




Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Details
Significance
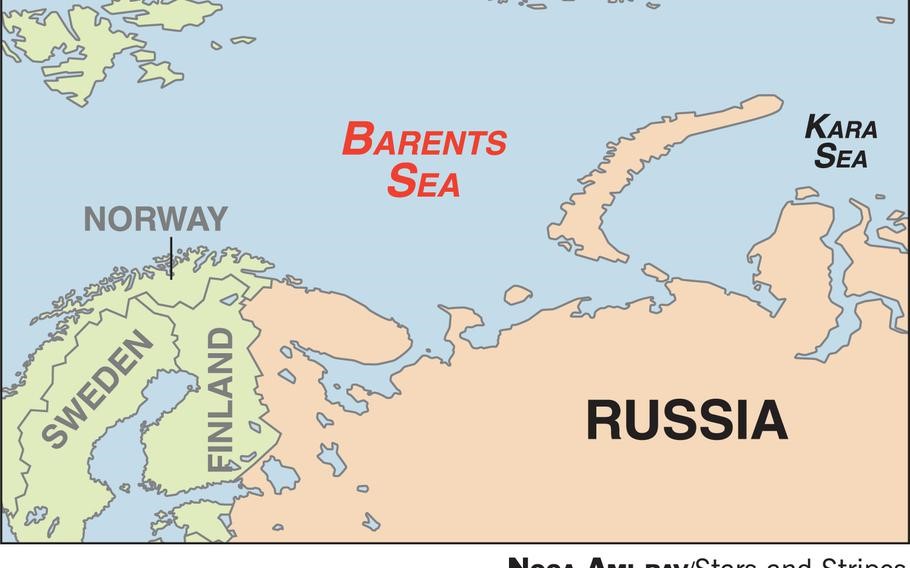
Barents Sea
About and Location
Division
Borders
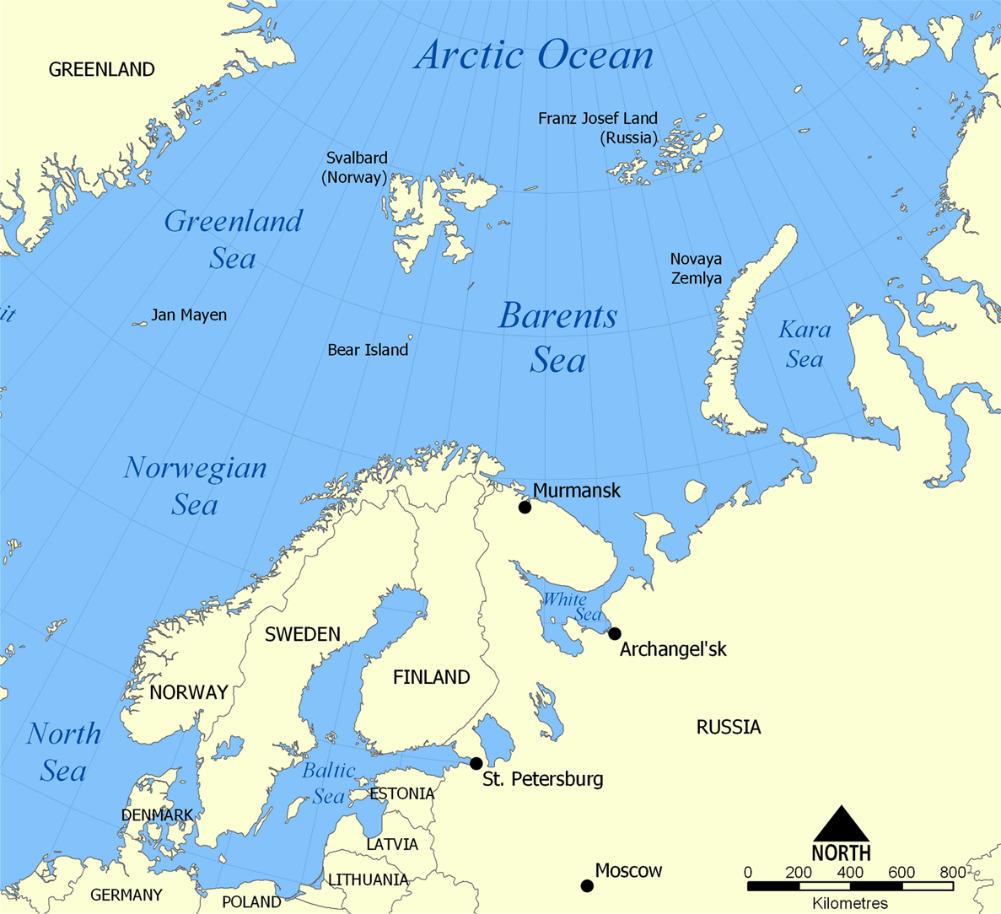
Separation from Kara Sea
Port
Ecology
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Match the following: 1. Barents Sea a. Port Said 2. North Sea b. Rotterdam Port. 3. Mediterranean Sea Coast c. Port of Busan 4. Nakdong River d. Port of Murmansk A. 1-d, 2-b, 3-a, 4-c B. 1-c, 2-a, 3-d, 4-b C. 1-c, 2-d, 3-a, 4-b D. 1-c, 2-a, 3-b, 4-d Answer: A |





© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved