Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Deposit flow from NRIs in the five-month period of April-August 2022 came down to $ 1.435 billion from $ 2.44 billion in August 2021.
Details
- The biggest decline was in the NRE scheme which came down to $ 906 million from $ 2.464 billion a year ago, according to data from the Reserve Bank of India.
- The fall is due to the rise in interest rates globally, especially the US, and yields.
- NRIs who deposited money on December 31, 2021 when the rupee was at 74.29 against the dollar are now sitting on a loss as Rupee has fallen 10.87 per cent since then. When conversion from the rupee to dollars happens on repatriation, more rupees are required due to the currency depreciation. On top of this, with interest rates rising in the US and other remittance regions, there’s hardly any incentive for NRIs to bring funds to India.
Must Read: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/strengthening-dollar-weakening-rupee
NRI Deposits
- An NRI Deposit allows NRIs to invest their money in India.
- Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) live overseas and most of their earnings is in international currencies such as the US dollar, Euro, and so on. As a result, NRIs might need an account that can hold and convert their securities and money in Indian rupees. An NRI account serves this purpose.
NRI Accounts

Types of NRI accounts
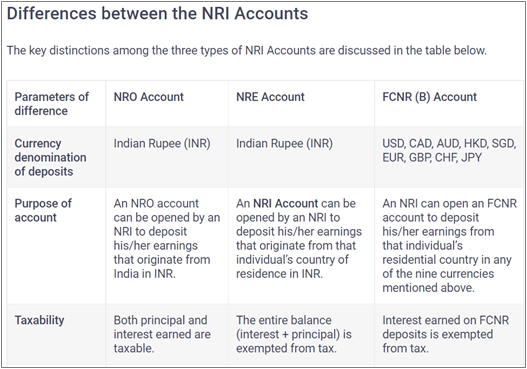
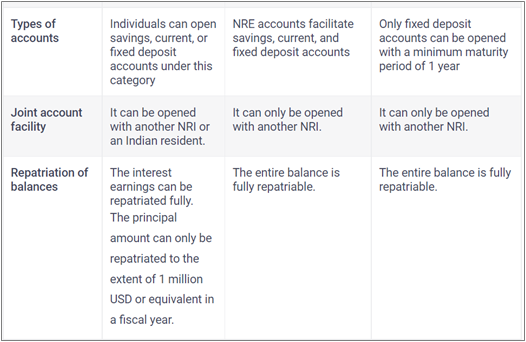
NRIs in India can open three types of accounts: NRE (Non-Resident External Account), NRO (Non-Resident Ordinary Account), and FCNR (Foreign Currency Non-Resident) bank accounts.
The key differences between the accounts are:
What is an NRE account?
- The Non-Resident External or NRE Account makes it easier to transfer money generated overseas to India.
- It is a rupee-dominated account that's repatriable, meaning one can send one’s international earnings back to India. The interest one earns on the NRE account is tax free.

What is an NRO account?
- With revenue received within India, a Non-Residential Ordinary or NRO Account can be formed and held in INR values in that deposit account. Rent, dividends, and other sources of income are all possibilities.
- There is no barrier to currency conversion in an NRO account because deposits are done in rupee denominations.

What is an FCNR (B) Account?
The FCNR (Foreign Currency Non-Residential Account) permits Non-Resident Indians or Persons of Indian Origin to make deposits in foreign currency. NRIs or POIs can make these payments in the denomination of currencies of their resident country, and they must be held in any of the foreign currencies prescribed by RBI in that account.
Principal amount and the interest in an FCNR Account are fully repatriable, i.e., transferable. Interest income earned on the money in an FCNR account is non-taxable in India.


Eligibility for opening NRI Account
Following is the eligibility criteria to open an NRI account:
- NRI (Non Resident Indian)
- An Indian citizen residing outside India for any of the following purposes:
- Studies, employment, business or vocation
- Officials deputed abroad by the Government of India or public sector undertakings.
- Individuals posted in the United Nations organization
- Indian nationals who may be Mariners or working in foreign registered airlines or oil rigs
- Person of Indian origin (PIO) or Overseas Citizen of India (OCI)
- An individual with a Foreign passport (other than Bangladeshi and Pakistani) who:
- Has held an Indian passport at any point in time
- Parent or grandparent was a Citizen of India by virtue of the Constitution of India or Indian Citizen Act, 1955.
- Is a spouse of an Indian Citizen or PIO.
Benefits of opening an NRI Account in India
Following are the advantages of NRI accounts:
Investments in India
- NRI accounts facilitate investments in India. NRIs who want to diversify their investment portfolio can do so by investing in India. And NRI accounts help them by purchase and sale of stocks, mutual funds and other assets.
Taxation
- Opening an NRE or an FCNR account allows investors to earn additional income in the form of interest, which is completely tax-free. Hence income from NRE account, NRE fixed deposits and FCNR deposits is exempt from tax. Interest from NRO accounts is taxable. But NRIs can avail of tax benefit under the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) in certain countries.
Repatriation
- Income from Indian investments made through NRE and FCNR accounts is also fully repatriable. Both the principal and interest amount are repatriable without limits in case of NRE and FCNR accounts.
- In the case of NRO accounts, the amount is repatriable with certain limits.
Low minimum balance
- Most banks have reduced the minimum balance requirement for these accounts to as low as INR 10,000. Hence NRIs need not worry about maintaining a high minimum balance in these accounts.
Deposits in more than one currency
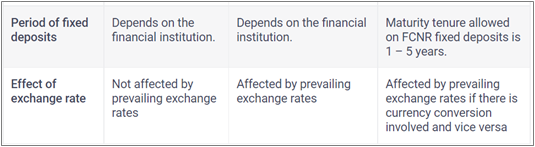
- NRIs can retain their deposits in the currency of their resident country which is allowed by RBI through FCNR deposits. Hence the risk of the exchange rate is minimized with this type of NRI account.
Convenience
- Banks allow NRIs to open an NRI bank account without having to visit the branch physically. NRIs can open an account with any authorized bank online. Moreover, they can operate the account from anywhere in the world with the help of internet banking facilities. They can even transact using international debit cards offered by these banks. FCNR deposits can be withdrawn only upon maturity. However, one can opt for premature withdrawal. Moreover, banks also give loans against fixed deposits or FCNR deposits.
Disadvantages of opening an NRI Account in India
Following are the disadvantages of NRI account in India:
Low liquidity
- Individuals who want to safeguard their deposits against exchange rate fluctuations can do so with an FCNR account. However, the tenure of a fixed deposit account ranges from one to five years.
Foreign exchange rate risk
- Deposits made in foreign currency are subject to conversion into Indian rupees. Therefore, these deposits may fluctuate in value with the change in exchange rates. Hence, there are chances of incurring losses during repatriation.
https://indianexpress.com/article/business/as-global-rates-rise-nri-deposits-decline-6-84-bn-in-april-august-8217023/#:~:text=Deposit%20flow%20from%20NRIs%20in,the%20Reserve%20Bank%20of%20India.


















