



The Tex-RAMPS Scheme is a new initiative with a ₹305 crore budget (FY 2025-2031) to boost textile sector through research, innovation, data, and supporting startups, aiming to enhance global competitiveness in sustainability and technology, addressing gaps in the ecosystem for future growth

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: newsonair
The Ministry of Textiles has signed Memorandum of Understanding (MoUs) with 15 States as part of the ‘Textiles focused Research, Assessment, Monitoring, Planning And Start-Up (Tex-RAMPS)’ scheme.
GDP Contribution
The textile and apparel industry contributes 2.3% to GDP, 13% to industrial production, and 12% to exports. (Source: PIB)
Employment
It is the second-largest employer after agriculture, providing direct employment to over 45 million people. (Source: PIB)
Exports
India exported textile items worth $34.4 billion in 2023-24, with apparel constituting 42% of the export basket, followed by raw materials/semi-finished materials at 34% and finished non-apparel goods at 30%. (Source: PIB).
The Textiles Focused Research, Assessment, Monitoring, Planning, and Start-up (Tex-RAMPS) Scheme, is a highly specialized Central Sector Scheme by the Ministry of Textiles.
It is designed to "future-proof" the textile ecosystem by focusing on research, data systems, and innovation.
It aims to address critical gaps in the textile sector's innovation and data infrastructure through five core pillars:
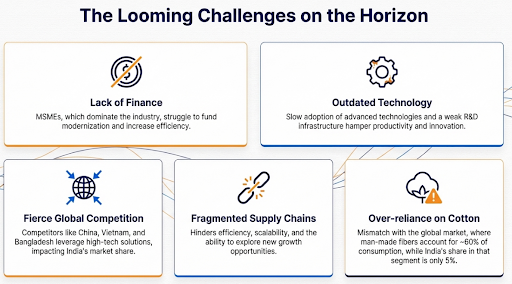
Structural & Scale Issues
The industry is highly fragmented, dominated by small-scale and unorganized players, which hinders economies of scale and technology adoption.
Global Competition
Intense competition from countries like Bangladesh and Vietnam, which benefit from lower labor costs and preferential trade agreements with key markets like the EU, the USA..
Technology & Value Chain
Over-dependence on cotton requires scaling up production and innovation in Man-Made Fibres (MMF) and Technical Textiles to align with global market trends.
Infrastructure & Logistics
High logistics costs and inadequate infrastructure in key textile clusters reduce competitiveness. Schemes like PM MITRA are designed to address this gap.
Sustainability & Compliance
Meeting stringent international environmental and social compliance standards (e.g., related to water usage, chemical discharge) is a major challenge, especially for MSMEs.
Enhancing Global Integration
Strategically negotiating and leveraging Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with key markets like the EU and USA to gain a competitive edge over rivals.
Promoting Public-Private Partnerships (PPP)
Encouraging PPP models for developing infrastructure in PM MITRA parks to ensure efficiency, timely execution, and optimal resource utilization.
Strengthening the R&D Ecosystem
Ensuring effective implementation of the Tex-RAMPS scheme to bridge the gap between research institutions and industry, leading to commercially viable innovations.
Focus on Sustainability
Promoting a circular economy by incentivizing the use of recycled fibers, sustainable manufacturing processes, and green technologies.
Inclusive Growth
Ensuring that the benefits of government schemes reach the highly fragmented informal sector and micro-enterprises through targeted outreach and simplified compliance norms.
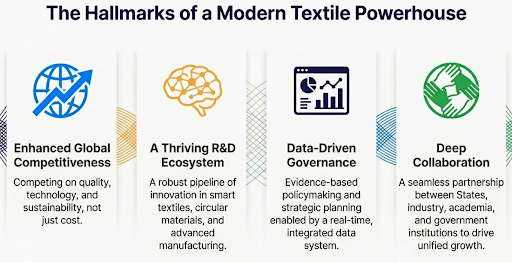
India aims to modernize the textile sector into a globally competitive industry through a holistic policy framework combining infrastructure (PM MITRA), production incentives (PLI), skilling (Samarth), and innovation (Tex-RAMPS).
Source: THEHINDU
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. How does the Tex-RAMPS scheme integrate the principles of 'Cooperative Federalism' to address regional textile clusters? (150 words) |
The full form is Textiles Focused Research, Assessment, Monitoring, Planning, and Start-up (Tex-RAMPS) Scheme.
The primary goal is to "future-proof" the Indian textile ecosystem by addressing gaps in data, research, and planning. It aims to build a robust data-driven policymaking framework to enhance the competitiveness of textile MSMEs.
The scheme involves signing MoUs with state governments to strengthen data systems and planning from the district level upwards. It provides financial assistance directly to states and districts to develop and execute their own action plans tailored to local needs, embodying a decentralized approach.





© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved