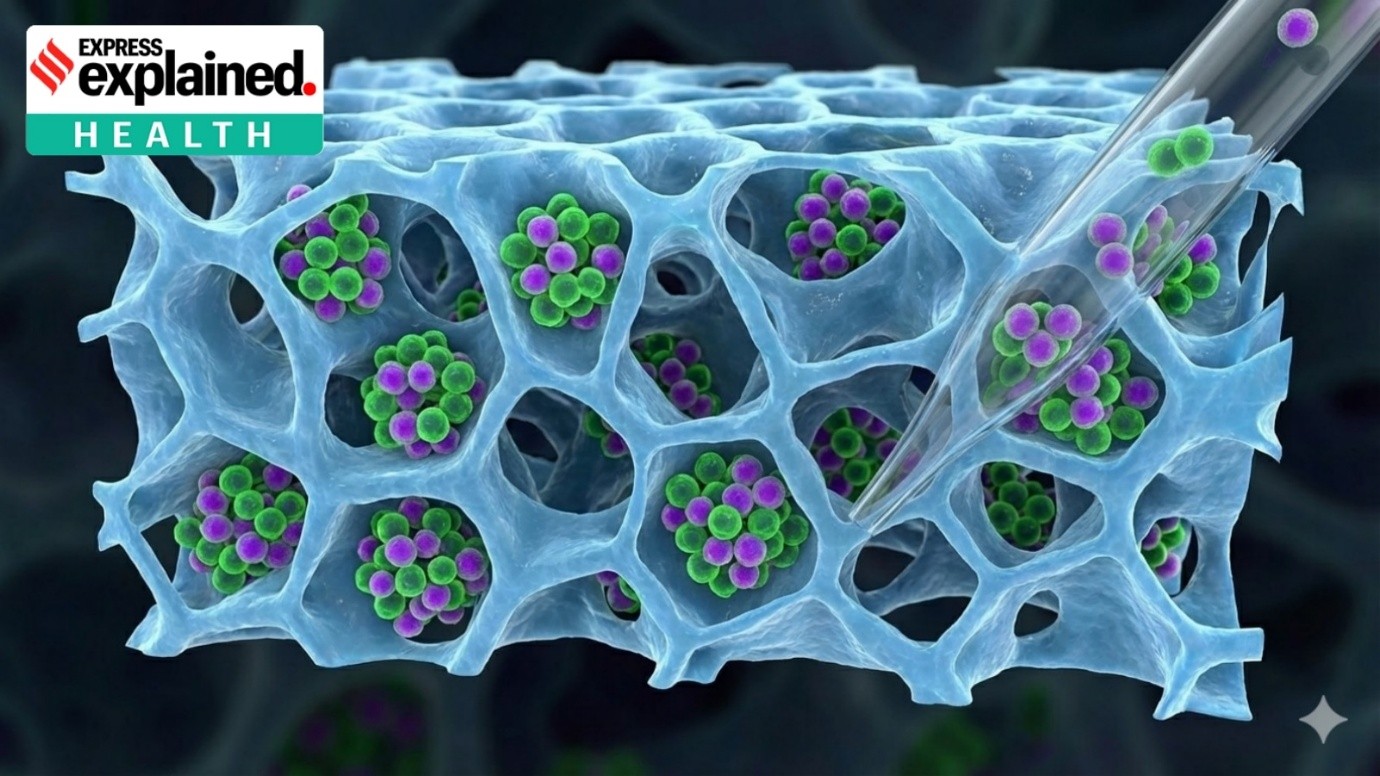
Hantavirus
Transmission
Geographic Distribution
Clinical Syndromes
Prevention and Control
Virus
|
Aspect |
Description |
|
Definition |
A virus is a microscopic infectious agent that can only replicate inside the living cells of organisms. |
|
Structure |
Consists of genetic material (DNA or RNA), a protein coat called a capsid, and sometimes a lipid envelope. |
|
Classification |
Classified based on nucleic acid type (DNA or RNA), symmetry (icosahedral, helical, complex), and envelope presence. |
|
Replication Cycle |
Involves attachment, penetration, uncoating, replication, assembly, and release. Can lead to lytic or lysogenic cycles. |
|
Types of Viruses |
DNA Viruses: Herpesvirus, Poxvirus, Adenovirus. RNA Viruses: Influenza, HIV, SARS-CoV-2. |
|
Transmission |
Spread through direct contact, airborne droplets, vectors (mosquitoes), and contaminated surfaces. |
|
Host Range |
Can infect animals, plants, fungi, bacteria (bacteriophages), and archaea. |
|
Diseases Caused |
Range from mild colds to severe diseases like AIDS, Ebola, Influenza, and COVID-19. |
|
Prevention |
Includes vaccination, antiviral drugs, hygiene practices, and quarantine measures. |
|
Zoonotic Potential |
Many viruses, like Influenza A, have zoonotic potential, meaning they can be transmitted from animals to humans. |
|
Impact on Humans |
Can cause acute infections, chronic infections, or asymptomatic cases. |
|
Viral Evolution |
Includes mutation, recombination, and reassortment, leading to new strains and potential pandemics. |
Common rodents
|
Common Name |
Scientific Name |
Physical Characteristics |
Habitat |
Diet |
Unique Features |
|
House Mouse |
Mus musculus |
Small, light brown or grey fur, large ears, long tail |
Human dwellings, fields |
Grains, seeds, insects |
Highly adaptable to various environments |
|
Brown Rat |
Rattus norvegicus |
Large, brown or grey fur, blunt nose, long tail |
Urban areas, sewers, fields |
Omnivorous: grains, fruits, small animals |
Known for spreading diseases like leptospirosis |
|
Black Rat |
Rattus rattus |
Sleek, black or dark brown fur, pointed nose, long tail |
Coastal areas, urban environments |
Fruits, seeds, insects |
Excellent climbers, often found in roofs |
|
Guinea Pig |
Cavia porcellus |
Robust body, short legs, no tail, various fur colors |
Domestic environments |
Vegetables, hay, pellets |
Commonly kept as pets, social animals |
|
Capybara |
Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris |
Largest rodent, webbed feet, brown fur, small ears |
Wetlands, riverbanks |
Grasses, aquatic plants |
Semi-aquatic, strong swimmers |
|
Squirrel |
Sciuridae family |
Bushy tails, sharp claws, varied fur colors (grey, red, black) |
Forests, urban parks |
Nuts, seeds, fruits |
Known for caching food, excellent climbers |
|
Beaver |
Castor canadensis |
Large, flat tail, webbed feet, thick brown fur |
Rivers, lakes, streams |
Bark, leaves, aquatic plants |
Known for building dams and lodges |
|
Porcupine |
Erethizon dorsatum |
Covered in sharp quills, large body, slow-moving |
Forests, grasslands |
Leaves, fruits, bark |
Uses quills as a defense mechanism |
|
Hamster |
Cricetinae subfamily |
Small, stout body, cheek pouches for food storage, varied fur colors |
Deserts, fields |
Seeds, fruits, vegetables |
Nocturnal, commonly kept as pets |
|
Prairie Dog |
Cynomys ludovicianus |
Tan fur, black-tipped tail, small ears |
Grasslands, prairies |
Grasses, seeds, insects |
Live in large colonies with complex burrow systems |
|
Chinchilla |
Chinchilla lanigera |
Dense, soft fur, large ears, bushy tail |
Andes mountains |
Hay, pellets, dried fruits |
Known for their incredibly soft fur, often kept as pets |
|
Lemming |
Lemmus lemmus |
Small, short tail, thick fur, various fur colors (brown, grey) |
Tundra, arctic regions |
Grasses, mosses, berries |
Known for population cycles and mass migrations |
|
Gopher |
Geomyidae family |
Small, fur-lined cheek pouches, strong claws for digging, brown fur |
Meadows, grasslands |
Roots, tubers, plants |
Create extensive burrow systems |
|
Vole |
Microtus genus |
Small, stocky body, short tail, brown or grey fur |
Meadows, forests, fields |
Grasses, seeds, bark |
Important part of the food chain, prey for many predators |
|
Marmot |
Marmota genus |
Large, stocky body, bushy tail, brown or grey fur |
Mountainous regions, grasslands |
Grasses, flowers, insects |
Hibernate during winter, live in colonies |
Rodent-borne diseases
|
Disease |
Causative Agent |
Symptoms |
Transmission |
Preventive Measures |
|
Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS) |
Hantaviruses |
Fever, muscle aches, fatigue, cough, shortness of breath |
Inhalation of aerosolized particles from rodent droppings, urine, saliva; direct contact |
Avoid contact with rodent excreta, seal entry points, clean areas infested by rodents safely |
|
Leptospirosis |
Leptospira bacteria |
Fever, headache, muscle pain, chills, vomiting, jaundice |
Contact with water, soil, or food contaminated with urine from infected animals |
Avoid stagnant water, ensure rodent control, wear protective gear |
|
Salmonellosis |
Salmonella bacteria |
Diarrhea, fever, abdominal cramps |
Ingestion of contaminated food or water |
Proper food handling, rodent control, sanitation |
|
Rat-Bite Fever |
Streptobacillus moniliformis, Spirillum minus |
Fever, rash, vomiting, muscle pain, headache |
Bites or scratches from infected rodents, contact with rodent secretions |
Avoid rodent contact, clean bites/scratches, seek medical attention |
|
Plague |
Yersinia pestis bacteria |
Bubonic: swollen lymph nodes, fever, chills; Septicemic: abdominal pain, shock; Pneumonic: respiratory symptoms |
Flea bites, direct contact with infected animals or tissues |
Flea control, avoid contact with wild rodents |
|
Tularemia |
Francisella tularensis |
Fever, skin ulcers, swollen lymph glands, sore throat |
Tick and deer fly bites, direct contact with infected animals, inhalation |
Use insect repellent, avoid handling wild animals, cook game meat thoroughly |
|
Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis (LCM) |
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) |
Fever, malaise, muscle aches, headache, nausea, meningitis |
Inhalation of dust contaminated with rodent excreta, direct contact |
Avoid contact with rodents, seal homes, maintain good hygiene |
|
Bartonellosis (Cat Scratch Disease) |
Bartonella bacteria |
Fever, enlarged lymph nodes, pustule at scratch site |
Scratch or bite from infected animals, flea bites |
Avoid scratches/bites from animals, flea control |
|
Murine Typhus |
Rickettsia typhi, Rickettsia felis |
Fever, headache, rash, muscle pain |
Flea bites |
Flea control, avoid contact with rodents |
Sources:
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q: Consider the following statements regarding Hantavirus:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? a) 1 and 2 only Answer: a) |







© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved