



NASA's TRACERS mission aims to study Sun-Earth interactions, improve space weather prediction, and protect global infrastructure. The mission focuses on examining key phenomena like magnetic reconnection and cusp electrodynamics. Space weather affects life on Earth through power grids, satellite operations, communication, and human health, as strong solar storms can damage satellites and disrupt navigation.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: SCIENCE
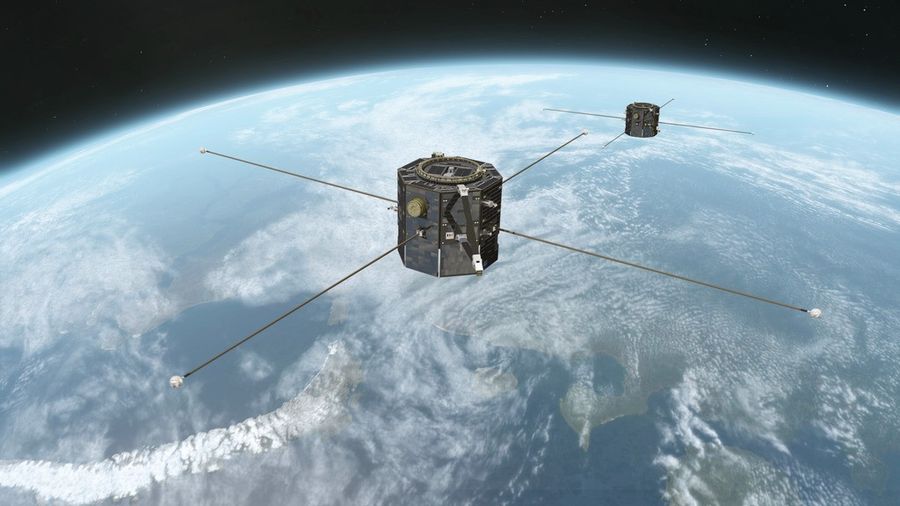
NASA’s twin TRACERS satellite was launched to study Sun-Earth interactions, to improve space weather prediction, and protect critical global infrastructure.
Space weather refers to the changing conditions in space that can affect Earth and technology.
The Sun provides light and heat, making life on Earth possible, however, it also sends powerful energy and particles. These include: Solar Flares, Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs), Solar Wind.
Earth has a built-in protective shield “magnetosphere”, which acts like a giant deflector, pushing away most of the harmful charged particles from the Sun, keeping earth safe. 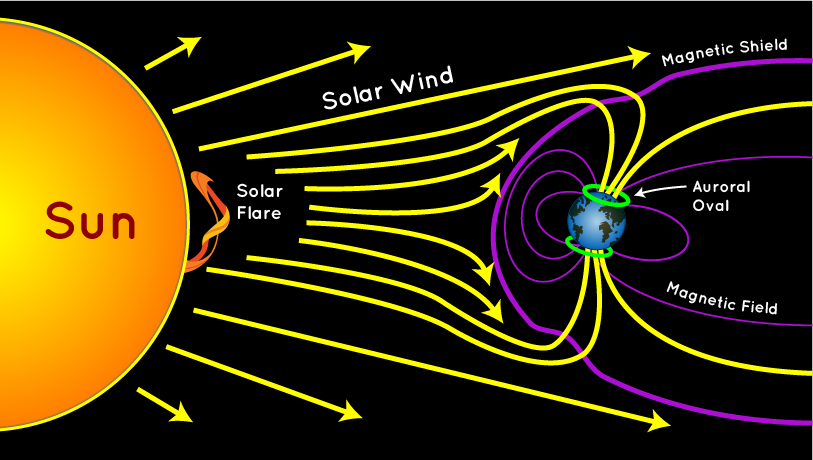
NASA's TRACERS (Two-Rocket for Aurora Coronal Mass Ejection Study) mission involves a pair of small satellites that fly through a specific region of space around Earth.
To study how the Sun's energy and particles interact with Earth's magnetic field.
To help scientists understand how energy from the Sun gets into Earth's magnetosphere.
Magnetic Reconnection => Process in space where magnetic field lines break and re-form, releasing huge amounts of energy.
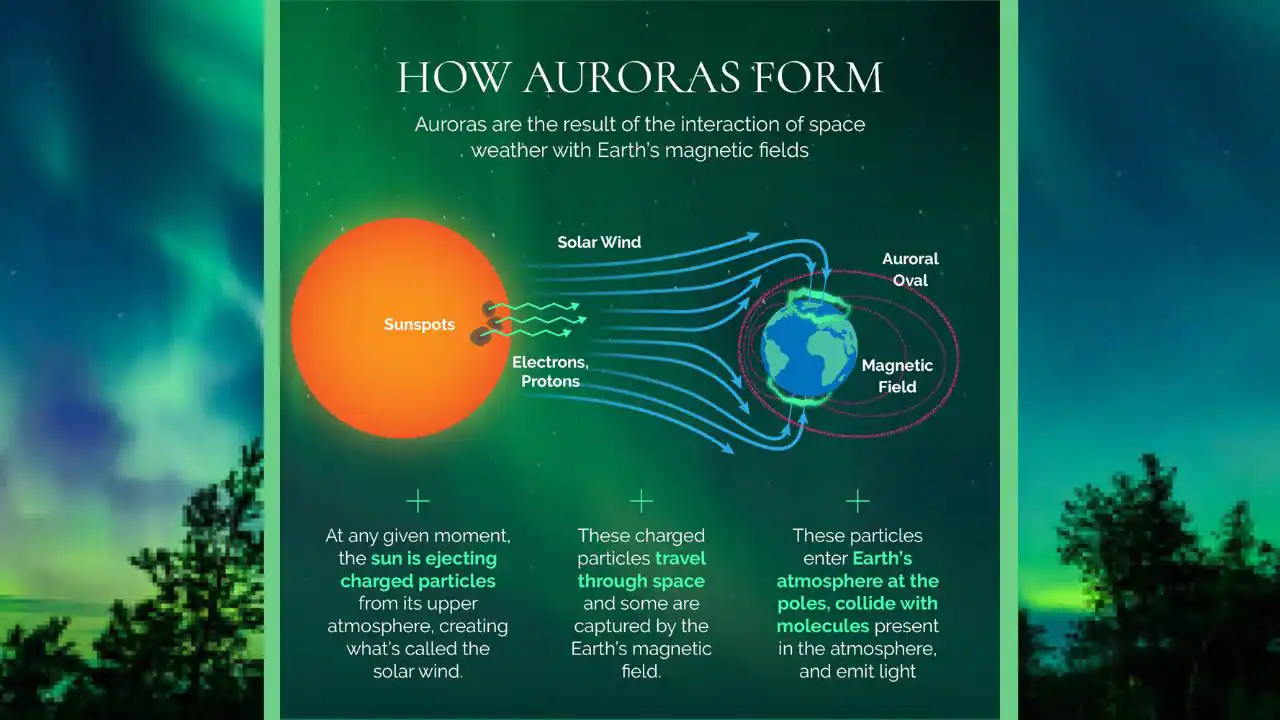
Cusp Electrodynamics => The "cusps" are like funnels at Earth's North and South magnetic poles where some solar wind particles can directly enter our atmosphere, and contribute to the aurora displays (the Northern and Southern Lights) seen in polar regions.
 How Space Weather Affects Life on Earth
How Space Weather Affects Life on EarthPower Grids => Strong solar storms can create powerful electrical currents in the ground, which then flow into power lines. These geomagnetically induced currents (GICs) can overload transformers and even cause widespread power outages.
Satellite Operations => Strong solar radiation and charged particles can damage satellite electronics, scramble signals, or even knock them out of orbit.
Communication & Navigation => Radio blackouts that disrupt airline communications and shortwave radio. It can also mess with GPS signals, making navigation less accurate.
Human Health and Safety => Astronauts in space and passengers on long-haul flights over the poles are exposed to higher levels of radiation during solar storms.
Must Read Articles:
'Super-sympathetic' solar flare event
Source: SCIENCE
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Consider the following statements regarding NASA's TRACERS mission: 1. It is the first mission to use a single satellite to study magnetic reconnection in the polar cusps. 2. Its objective is to understand how the Earth's magnetic shield protects against space weather. 3. Data from TRACERS will improve forecasts for phenomena like auroras and satellite disruptions. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? A) 1 only B) 2 and 3 only C) 1 and 3 only D) 1, 2 and 3 Answer: B Explanation: Statement 1 is incorrect: TRACERS is the first mission to explore the process in the cusp with two spacecraft (twin satellites), providing observations of how processes change over both space and time. Statement 2 is correct: The mission objective is to study how Earth's magnetic shield protects the planet from space weather effects by understanding magnetic reconnection. Statement 3 is correct: Improved understanding of magnetic reconnection directly leads to better space weather forecasting, impacting phenomena like auroras, satellite operations, communications, and power grids. |
The main goal is to understand how Earth's magnetic shield protects our planet from space weather by studying magnetic reconnection in the polar cusps.
Magnetic reconnection is an explosive process where magnetic field lines break and re-form, releasing huge amounts of energy and accelerating charged particles, often allowing solar energy into Earth's atmosphere.
Polar cusps are funnel-shaped regions near Earth's magnetic poles where the planet's magnetic field lines dip down, creating pathways for solar wind particles to enter the upper atmosphere.







© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved