



IIT Kanpur's team has unearthed an ancient Buddhist stupa in Haryana using the Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) technology. This non-destructive method, leveraging high-frequency electromagnetic pulses, allows to "see" beneath the soil, revealing hidden structures without excavation. For UPSC GS-I (Culture) and GS-III (Science & Technology) papers.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: TIMES OF INDIA
The Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) technology helped a team from the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kanpur to discover signs of ancient Buddhist stupas and other structural remains buried beneath the soil.
The discovery occurred in the Yamuna Nagar, Haryana. Researchers believe this site dates back about 2,000 years.
The GPR technology detected circular structures, old walls, and chamber-like rooms. These findings were located at a depth of approximately 6 to 7 feet.
GPR is a geophysical method that employs high-frequency electromagnetic pulses to image the Earth's subsurface or other solid materials.
It acts as a non-destructive detection and imaging method, identifying subsurface elements either underground or within surfaces like concrete.
How does GPR work?
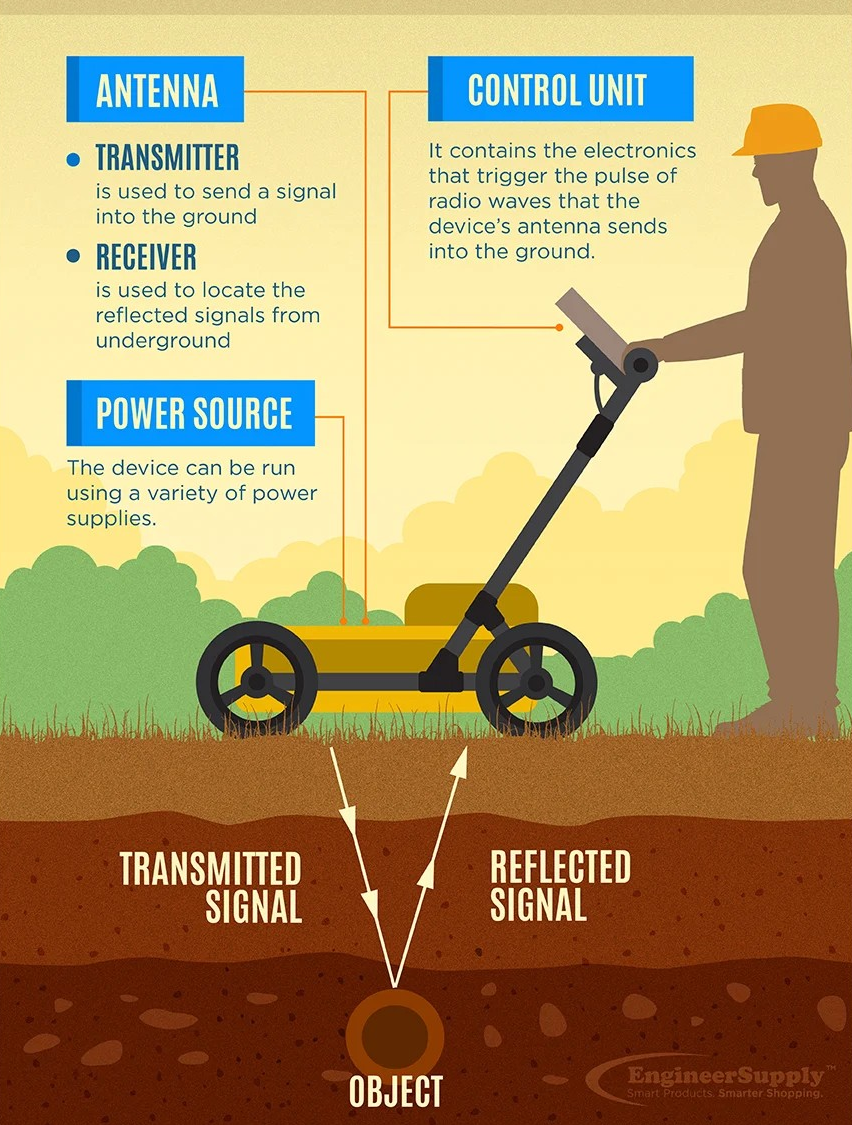 What are some general applications of Ground Penetrating Radar technology?
What are some general applications of Ground Penetrating Radar technology?
Archaeology and Historical Preservation => Locating ancient structures, burial sites, and artifacts without destructive excavation.
Utility Detection => Revealing underground utilities, including electrical conduits, steam pipes, telecommunications lines, gas and oil lines, and water and sewer pipes.
Geology and Environmental Studies => Mapping bedrock, studying soil layers, detecting groundwater, and identifying contamination plumes.
Forensics => Locating buried evidence or clandestine graves.
Infrastructure Inspection => Assessing the integrity of roads, bridges, and concrete structures by detecting voids, rebar, or cracks.
Mining => Identifying ore bodies and geological hazards.
|
FAQ Q. What major archaeological find recently utilized Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)? IIT Kanpur's team discovered signs of ancient Buddhist stupas and structural remains buried in Haryana's Yamuna Nagar district using GPR. Q. How does GPR technology non-destructively detect objects beneath the surface? GPR transmits high-frequency electromagnetic waves into the ground; a receiver records reflected energy from buried objects/boundaries to create subsurface images. Q. Beyond archaeology, what are other key applications of GPR technology? GPR detects metallic/non-metallic objects, identifies various utilities (electrical, gas, water lines), and inspects surfaces like concrete for hidden elements. |
Must Read Articles:
BUDDHIST TERMINOLOGIES IMPORTANT FOR UPSC
Source: TIMES OF INDIA
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Consider the following statements about Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) technology: 1. It operates as a non-destructive geophysical method. 2. It utilizes low-frequency sound waves to image subsurface elements. Which of the above statements is/are correct? A) 1 only B) 2 only C) Both 1 and 2 D) Neither 1 nor 2 Answer: A Explanation: Statement 1 is correct: GPR is recognized as a non-intrusive and non-destructive geophysical method used to image the subsurface without requiring excavation or drilling. Statement 2 is incorrect: GPR operates by transmitting and receiving electromagnetic (EM) waves, also known as radar pulses or radio waves. |







© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved