



The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) marked its 50th anniversary in Lagos, Nigeria, highlighting its role as a model for African integration. Praised for peacekeeping, economic projects like the West African Power Pool, and promoting democracy, ECOWAS faces challenges like regional insecurity, political withdrawals (Burkina Faso, Mali, Niger), and socio-economic issues.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: ECOWAS
Context:
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) celebrated its 50th anniversary with a high-level conference in Lagos, Nigeria.
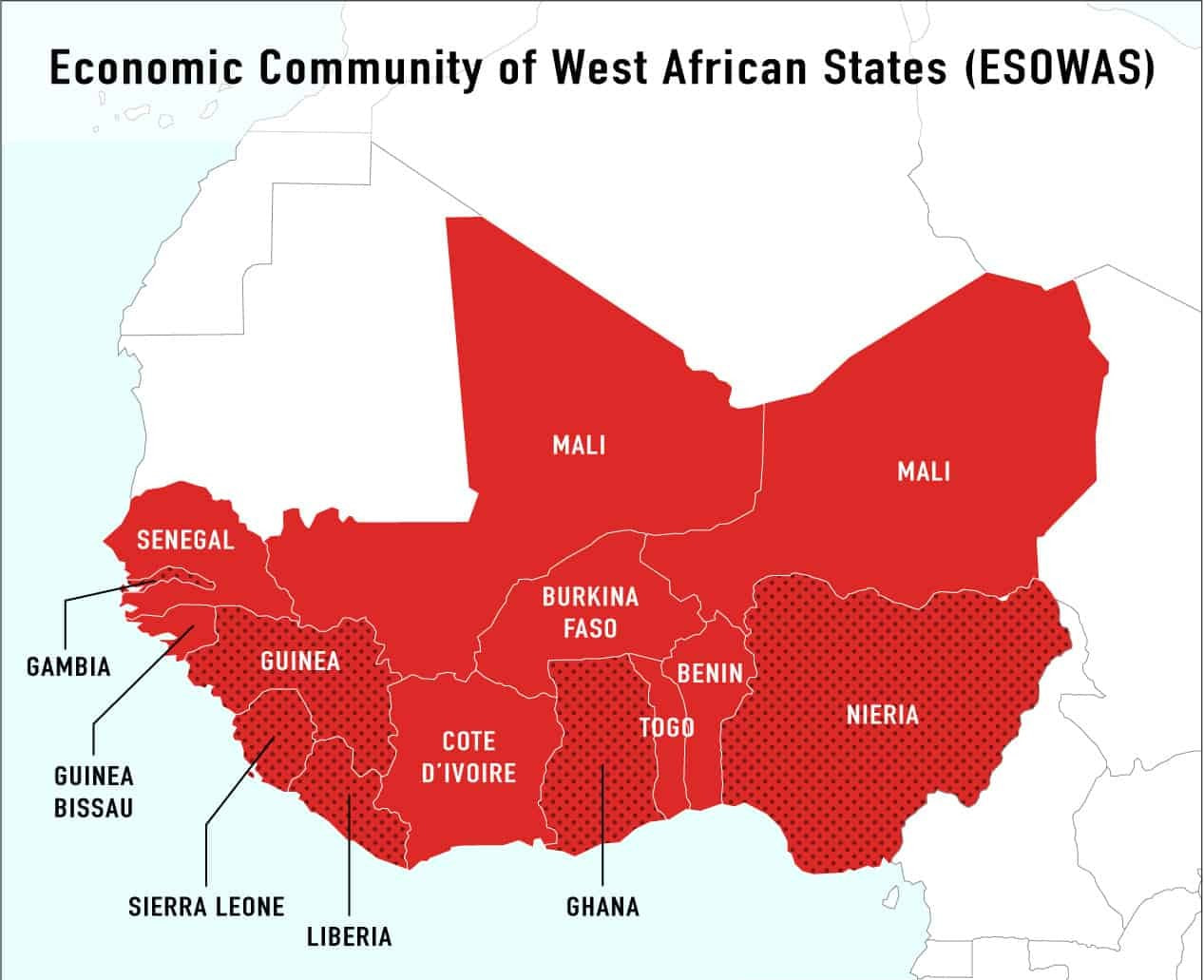
It is a regional political and economic union of fifteen countries located in West Africa.
Its main goal is to promote economic cooperation and integration among its member states to raise living standards and promote stability in the region.
ECOWAS was founded in 1975, through the signing of the Treaty of Lagos. Its founding was driven by the vision of creating a large trading bloc to promote economic self-sufficiency for its member nations.
Primary Goals:
Member States
ECOWAS currently comprises 12 member states: Benin, Cabo Verde, Côte d'Ivoire, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, and Togo.
Burkina Faso, Mali, and Niger announced their withdrawal from ECOWAS in January 2024, forming a separate bloc called the Alliance of Sahel States.
 Copyright infringement not intended
Copyright infringement not intended
The Authority of Heads of State and Government => This is the supreme decision-making body, comprising the leaders of all member states.
The Council of Ministers => This council is made up of ministers from each member state (usually Foreign Affairs and Economic Planning ministers). It oversees the functioning of the organization and makes recommendations to the Authority.
The ECOWAS Commission => This is the executive arm, similar to a secretariat. Headed by a President, it implements the policies and decisions made by the Authority and Council. It is based in Abuja, Nigeria.
The Community Court of Justice => This court ensures the interpretation and application of ECOWAS treaties. Its rulings are binding on member states, and it also handles cases of human rights violations.
The Community Parliament =>This body provides a forum for dialogue and consultation. While it is currently not a legislative body with law-making powers, it plays an important advisory role.
Free Movement of People: The ECOWAS Protocol on Free Movement of Persons, Residence and Establishment allows citizens of member states to travel to other member countries without a visa for up to 90 days.
Peacekeeping and Conflict Resolution: ECOWAS has a strong record of military and diplomatic intervention to restore peace and order. Its military wing, ECOMOG (ECOWAS Cease-fire Monitoring Group), played a key role in ending civil wars in Liberia and Sierra Leone.
Economic Integration: Creating a customs union with a Common External Tariff (CET); member states apply the same customs duties to imports from outside the region, which simplifies trade.
Must Read Articles:
West African Bloc Urges Stability in Senegal
Source:
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Consider the following countries: 1. Nigeria 2. Gambia 3. Ghana 4. Guinea 5. Senegal How many of the above countries are the members of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)? A) Only two B) Only three C) Only four D) All five Answer: D Explanation: ECOWAS currently comprises 12 member states: Benin, Cabo Verde, Côte d'Ivoire, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, and Togo. |




© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved