Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.3blmedia.com/news/gri-and-cdp-deliver-enhanced-reporting-biodiversity
Context: The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) has introduced an updated transparency standard, known as the GRI Biodiversity Standard, to address the global biodiversity crisis.
Details
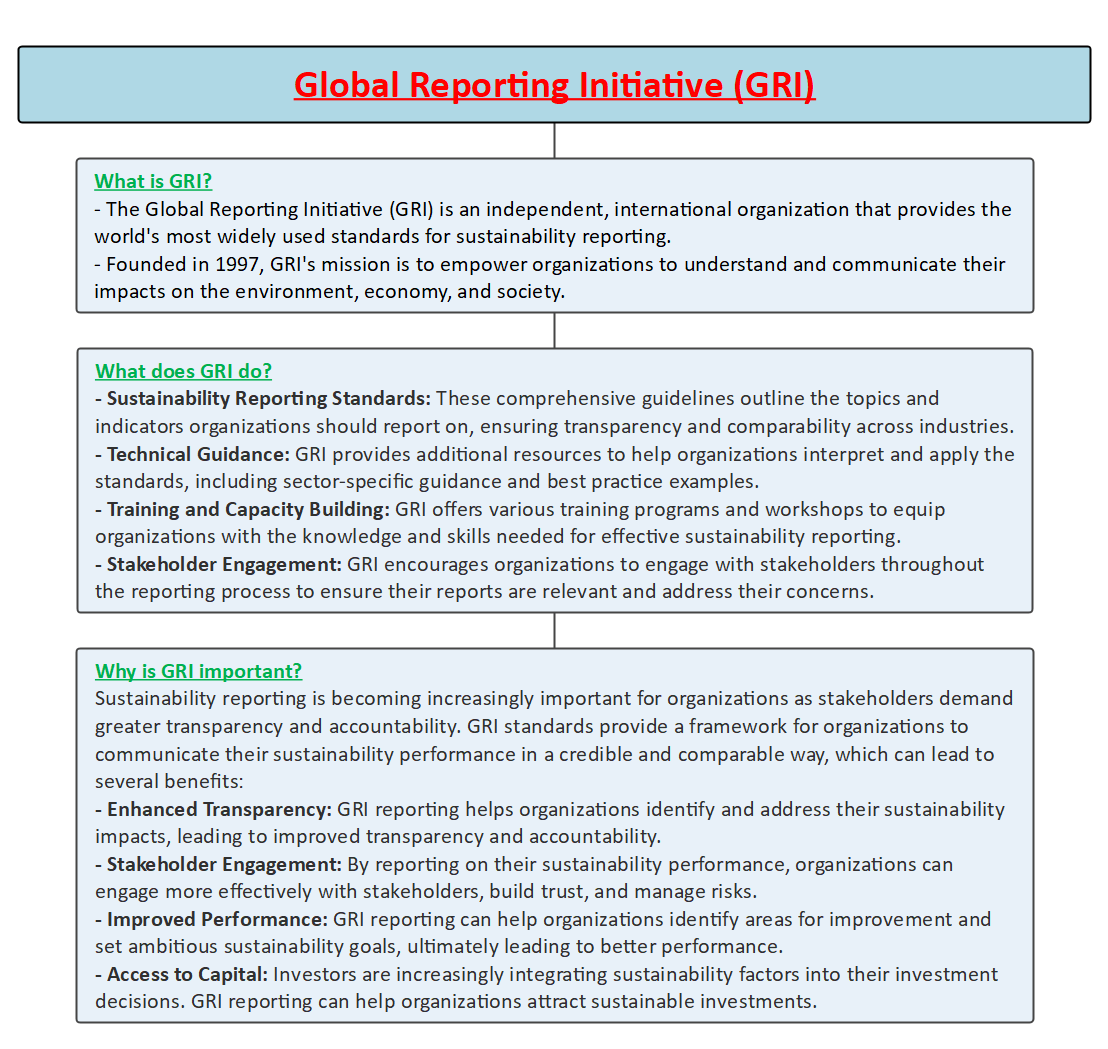
- The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) new standards aim to assist businesses, governments, and other entities in understanding and reporting their impacts on biodiversity, alongside issues related to climate change, human rights, and corruption.
- Developed by the Global Sustainability Standards Board (GSSB), the GRI Biodiversity Standard demands accountability from organizations regarding their impacts on biodiversity through supply chains and operations.
- The GRI Biodiversity Standard aims to provide a comprehensive framework for reporting biodiversity impacts, thereby enabling organizations to understand and address their environmental responsibilities.

Key points about the GRI Biodiversity Standard
- Effective Date and Implementation: The new standard, named GRI 101: Biodiversity 2024, will be formally implemented for reporting purposes from January 1, 2026. This gives organizations time to familiarize themselves with the standard and make necessary adjustments to comply with its requirements.
- Piloting and Community Engagement: In the two years leading up to the implementation, GRI plans to pilot the use of the standard with early adopters and prioritize engagement with community members. This approach ensures that the standard is practical and meets the needs of diverse stakeholders.
- Alignment with Global Developments: The GRI Biodiversity Standard is aligned with crucial global developments in the biodiversity field, including the United Nations Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework, the Science-Based Target Network, and the Taskforce on Nature-Related Financial Disclosures. This alignment ensures that reporting under the standard is consistent with international biodiversity goals and frameworks.
- Transparency and Accountability: The standard promotes transparency throughout the supply chain, addressing the underreporting of major biodiversity impacts. It requires organizations to disclose location-specific impacts, including countries and operational sites, as well as direct drivers of biodiversity loss such as land use, pollution, invasive species, and climate change.
- Impacts on Communities and Indigenous Peoples: The standard also emphasizes the impacts of organizations on communities and Indigenous Peoples, as well as the importance of engaging with local groups to restore affected ecosystems. This reflects a holistic approach to biodiversity conservation that considers social and cultural dimensions.
Conclusion
- The GRI Biodiversity Standard sets a benchmark for organizations to report their impacts on biodiversity and demonstrates their commitment to environmental stewardship. By providing a structured framework for transparency and accountability, the standard contributes to global efforts to halt and reverse biodiversity loss and build a nature-positive future.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. To what extent can technological advancements like carbon capture and storage or geoengineering be ethically and sustainably used to mitigate climate change, considering potential unintended consequences and the inherent uncertainty of these solutions?
|