Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- The project for the construction & maintenance of a Cable Stayed Bridge across River Chambal on Kota Bypass on NH-76 of East-West Corridor in Rajasthan is completed.
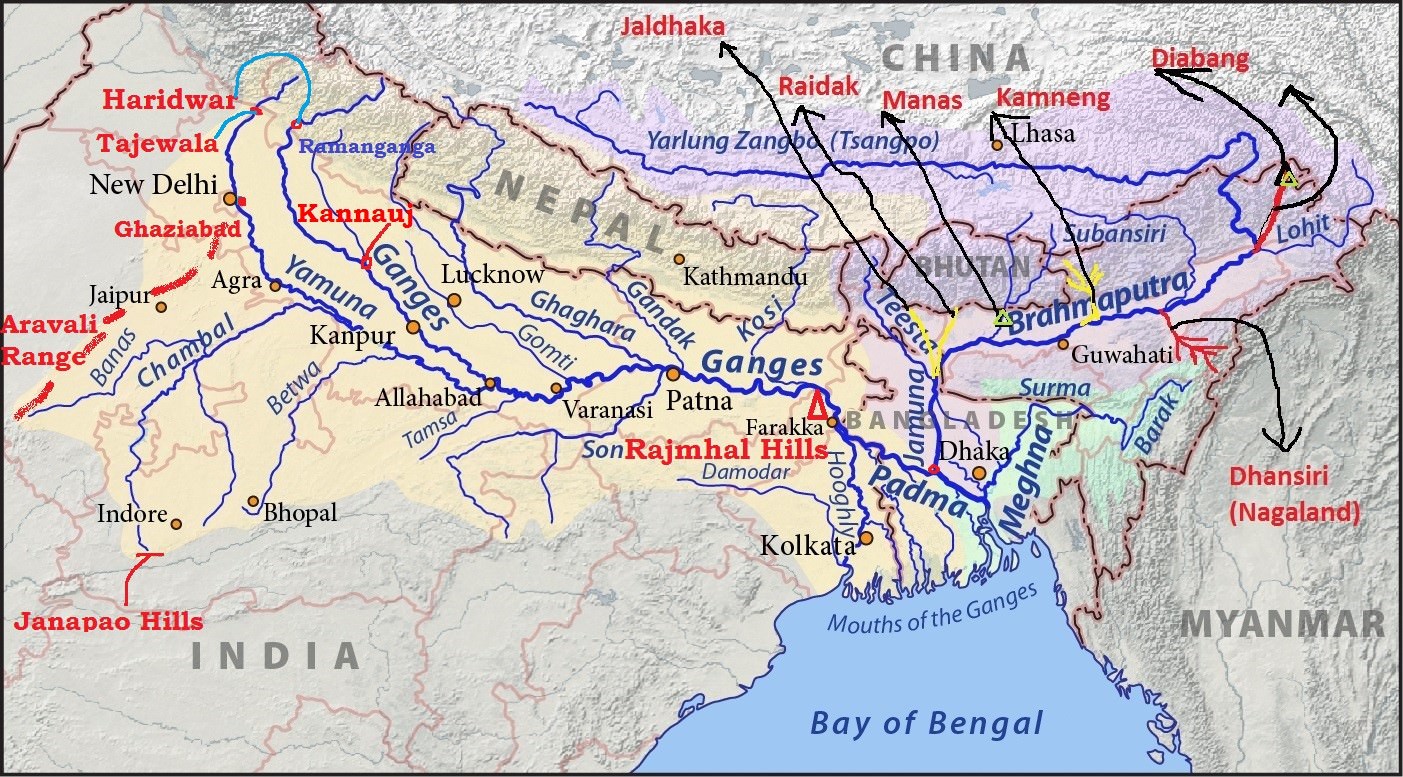
About Chambal River
- The Chambal River is located in northern India and flows through three Indian states: Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh. The Chambal also forms part of the Rajasthan-Madhya Pradesh boundary.
- The perennial Chambal originates at Janapav, south of Mhow town, near Manpur, Indore, on the south slope of the Vindhya Range in Madhya Pradesh.
- About 885 km (550 miles) long, after rising in the old Vindhya Range and flows in northeastern direction. There, it becomes the second biggest tributary of the Yamuna River, which is the largest tributary of the Ganges.
- The Chambal and its tributaries drain the Malwa region of northwestern Madhya Pradesh, while its tributary, the Banas, which rises in the Aravalli Range, drains southeastern Rajasthan. It ends a confluence of five rivers, including the Chambal, Kwari, Yamuna, Sind, Pahuj, at Pachnada near Bhareh in Uttar Pradesh state, at the border of Bhind and Etawah districts.
- The main tributaries of Chambal include the Banas and Mej rivers on the left and the Parbati, Kali Sindh and Shipra rivers on the right.
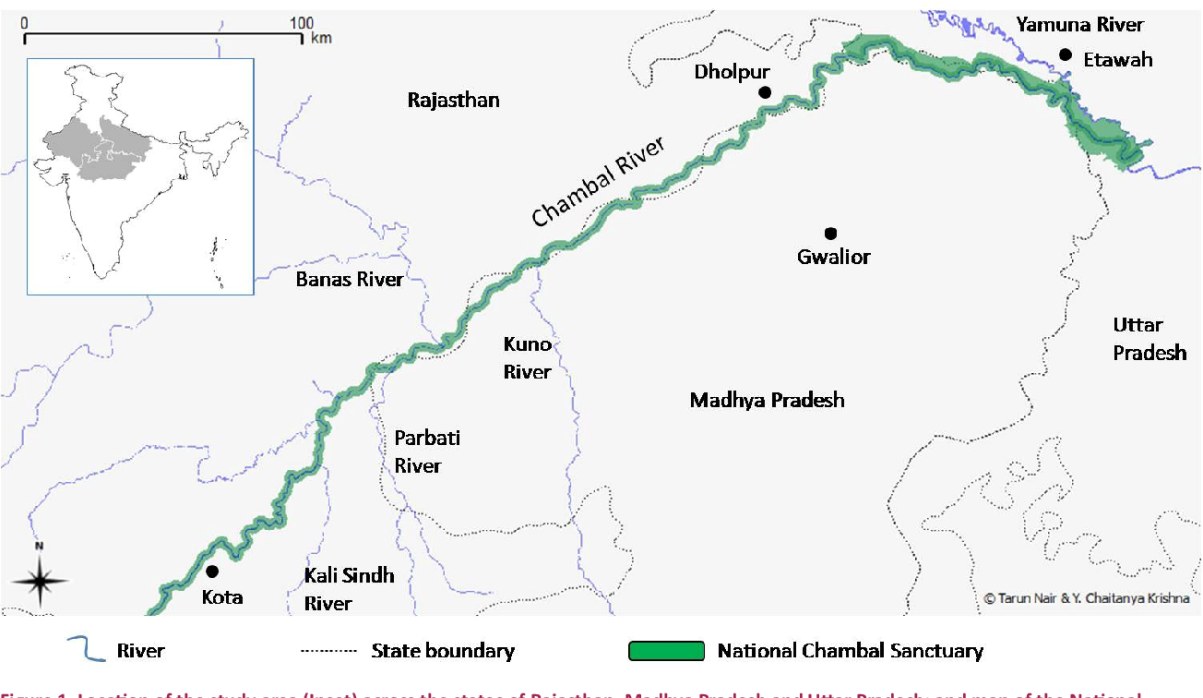
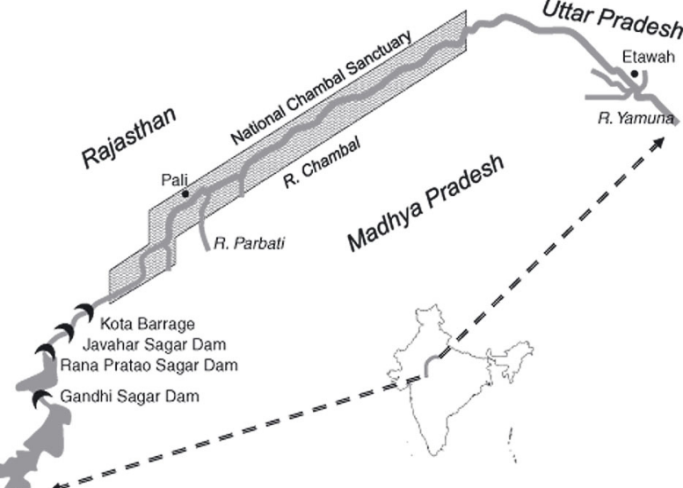
Economic importance
- From an economical point of view, the Chambal River is very important to India as it houses four dams. The oldest of these, the Gandhi Sagar is located at the entrance of the Kanjarda Plateau. This dam has five generators, each of them producing 23 MW of energy.
- Another dam, near Kota, that is Kota Barrage was started in 1952 as part of India’s first 5-year plan.
- The third dam, the Jawahar Sagar dam was the third to be built on Chambal, and the last dam is the Rana Pratap Sagar Dam.
- Keoladeo National Park is supplied with water from Chambal river irrigation project.
Chambal River as a Tourist Attraction
- The Chambal River was relatively pollution free, especially when compared to other Indian rivers.
- In 1979 the National Chambal Sanctuary was set up. The sanctuary is 425 km long, and 2-6 km wide. It is a place where eco-tourism is widely practiced, and the site is excellent for bird watching or crocodile watching.
- Chambal hosts a diverse riverine faunal assemblage including 2 species of crocodilians – the mugger and gharial, 8 species of freshwater turtles, smooth-coated otters, gangetic river dolphins, skimmers, black-bellied terns, sarus cranes and black-necked storks, amongst others.
- However, in recent years the human pollution has made its way into the river, threatening the eco system that thrived with little human interaction. Unfortunately, factory and farming runoff as well as garbage are starting to affect the region.
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1833725
1.png)














