Description
Copyright infringement not intended
Source: High North News
Context
Russia launched its Bastion coastal defense missile launchers into the Barents Sea, marking the start of the navy-wide exercise "July Storm."
About the Barents Sea
- The Barents Sea borders the Norwegian and Greenland Seas to the west, the Arctic Sea to the north, and the Kara Sea to the east.
- The Barents Sea is divided between Russia and Norway under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
- Vikings and medieval Russians called the sea the Murmean Sea.
Copyright infringement not intended
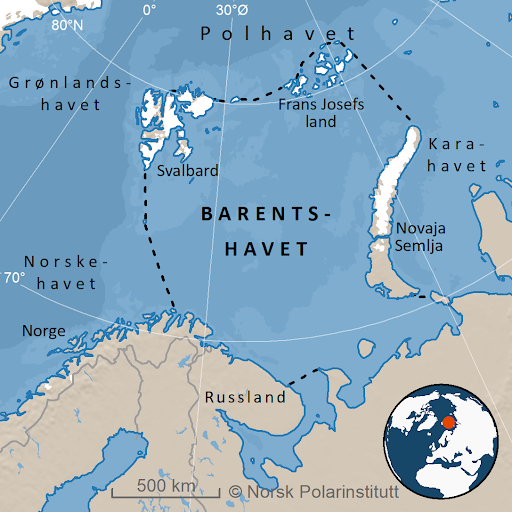
Source: Norsk Polarinstitut
Boundaries of Barents Sea
- It is surrounded by the Svalbard archipelago in the northwest, the Franz Josef Land islands in the northeast, the Novaya Zemlya archipelago in the east, the Norwegian Sea and the Greenland Sea in the west, and the Kola Peninsula in the south.
- It is divided from the Kara Sea by the Kara Strait and the Novaya Zemlya archipelago.
- The White Sea and the Pechora Sea are both sections of the Barents Sea.
- The White Sea is the southern arm of the Barents Sea, separating the Kola Peninsula from Russia's mainland.
- The Pechora Sea is located in the southeast part of the Barents Sea.
Ecological Significance
- High Biological Productivity
- The North Atlantic Drift warms the Barents Sea, leading to higher biological productivity than other oceans at similar latitudes.
- Early Spring Phytoplankton Bloom occurs near the ice edge as freshwater from melting ice forms a stable upper layer, aiding photosynthesis.
- Food Chain Dynamics
- Phytoplankton supports zooplankton species like Calanus finmarchicus, Calanus glacialis, Calanus hyperboreus, Oithona spp., and krill.
- Zooplankton feeders include young cod, capelin, polar cod, whales, and little auk (a seabird).
- Capelin is a keystone species, serving as primary prey for:
- North-east Arctic cod
- Harp seals
- Seabirds like Common Guillemot and Brünnich's Guillemot
- Economic Significance
- The Barents Sea fisheries, especially cod fisheries, are crucial for Norway and Russia.
- Marine Mammal Impact on Fisheries
- Older theories suggested whales caused fish stock depletion.
- Recent studies show marine mammals have minimal impact on fisheries.
- Fisheries pressure and climate change are the primary drivers of fish population trends.
Source: Eurasiantimes.com
Practice Question:
Q. The Barents Sea, often seen in climate and geopolitics discussions, is located:
A) Between Greenland and Iceland
B) Between Norway and Russia
C) North of Alaska, between the US and Russia
D) Between Canada and Greenland
Answer:
B) Between Norway and Russia
|










