



A clinical trial found that zimislecel therapy, infused with stem cell-derived islet cells, improved blood sugar control in type 1 diabetes patients. This therapy restores the body's natural ability to produce insulin, a hormone crucial for blood sugar regulation. However, access to advanced diabetes care remains uneven, highlighting the need for improved healthcare.
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: THE HINDU
A clinical trial in The New England Journal of Medicine found that zimislecel therapy, infused with stem cell-derived islet cells, improved blood sugar control in type 1 diabetes patients.
Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) is an autoimmune disease; the body's own immune system wrongly attacks and destroys the specific cells in pancreas that produce insulin.
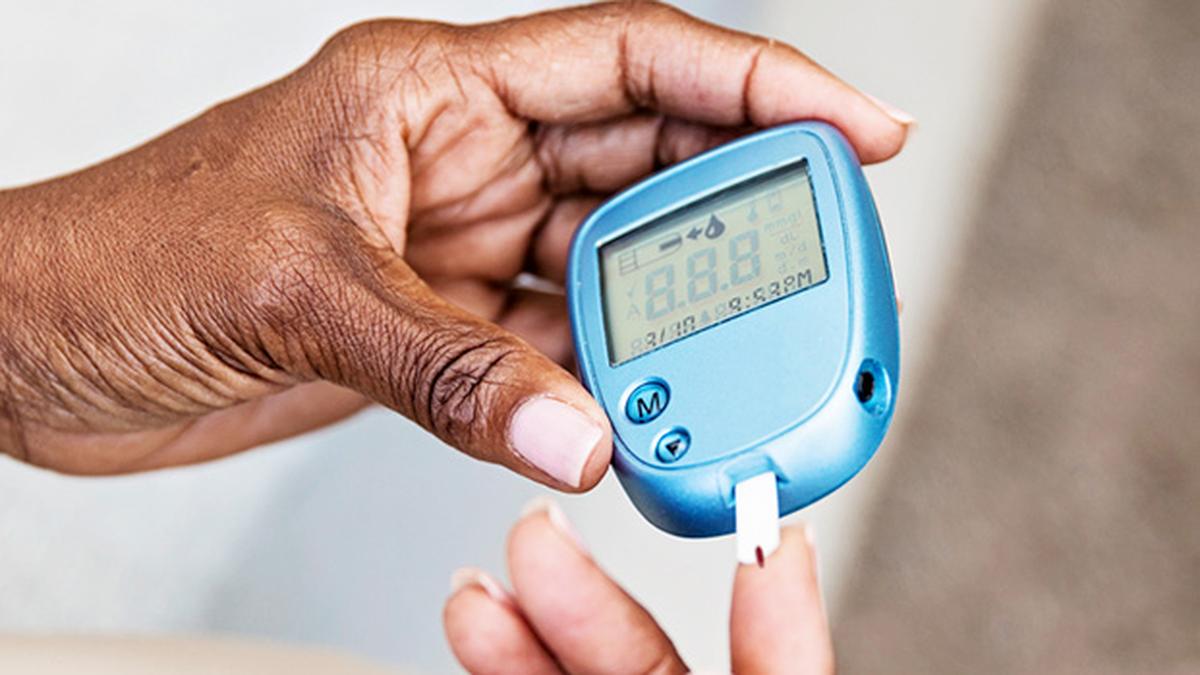
Traditional management of Type 1 Diabetes depends on insulin therapy, which involves regular insulin injections or using insulin pumps to deliver insulin.
It uses lab-grown cells to treat Type 1 Diabetes, to restore the body's natural ability to produce insulin.
How it Works:
Stem Cell Cultivation => Scientists grow insulin-producing cells (islet cells) in the lab using special pluripotent stem cells. These are "master cells" that can become many different cell types.
Infusion => The lab-grown, matured islet cells are then put into a patient's liver through a specific vein (hepatic portal vein).
Insulin Production => These new cells settle in the liver, survive, and start making insulin naturally, just like a healthy pancreas.
There are an estimated 9.5 million people living with T1D globally.
In India, about 1.3 lakh young people are registered in the national Young Diabetes Registry.
Access to advanced diabetes care, such as continuous glucose monitors and insulin pumps, is very uneven across India. For most people, these technologies remain too expensive or unavailable.
National Programme for Prevention & Control of Non-Communicable Diseases (NP-NCD) focuses on early diagnosis, proper management, and referral for NCDs like diabetes.
Jan Aushadhi Scheme makes quality medicines, including insulin, more affordable and accessible to the public.
Must Read Articles:
Growing Diabetes Epidemic in India
Source: THE HINDU
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. With reference to Zimislecel therapy, consider the following statements: 1. It involves infusing lab-grown stem cell-derived islet cells into the liver of Type 1 Diabetes patients. 2. It aims to restore the body's natural insulin production. 3. The therapy eliminates the need for any immunosuppressive drugs. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? A) 1 only B) 2 only C) 1 and 2 only D) 1, 2 and 3 Answer: C Explanation: Statement 1 is correct: Zimislecel (VX-880) uses lab-grown, stem cell-derived, fully differentiated, insulin-producing islet cells. Doctors infuse these cells into the hepatic portal vein, which leads to the liver of Type 1 Diabetes patients. Statement 2 is correct: The therapy aims to restore pancreatic islet cell function, including glucose-responsive insulin production, thereby restoring the body's ability to regulate glucose levels. Statement 3 is incorrect: Zimislecel requires chronic immunosuppressive therapy to protect the infused islet cells from immune rejection by the patient's body. Vertex Pharmaceuticals had a different program (VX-264) that aimed to avoid immunosuppression through encapsulation, but they discontinued it. |
T1D is an autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing islet cells in the pancreas.
Zimislecel involves growing insulin-producing islet cells from pluripotent stem cells in the lab and then infusing them into the patient's liver.
These are special cells that have the ability to develop into many different cell types in the body, making them valuable for regenerative medicine.







© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved