



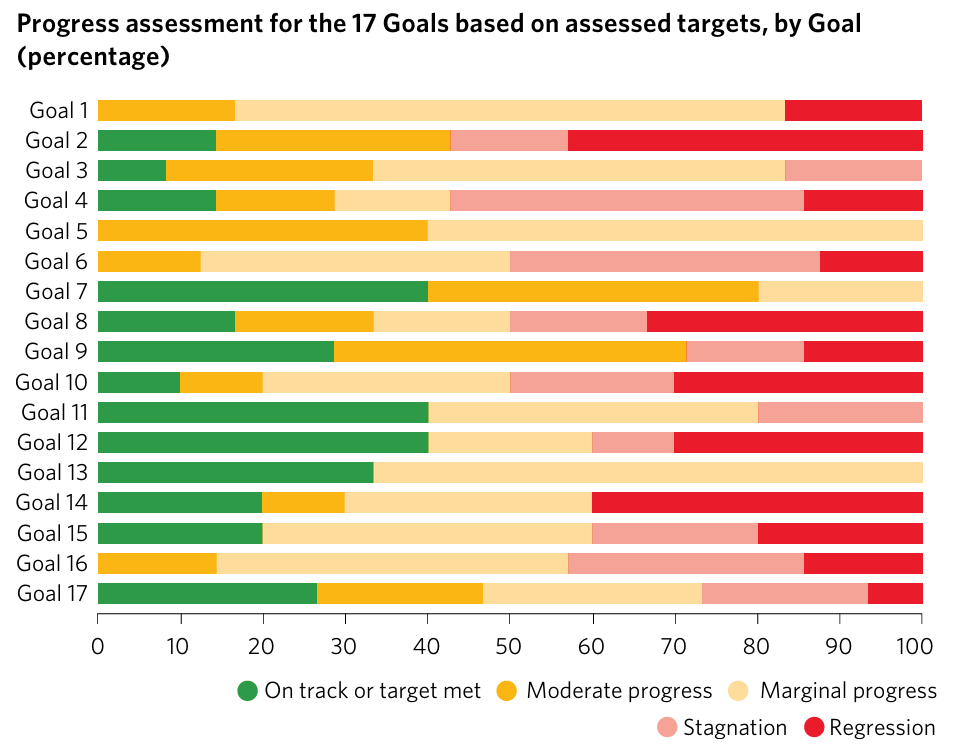
The UN SDG Report 2025 reveals that 35% of SDG targets have stalled or regressed, with Zero Hunger (SDG2), Quality Education (SDG4), Clean Water and Sanitation (SDG6), Decent Work and Economic Growth (SDG8), and Reduced Inequalities (SDG10) most affected. Global hunger, economic instability, and climate challenges drive setbacks. Crucial for UPSC GS II & III.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: DOWN TO EARTH
According to the 10th edition of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) Report 2025, around 35% of the targets have stalled or are moving backward.
|
What are the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)? All 193 member countries of the United Nations adopted the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) as part of the "2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development". It was adopted in 2015, outlines 17 interconnected goals with 169 targets, that aims to address global challenges such as poverty, inequality, climate change, and environmental degradation. |

It is the only official UN report monitoring global progress on the 2030 Agenda, based on data from more than 200 countries.
It is prepared by the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA) in collaboration with over 50 international and regional agencies.
Only 35% of the 139 assessed targets are on track or making moderate progress.
Nearly half (48%) of the targets show insufficient progress, with 31% making only marginal gains and 17% showing no progress.
18% of targets are moving backward from their 2015 baseline levels.
 What achievements does the SDGs report highlight?
What achievements does the SDGs report highlight?Basic Services and Infrastructure => By 2023, 92% of the world's population had access to electricity, and Internet use grew to 68% in 2024 from 40% in 2015.
Health Improvements => Decline in under-5 and neonatal mortality rates, decline in new HIV infections, and efforts to prevent malaria have saved millions of lives.
Social Protection => More than half of the world's population (52.4%) now benefits from some form of social protection.
Gender Progress => Child marriage and child mortality rates have fallen. Women now hold 27% of parliamentary seats worldwide.
Regional Successes => East and South Asia are leading regional progress, with countries like Nepal, China, and India among the top improvers in certain areas. For example, India has improved its overall SDG ranking, securing 99th position among 167 countries, up from 109th in 2024.
Global Conflicts and Instability => In 2024, conflict claimed nearly 50,000 lives, and 123.2 million people were forcibly displaced. Conflict also intensifies hunger and food insecurity.
Climate Change and Environmental Crises => Extreme weather, rising sea levels, pollution, overfishing, and biodiversity loss continue to threaten oceans and land.
Financial Constraints and Debt Burdens => Developing countries face record-high debt servicing costs ($1.4 trillion in 2023), limiting their ability to invest in sustainable development.
Data Deficiencies => Lack of timely, inclusive, and actionable data for many SDG indicators.
Financial Reform => Reforms in the global financial structure to provide affordable capital to developing countries.
The SDG 2025 report calls for focused efforts on six priority areas: Food Systems, Energy, Digital Inclusion, Education, Jobs and Social Protection, and Climate and Biodiversity.
Data Systems => Implementing frameworks like the Medellín Framework for Action, adopted at the 2024 World Data Forum, designed to guide policy-making and track SDGs progress.
Multilateral Cooperation => International cooperation based on evidence, equity, and mutual accountability. Increased investments and coordinated action from all partners are essential.
|
FAQ Q. What is the main finding of the UN SDG Report 2025? The SDGs report warns that progress towards 35% of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) targets has either stalled or is reversing. Q. What are the primary drivers behind the deepening global food insecurity? High global hunger is driven by conflict, climate variability, and economic instability, compounded by inequalities and lack of food access. Q. What key solutions the UN report proposes to accelerate SDG progress? The SDGs report calls for urgent multilateral action, financial reform (including tripling multilateral development bank lending), and outlines a roadmap across six priority areas, such as transforming food systems and expanding energy access. |
Must Read Articles:
India Enters Top 100 in SDG Ranks
Source: DOWN TO EARTH
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Discuss the challenges faced by India in localizing and implementing the Sustainable Development Goals at the sub-national and grassroots levels. 250 words |



© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved