



Small Modular Reactors (SMRs), with up to 300 MWe capacity, enable rapid, flexible, factory-built clean power. Despite higher costs, they offer fast deployment, reliable baseload, and emissions-free energy, supporting India’s decarbonization, energy security, and global climate goals.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: DOWNTOEARTH
According to the report titled "What if Southeast Asia goes nuclear?" by energy consultancy Wood Mackenzie, Southeast Asia will need investments of about $208 billion to develop 25 gigawatts (GW) of nuclear power capacity by 2050, with small modular reactors (SMR) emerging as the preferred choice.
|
Read all about: SMALL MODULAR REACTORS |
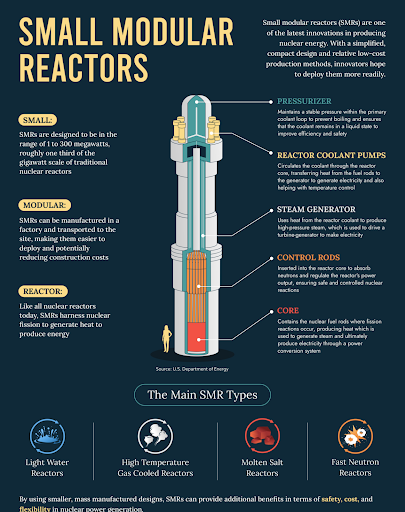
SMRs are compact nuclear reactors generating up to 300 MW per unit, about one-third the capacity of traditional reactors. Unlike large reactors, SMRs are factory-built, modular, and designed for quick deployment.
SMRs are pre-fabricated, allowing rapid installation like plugging in a device, ideal for regions needing quick energy solutions.
SMRs produce a large amount of low-carbon electricity, are:
Southeast Asia’s electricity demand is projected to triple by 2050, from 1,200 TWh in 2022 to 4,300 TWh. (Source: Energy for Growth Hub)
SMRs address regional needs:
India aims for Net Zero by 2070, with nuclear power targeted to reach 100 GW by 2047 from 8.8 GW in 2025.
In the Budget 2025, government launched a Nuclear Energy Mission with an outlay of ₹20,000 crore for research and development of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs).
Currently, the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) and Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) are researching SMRs for rural electrification and industrial use.
Source: DOWNTOEARTH
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Critically analyze the potential of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) as a viable alternative to conventional nuclear power plants. 150 words |
SMRs are advanced nuclear reactors with a power capacity of up to 300 MWe, designed for factory fabrication and modular assembly.
SMRs are smaller, modular, and can be built off-site and deployed more quickly than large, conventional nuclear power plants.
SMRs provide emissions-free baseload power, helping nations reduce their reliance on fossil fuels like coal and natural gas.




© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved