



In FY25, PSU dividends nearly doubled to ₹74,017 crore, contributing to the government's non-tax revenue. While these funds promote national development and reduce the fiscal deficit, the main obstacle is balancing government revenue needs with PSUs' reinvestment in growth. The delicate balance of fiscal needs and PSU autonomy decides India's economic future.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: THE HINDU
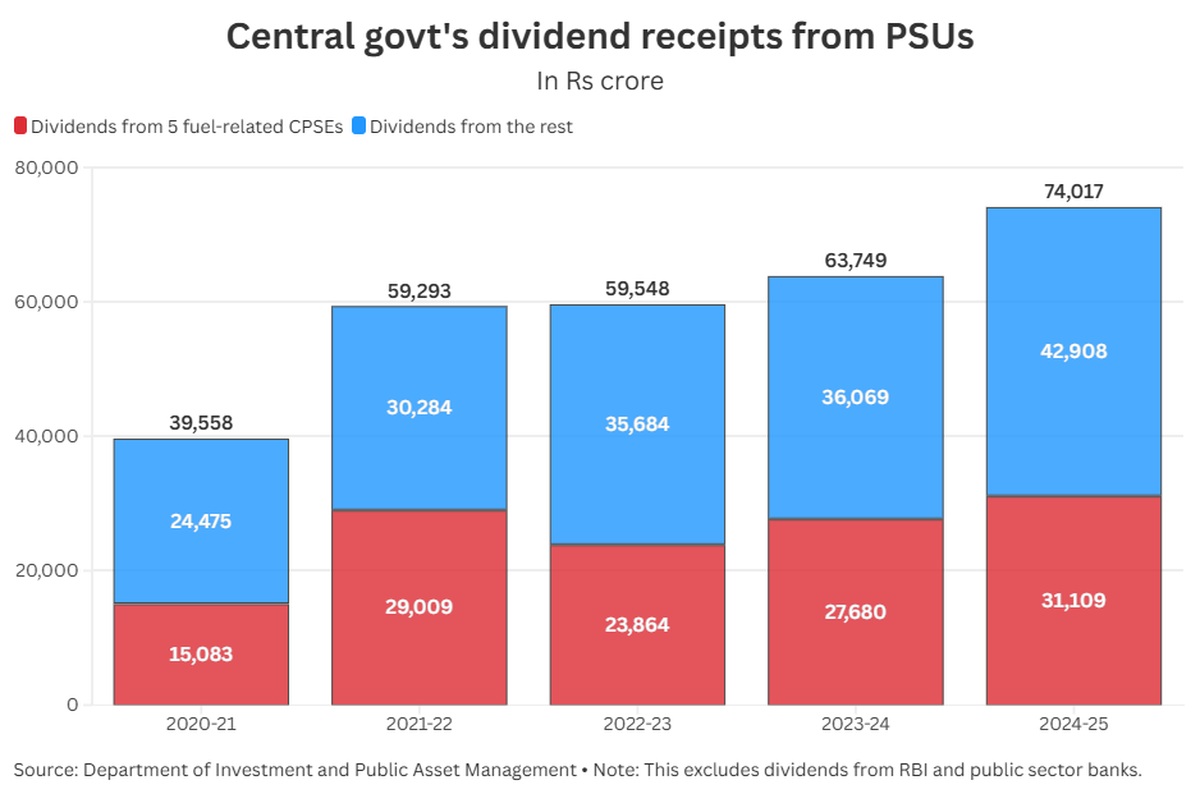
An analysis of company-specific dividend data from the Department of Investment and Public Asset Management (DIPAM) for the last five years reveals that five fuel-related PSUs accounted for 42% of the total dividends collected by the government since fiscal year 2020-21.
These companies perform commercial functions on behalf of the government, operating in vital areas like energy, mining, banking, and heavy industries.
|
Prelims Booster => Article 12 of the Constitution defines "the State" for the purpose of Fundamental Rights in the Constitution. In the Rajasthan Electricity Board vs Mohan Lal case, the Supreme Court broadly interpreted Article 12 to include Public Sector Undertakings. |
The government classifies the PSUs into various categories such as Maharatna, Navratna, and Miniratna.
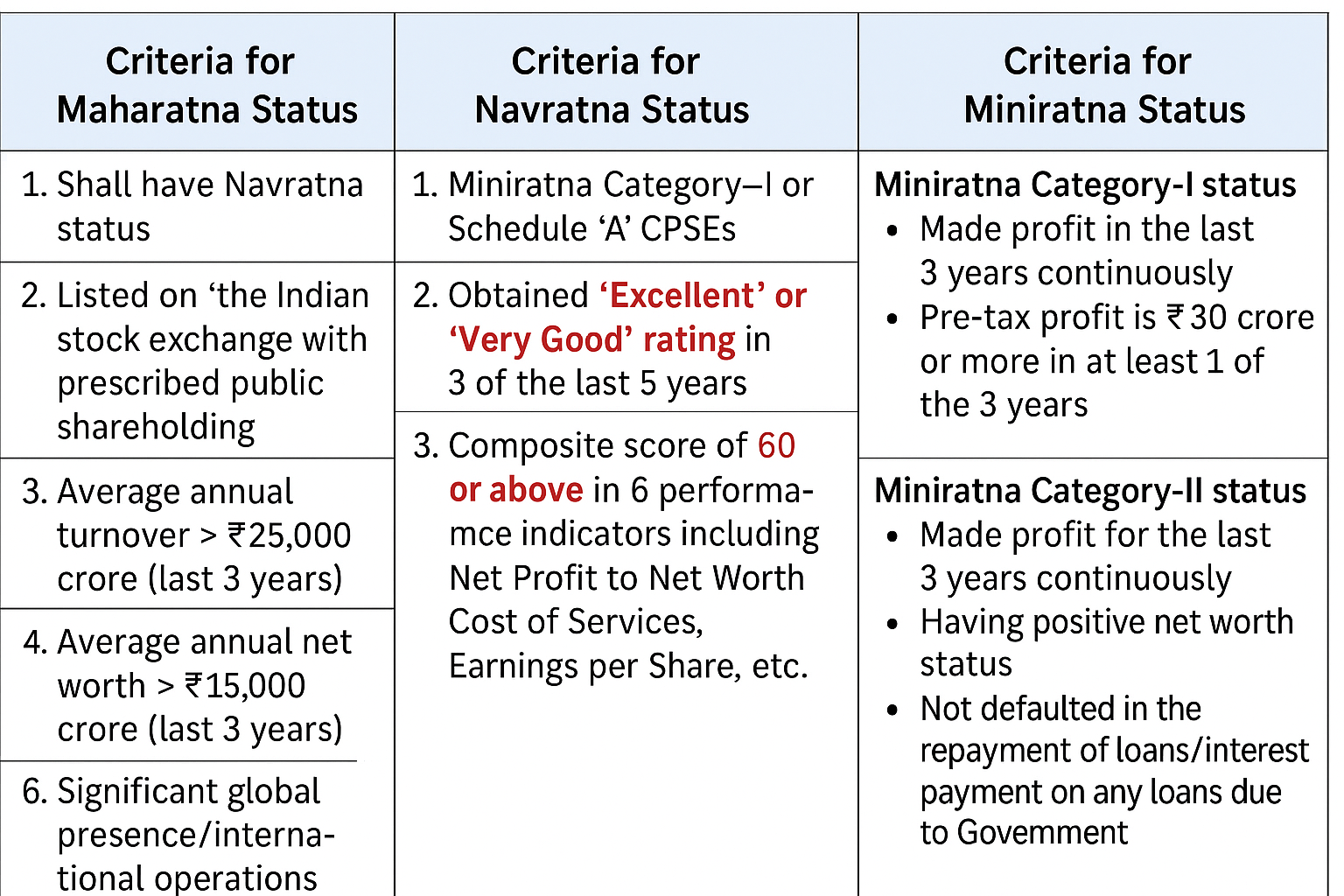
|
How does the Parliament oversee PSUs? The Parliament exercises oversight over PSUs through the Committee on Public Undertakings. This committee is responsible for:
|
When the PSUs make profit, they share a portion of that profit with their largest shareholder: the Indian government. This share of the profit is known as a "PSU dividend."
In the financial year 2024-25, the government received Rs 74,017 Crore as dividends from non-banking PSUs.
 How the government's rules for PSU dividends have changed over time?
How the government's rules for PSU dividends have changed over time?
The 2024 guidelines mandated Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs) to pay a minimum annual dividend of 30% of their Profit After Tax (PAT) or 4% of their Net Worth, whichever amount was higher.
The energy sector contributes highest to the government's dividend receipts. The five companies collectively contributed over 42% of the total dividends the Centre received from non-banking PSUs between the financial years 2020-21 and 2024-25.
The government requires funds for expenditures and development initiatives, encourages or mandates high dividend payouts from PSUs. However, PSUs require capital for modernization, technological upgrades, and expansion to remain competitive in their respective markets.
Optimal Balance => Finding a smart balance between how much profit PSUs pay out as dividends and how much they reinvest in their own future development (capital expenditure).
Enhanced Autonomy and Efficiency => Giving PSUs more freedom in their operations, pushing them to become more efficient, so they can compete effectively and generate higher profits independently.
Strengthened Corporate Governance => Improving and uniformly applying strong corporate governance standards across all PSUs, to reduce political interference and enhance accountability.
Transparent and Predictable Policy Framework => For dividends and investments, to help PSUs plan better and attract more investors.
Must Read Articles:
Role of Public Sector Undertakings
SEBI's Startup and PSU Reforms
Source: THE HINDU
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. The recent increase in dividend payouts by Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs) has boosted government revenue. However, critics argue this may hinder the long-term growth and operational efficiency of these enterprises. Suggest measures for achieving an optimal balance. Answer in 250 words |
PSU dividends serve as a non-tax revenue source, helping fund government expenses and manage the fiscal deficit.
The Department of Investment and Public Asset Management (DIPAM), under the Ministry of Finance sets these guidelines.
While high profits lead to high dividends, consistently high payouts without adequate reinvestment can hinder a PSU's long-term growth and modernization.






© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved