Description

Source:
DownToEarth
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
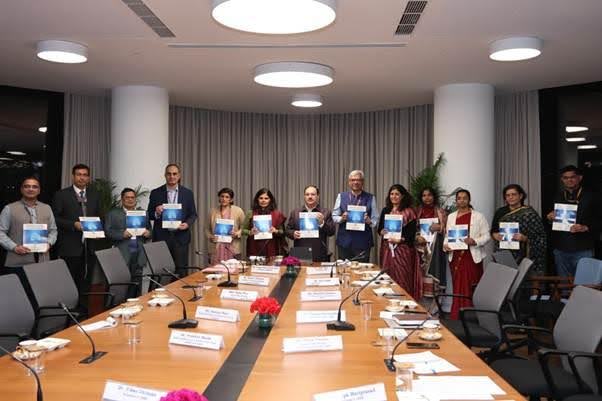
- On June 3, 2024, the 77th World Health Assembly made historic strides by adopting significant amendments to the International Health Regulations (IHR).
- These amendments aim to enhance global preparedness and response to future pandemics, emphasizing improved access to medical products and financing.
Details
Key Amendments and Decisions
- Definition of Pandemic Emergency: The IHR now includes a precise definition of a “pandemic emergency,” facilitating more effective international collaboration in responding to events that are nearing or have already become pandemics.
- Improved Access and Financing: Member countries pledged to ensure better access to medical products and financing, reinforcing health systems to protect against future outbreaks.
- Strengthening National Capacities: Enhancements are aimed at improving countries' abilities to detect and respond to outbreaks. This includes better disease surveillance, information sharing, and national response plans.
Significance of the Amendments
- Global Coordination: The amendments are designed to improve global coordination on disease surveillance, information sharing, and response efforts.
- Equity and Collective Preparedness: The changes are underpinned by a commitment to equity and the recognition that health threats transcend national borders, making preparedness a collective responsibility.
- States Parties Committee: This new committee will facilitate the effective implementation of the amended regulations, ensuring better coordination both within and between countries.
- National IHR Authorities: These authorities are created to enhance the coordination of regulation implementation, ensuring that all nations have the resources and plans needed to effectively respond to health threats

Future Directions
- Pandemic Agreement: Member countries will continue working on the proposed Pandemic Agreement, focusing on improving international coordination, collaboration, and equity in pandemic preparedness and response.
- Intergovernmental Negotiating Body: Established in December 2021, its mandate has been extended to finalize the Pandemic Agreement by the World Health Assembly in 2025, or earlier if possible, at a special session in 2024.
|
International Health Regulations (IHR)
- The International Health Regulations (IHR) are a legally binding framework established by the World Health Organization (WHO) to ensure global public health security.
- Objective: To prevent, protect against, control, and provide a public health response to the international spread of disease.
Historical Background
- Origins: The first IHR were adopted in 1969, focusing on six diseases: cholera, plague, yellow fever, smallpox, relapsing fever, and typhus.
- Revisions: The IHR were revised in 2005 to address a broader range of public health threats, including emerging diseases and other health events of international concern.
Key Components of IHR (2005)
- Core Capacities:
- Surveillance: Countries must develop and maintain capabilities to detect, assess, report, and respond to public health events.
- Response: Establishment of national public health emergency response plans and coordination mechanisms.
- Notification and Reporting:
- Timely Reporting: Countries must report public health emergencies of international concern (PHEIC) to the WHO within 24 hours.
- Information Sharing: Continuous exchange of information with the WHO regarding public health risks and response measures.
- Public Health Measures:
- Containment: Implementation of measures to prevent the spread of disease at points of entry, including airports, ports, and ground crossings.
- Quarantine and Isolation: Enforcing isolation and quarantine when necessary to contain infectious diseases.
- International Collaboration:
- Coordination: Working with the WHO and other countries to manage health risks and share best practices.
- Technical Support: Receiving assistance from the WHO for capacity building and emergency response.
|
Must read articles:
WorldHealthAssembly
Sources:
DownToEarth
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. The 77th World Health Assembly’s adoption of critical IHR amendments marks a significant step towards enhanced global health security. Discuss. (250 Words)
|