Description

Copyright infringement is not intended
Context: Russia has blocked an agreement at the UN that was aimed at bolstering the nuclear non-proliferation treaty because Moscow objected to a clause about control over the Zaporizhzhia power plant in Ukraine.

Details:
- The failure to agree to a joint statement after four weeks of debate and negotiation among 151 countries at the UN in New York is the latest blow to hopes of maintaining an arms control regime and keeping a lid on a rekindled arms race.
- The closing session was put off for more than four hours over Russian refusal to agree to a lengthy statement of support for the NPT which included a reference to the Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant, which is occupied by Russian forces close to the frontline in Ukraine’s south-east.
- The Russian delegation was the only one to speak against the agreed text, but blamed the breakdown of the conference on Ukraine and its “protectors”, calling the negotiations a “one-sided game”. After delivering its statement, the Russian delegation walked out of the UN chamber.
- The NPT was a deal struck in 1968 in which nuclear weapons states pledged to disarm while states without nuclear weapons promised not to acquire them.
- At the time there were five acknowledged nuclear powers, though Israel had secretly developed a weapon of its own by then. There are now nine states which possess nuclear warheads. Before the NPT came into force, some had predicted there would be dozens countries with their own arsenals.
- It is the second five-yearly review conference that has failed to issue a joint statement recommitting to the goals of the treaty. It has been 12 years since there was even partial agreement.
Copyright infringement is not intended
About Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT):
- It is an international treaty.
- Objectives:
- To prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and weapons technology
- To promote cooperation in the peaceful uses of nuclear energy, and
- To achieve nuclear disarmament and general and complete disarmament.
- Entered in forcein 1970.
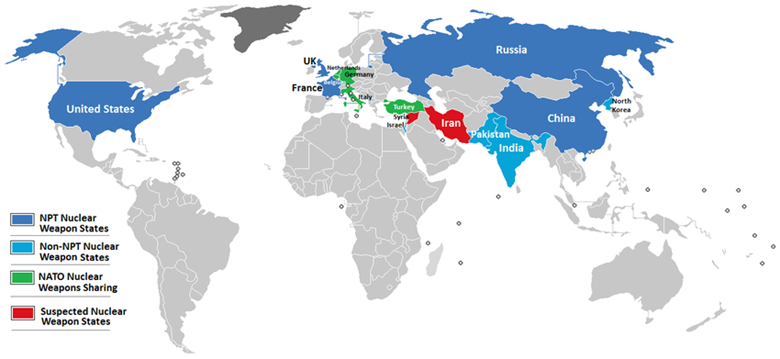
- Parties to the treaty:191 states have become parties to the treaty, though North Korea, which acceded in 1985 but never came into compliance, announced its withdrawal from the NPT in 2003.
- Non- signatory states: Four UN member states have never accepted the NPT, three of which possess or are thought to possess nuclear weapons: India, Israel, and Pakistan. In addition, South Sudan, founded in 2011, has not joined.
- Defines nuclear-weapon states:States that have built and tested a nuclear explosive device before 1 January 1967; these are the United States, Russia, the United Kingdom, France, and China.
- The treaty is reviewed every five yearsin meetings called Review Conferences.
- India did not sign NPT because it found NPT a flawed treaty with no basis of recognizing stateswhich should have the nuclear energy.
https://www.theguardian.com/world/2022/aug/27/russia-blocks-un-nuclear-treaty-agreement-over-zaporizhzhia-clause










