Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- The Ministry of Coal and the Ministry of New & Renewable Energy decided to work together for the promotion of green energy.
Green energy
- Green energy is any energy type that is generated from natural resources, such as sunlight, wind, or water.
Green Energy vs Renewable Energy
- Green Energy often comes from renewable energy sources although there are some differences between renewable and green energy.
- Renewable energy comes from sources that are constantly and naturally renewed, such as wind power and solar power. Renewable energy is also often called sustainable energy.
- A renewable energy source may not be considered ‘green’ if, for example, some carbon emissions are associated with the processes used to generate the energy – such as the building of infrastructure.
.jpg)
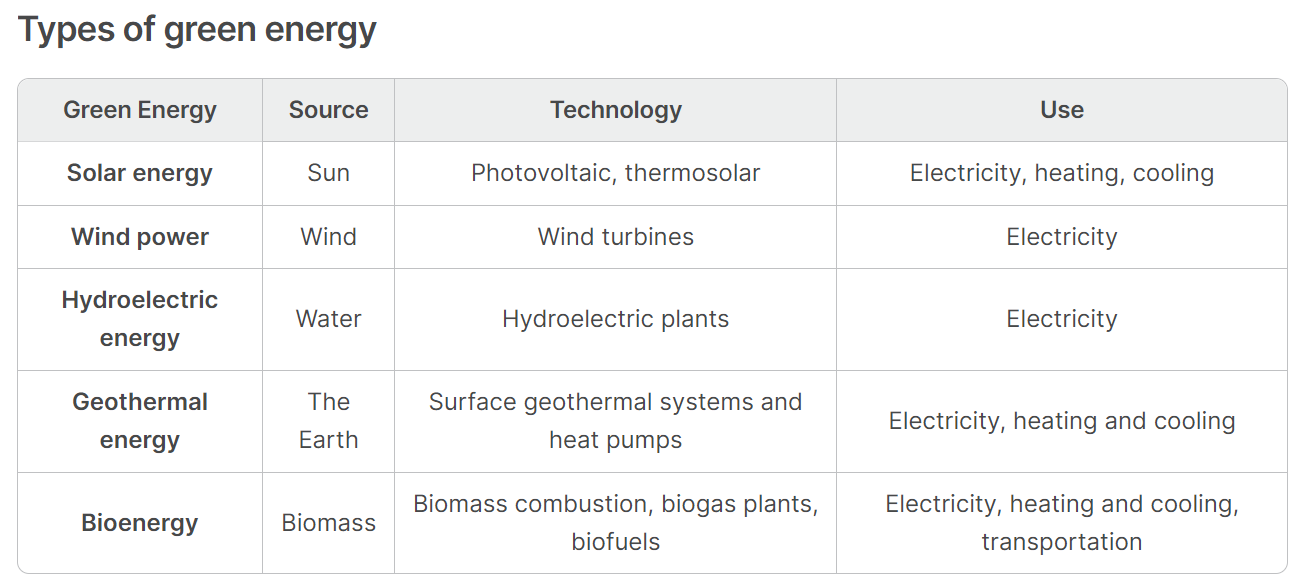
Forms of Green Energy
- The main sources are wind energy, solar power, and hydroelectric power (including tidal energy, which uses ocean energy from the tides in the sea).
Let's take a closer look at each green energy source and how they work:
- Solar energy: Solar panels use silicone sheets with energy-absorbing cells to convert sunlight into electricity. Solar power is a relatively accessible resource, and people can harness solar power industrially or individually by installing solar panels on buildings and homes.
- Wind power: Wind turbines generate kinetic energy that we then use to create electricity. The harnessing of wind power doesn't require much human labour, and it is known as one of the most environmentally friendly resources.
- Hydropower: Hydropower plants capture kinetic energy from the currents flowing in streams and rivers. This is done through the use of a turbine built into a dam.
- Biomass: Energy can be generated from agricultural, urban, and industrial waste. Biomass can be harnessed by burning wood and energy crops grown specifically for this purpose. Wheat, sugar beet, sugar cane, and maize are often fermented to produce bioethanol.
- Geothermal: The heat held within the fluids and rocks beneath the Earth's crust can create energy. To harness geothermal energy from the steam and hot water, workers dig mile-deep wells into underground reservoirs. They then use this steam and hot water to power turbines connected to electricity generators.
Drawbacks of Green Energy
- Unreliability: Some sources of renewable energy depend on weather and atmospheric conditions to function. Hydroelectric dams need enough rainfall to fill the dam and to have a constant supply of flowing water. Wind turbines require wind blowing at a minimum wind speed to move the blades. Solar panels need skies to be clear and filled with enough sunshine to generate electricity. In addition, solar panels cannot generate electricity at night.
- Lower efficiency: More work still needs to be done to make renewable energy more efficient at harvesting energy and converting it to electricity. Because of this, installation projects and the maintenance of some renewable energy sources can be pretty expensive at times, discouraging investment from companies and governments.
- Space: Compared to other sources of energy, renewable energy sources take up space to produce energy. Solar energy can use over 100 acres of solar panels to produce around 20 megawatts of power. In comparison, a nuclear facility that is 650 acres can produce about 1,000 megawatts of electricity, whereas a solar plant the same size would only have 200 megawatts. A two-megawatt wind turbine requires 1.5 acres of space.
- Storage can be expensive: Renewable energy often needs to be stored in a battery. Just one battery can cost $10,000 to $25,000.
- Generation capacity is still lower: Currently, renewable energy generation capacity is not large enough to meet our energy demands. As renewable energy technologies improve and energy consumption decreases due to more efficient appliances, electronics, and lighting, there may be a time when our construction of new and additional renewable energy plants will catch up to meet our energy needs. We are not there quite yet, and will still use fossil fuels and nuclear energy to supply a good portion of our energy until then.
Even though green energy is needed for the future, plenty more work is required to make renewables our primary energy source.
What are the benefits of green energy?
- For many people and organizations, green energy's main draw is that it's less harmful to the environment. Green energy sources like wind and solar power are superior options for avoiding harmful greenhouse gas emissions. While installing wind turbines on homes may not be possible, we can choose utility providers that supply green energy.
- Green energy is also better for our physical health as it is far less responsible for polluting our air and water.
- According to the World Health Organization, household and ambient air pollution causes 4.2 million deaths around the world annually.
- Most of these deaths occurred in low- to middle‐income countries, especially Southeast Asia and the Western Pacific regions.
- For this reason, we must focus more on renewable energy sources that cause less damage than their unsustainable counterparts, especially in less affluent countries.
- Green energy sources like wind energy and solar power are far more sustainable options compared to fossil fuels. They offset the emissions of oxide, nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide, saving substantial health issues.
- Another advantage of green energy is that the naturally occurring resources used to harness it will not deplete over time.

Advantages of Green Energy
- Clean energy;
- Inexhaustible energy source;
- No carbon emissions or greenhouse gases;
- Energy independence;
- Self-sufficient;
- Sustainability;
- Environmentally friendly and slows down climate change.
- In addition to contributing to the protection of the environment, using green electricity and green gas can also help you make savings on your bills.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. What is Green Energy? What are the forms of Green Energy? Shed light on the drawbacks and advantages of Green Energy.
|












