Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/special-categories-voters-9351088/
Context: India's electoral framework ensures inclusivity by providing alternative voting methods, such as postal ballots, facilitation centres, and home voting, for voters who cannot reach polling stations on Election Day.
Details
- India's electoral framework ensures that all eligible voters can exercise their right to vote, even if they cannot physically be present at the polling station on Election Day. Special exceptions and alternative voting methods are provided for various categories of voters.
Postal Ballots
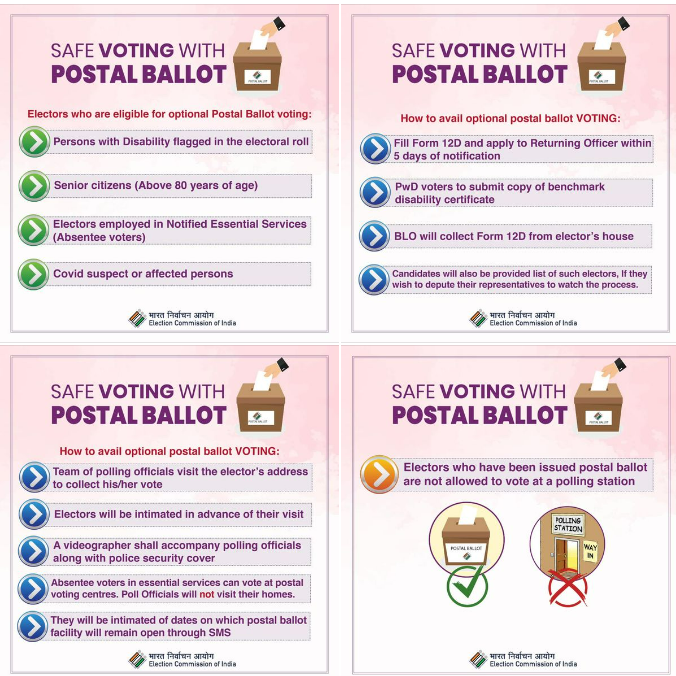
Eligibility
- Special Voters: High-ranking officials such as the President, Vice President, Governors, Cabinet Ministers, and their spouses.
- Service Voters: Members of the Indian armed forces, paramilitary forces, armed state police serving outside their state, government employees stationed abroad, and their spouses.
- Voters on Election Duty: Includes election observers, presiding officers, polling officers, agents, police personnel, and public servants on official tasks during polling. This also covers non-government staff involved in election duties like videographers and drivers.
- Electors Under Preventive Detention.
- Absentee Voters (under Section 60(c) of the RPA, 1951): Senior citizens aged 85+ (AVSC), persons with disabilities (AVPD), Covid-19 suspects or affected individuals (AVCO), and persons employed in essential services (AVES).
Process
- Eligible voters must formally apply for postal ballots within a specified timeframe.
- Service voters and those under preventive detention automatically receive postal ballots.
- Voting occurs before the official poll date, outside the polling station, and without EVMs.
- Electronically Transmitted Postal Ballot System (ETPBS) is available for service voters, enabling encrypted ballot transmission via a secure portal, while completed ballots are returned by post at no cost.
Facilitation Centres and Postal Voting Centres
Facilitation Centres
- Established for voters on election duty to vote using postal ballots.
- Located at training venues and designated offices.
- The voting process is videotaped to ensure security.
- Votes are cast into a steel trunk, and postal ballots are stored in labelled cotton bags in a strong room.
Postal Voting Centres (PVC)
- Designated venues for absentee voters in essential services (AVES) to receive and cast their postal ballots.
- Operate on fixed schedules before the election (three fixed days from 9 AM to 5 PM).
- Candidates can send observers to these centres.
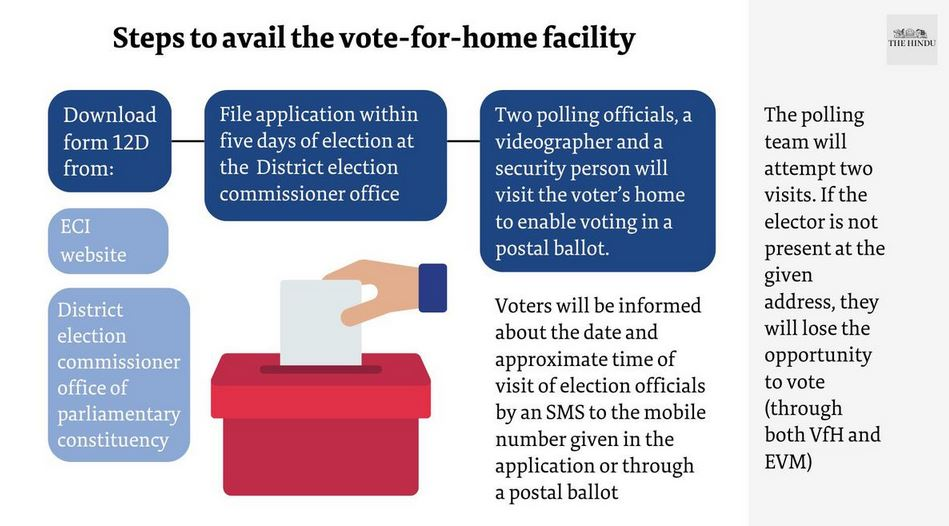
Home Voting
Eligibility
- Senior citizens aged 85+ (AVSC), persons with disabilities (AVPD), and COVID-19 suspects or affected individuals (AVCO).
Process
- Booth Level Officers (BLOs) deliver and collect Form 12D from eligible voters.
- Teams consisting of two poll officers, a police security officer, a micro-observer, and a videographer visit the voters' homes for voting.
- Notifications are sent via SMS, post, or BLO.
- Visits are completed a day before the polls, with candidates or their agents observing the process.
Voting in a Different Polling Centre
Election Duty Certificate (EDC)
- Issued to individuals on election duty within their enrolled constituency, allowing them to vote at the polling station where they are deployed via EVM. If deployed in another constituency, they are entitled to a postal ballot.
Proxy Voting
- Eligibility: Service voters in the armed and paramilitary forces.
- Process: Service voters appoint a local resident as their proxy to vote at the designated polling station. The proxy's left middle finger is marked with indelible ink to indicate they have voted on behalf of the service voter.
Assisted Voting
- Eligibility: Electors unable to vote due to blindness or other disabilities.
- Process: The Presiding Officer may allow a companion over 18 to assist the voter in the booth. The companion's right index finger is marked with indelible ink.

Conclusion
- These alternative voting methods ensure that every eligible voter in India can participate in the democratic process, regardless of their circumstances.
Must Read Articles:
POSTAL BALLOT
Source:
Indian Express
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. What is the purpose of the Electronically Transmitted Postal Ballot System (ETPBS) introduced in India?
A) To enhance cybersecurity during elections
B) To facilitate voting for senior citizens
C) To expedite the delivery of postal ballots to service voters
D) To increase voter turnout in rural areas
Answer: C
|











