Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Context: India and Germany agreed on a vision statement to enhance cooperation on innovation and technology during Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s meeting with visiting German Chancellor Olaf Scholz.
Details:heritage
Highlights:
- The statement said the two countries share a long history of cooperation in science and technology, research and innovation, institutionalised under the framework of the Inter-Governmental Agreement on ‘Cooperation in Scientific Research and Technological Development’, signed in May 1974.
- The leaders discussed progress on Green and Sustainable Development Partnership (GSDP), which India and Germany had launched during Modi’s visit to Berlin for the 6th IGC.
- The GSDP is an umbrella partnership that provides political guidance and steer to robust ties in climate action and SDGs.
- Under this, Germany will also place €10 billion in new and additional commitments under their development cooperation portfolio in India.
- India and Germany also agreed to cooperate on Green Hydrogen.
- The Indo-German Green Hydrogen Task Force was constituted in September 2022 and an Action Plan is close to finalisation.
- On “Triangular Development Cooperation”, during the sixth IGC, India and Germany agreed to work on development projects in third countries. The four projects, announced in May 2022, are now in different stages of implementation:
- Cameroon:Potato Seed Production through Rooted Apical Cuttings (RAC) Technology.
- Malawi:Agri Business Incubator Models for Women in Agriculture & Food Systems
- Ghana:Developing Bamboo-Based Enterprises for Sustainable Livelihood and Income Generation in Ghana
- Peru:Development of a geospatial portal prototype for planning, monitoring, and evaluation of the Ministry of Development and Social Inclusion of Peru (MIDIS) interventions and social programs.
- Germany has come on board the Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI).
- The two sides continued discussion on the proposed deal for Germany to build jointly with India six conventional submarines for the Indian Navy. “
- The Modi-Scholz meeting resulted in two intergovernmental documents – India-Germany Vision to Enhance Cooperation in Innovation and Technology and a Letter of Intent between Department of Science and Technology of the Government of India and the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems of Germany for Cooperation in Green Hydrogen and Clean Energy Technologies.
.jpeg)
Background of relations:
Relations over the years:
- Bilateral relations between India and Germany are founded on common democratic principles and are marked by a high degree of trust and mutual respect.
- India was amongst the first countries to establish diplomatic ties with the Federal Republic of Germany after the Second World War.
- Relations grew significantly following the end of the Cold War and the reunification of Germany.
- In the last decade, both economic and political interaction between India and Germany has increased significantly.
- Today, Germany is amongst India’s most important partners both bilaterally and in the global context.
- India and Germany have a “Strategic Partnership” since 2001
High-level consultations:
- Relationship has been further strengthened with the Inter-Governmental Consultations (IGC) at the level of Head of Governments which allows for a comprehensive review of Cooperation and identification of new areas of engagement.
- India is amongst a select group of countries with which Germany has such a high-level Consultations.
- Regular visits take place from both sides, including at the highest level
- There is an Indo-German Parliamentary Friendship Group, in German Bundestag since 1971.
- Some States and Cities of India and Germany have entered into twinning arrangements. Karnataka and Bavaria have Sister State arrangement since 2007. Mumbai and Stuttgart are sister cities since 1968. In January 2015, Maharashtra and Baden-Wurttemberg signed an MoU to establish a Sister State relationship.
Institutional Cooperation Arrangements:
Several institutionalized arrangements exist between India and Germany to discuss bilateral and global issues of interest namely, Foreign Office Consultations, High Defence Committee, Indo-German Energy Forum, Indo-German Environment Forum, S&T Committee, and Joint Working Groups in various fields, including skill development, automotive, agriculture, coal, tourism, water and waste management.
Defence Cooperation:
- India-Germany Defence Cooperation Agreement (2006) provides a framework for bilateral defence cooperation.
- To further enhance the Defence Industry and defence cooperation between Germany and India, an Arrangement on Implementation of the Agreement concerning Bilateral Defence Cooperation was signed in 2019
Economic & Commercial Relations:
- Germany is India's largest trading partner in Europe.
- Bilateral trade grew from Euro 15.96 billion to Euro 20.41 bn in 2018.
- Germany is the 7th largest foreign direct investor in India since April 2000.
- A Fast-Track System for German companies has been operating in Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) since March 2016

Science & Technology:
- Indo-German Science & Technology cooperation started with the signing of the Intergovernmental S&T Cooperation Agreement in 1971 and 1974.
- There are more than 150 joint S&T research projects and 70 direct partnerships between Universities of both countries.
Development Cooperation:
- Germany has been an important development cooperation partner for several decades.
- Total bilateral Technical and Financial Cooperation since it began in 1958, amounts to approx. Euro 17 billion.
- Energy, sustainable economic development and environment & management of natural resources are priority areas.
- Financial assistance from Germany is mainly as soft loan, composite loans or grants routed through KfW, German Government’s Development Bank.
Indians in Germany:
- There are about 1.7 lakh Indians and people of Indian origin in Germany.
- The Indian diaspora mainly comprises of professionals, technocrats, businessmen/traders and nurses.
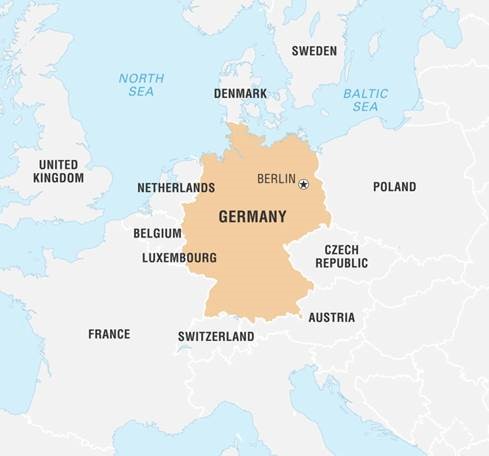
Germany:
- Germanyis formally known as the Federal Republic of Germany.
- It is located in Central Europe.
- It is the 2nd most populous country in Europe after Russia.
- It is the most populous country in the European Union.
- Germany is located between the Baltic and North Sea in the north.
- Germany shares borders with;
- The Alps in the South.
- Denmark in the north.
- Poland and the Czech Republic in the east.
- Austria and Switzerland in the south.
- France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands in the west.
- It is the 7th largest country in Europe.
- Most people follow Christianity.
- The official language is German.
- The capital is Berlin; it is also the largest city.
- Germany has the largest economy in Europe.
- It is the world's 4th-largest economy by nominal GDP and the 5th-largest by Purchasing power parities (PPPs).
- It is both the world's third-largest exporter and importer of goods.
- It is categorised as a developed country, it ranks very high on the Human Development Index.
- Areas of Rhine, Danube and Elbe are rich in natural resourcesincluding iron ore, coal, potash, timber, lignite, uranium, copper, natural gas, salt, nickel, etc.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q) There is tremendous scope for India and Germany to enhance cooperation in the areas of innovation and technology. (250 words)
|

https://epaper.thehindu.com/ccidist-ws/th/th_delhi/issues/26504/OPS/G5EAU29G6.1.png?cropFromPage=true










