



The EU-Mercosur FTA, signed in January 2026, seeks to form a major free-trade zone and counter China’s influence. Ratification faces resistance over Amazon deforestation, EU regulations, and farmer protests. For India, it risks trade diversion but offers lessons for negotiating its own EU trade agreement.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: DOWNTOEARTH
Context
The European Union (EU) and the Mercosur bloc of South American nations signed the Free Trade Agreement (FTA) to create one of the world's largest free trade areas.
Key Details of the 2026 Agreement
Tariff Elimination: The pact will eliminate more than 90% of tariffs on goods traded between the two regions.
Geopolitical Significance: EU leaders framed the deal as a strategic move to promote multilateralism and fair trade in response to rising global protectionism.
Next Steps: Agreement requires formal consent from the European Parliament and ratification by the national legislatures of the Mercosur member countries before it can fully enter into force.
What is European Union (EU)?
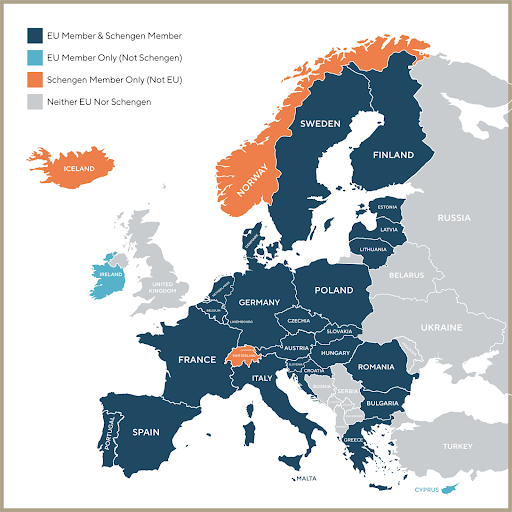
The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union comprising 27 member states located primarily in Europe.
It functions through a standardized legal system and a single internal market that ensures the free movement of people, goods, services, and capital.
Member States
Member Countries: Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, and Sweden.
The Eurozone: 21 members use the Euro (€) as their official currency, with Bulgaria being the most recent to join the euro area.
Schengen Area: A border-free zone encompassing most EU members (excluding Ireland and Cyprus for now) and four non-EU countries (Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland), allowing travel without passport checks.
Governance & Institutions
What is Mercosur?
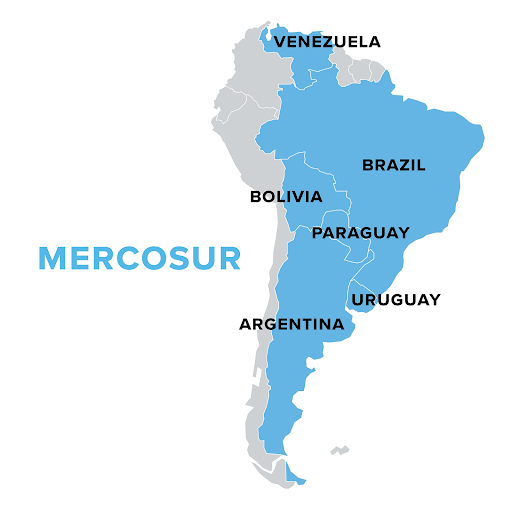
Mercosur is a South American trade bloc established in 1991 to promote free trade and the fluid movement of goods, people, and currency.
Membership and Structure
Source: DOWNTOEARTH
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. The Mercosur bloc, which recently signed a free trade agreement (FTA) with the European Union, comprises which of the following countries? (a) Brazil, Argentina, Chile, and Uruguay (b) Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay, and Uruguay (c) Brazil, Bolivia, Paraguay, and Venezuela (d) Argentina, Peru, Colombia, and Brazil Answer: b Explanation: Mercosur is composed of six sovereign member states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay and Venezuela (suspended since 2016). |
MERCOSUR (Southern Common Market) is a South American trade bloc formed in 1991 by Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay to create a common market with free trade, capital, goods, and people movement, evolving into a customs union with a common external tariff.
The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union comprising 27 member states located primarily in Europe. Established to ensure peace and prosperity following World War II, it operates as a "single market," allowing for the free movement of people, goods, services, and capital.
Brexit is the term for the United Kingdom's withdrawal from the European Union (EU), resulting from a 2016 referendum where 52% of UK voters chose to leave, leading to the UK's formal departure on January 31, 2020, ending its membership in the political and economic bloc it joined in 1973.


© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved